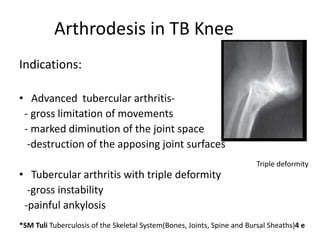
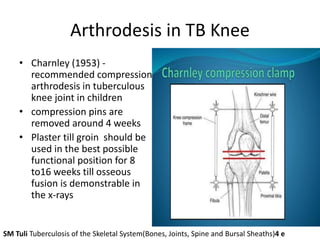
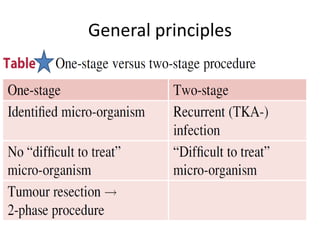
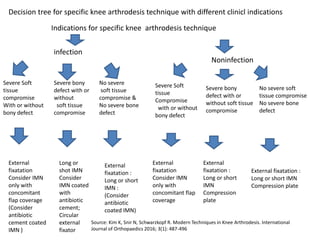
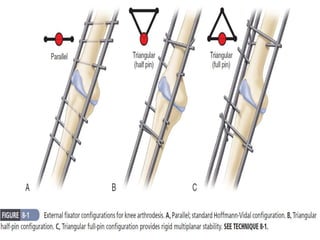
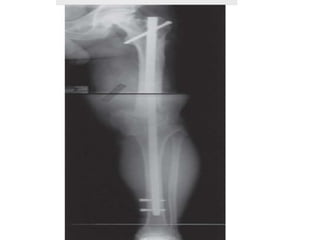
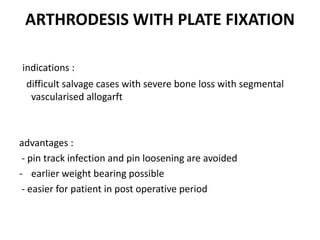
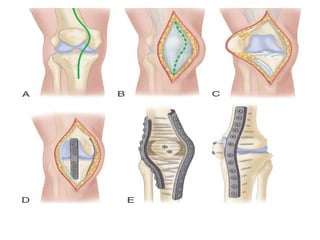
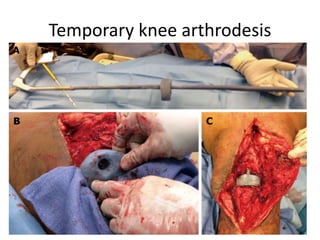
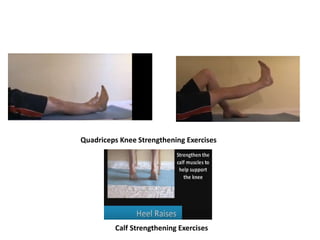
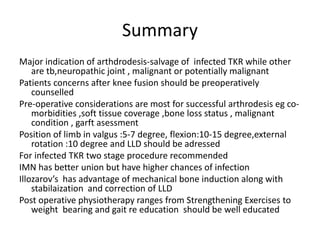
Arthrodesis, or fusion, of the knee joint can provide relief for patients with failed knee replacements or severe deformities. Various techniques are used depending on factors like bone loss and soft tissue integrity. Compression arthrodesis with external fixation is best for infected knees with minimal bone loss, applying compression across the joint. Intramedullary rod fixation is best for extensive bone loss as it allows immediate weight bearing but risks fat embolism or disseminating infection. The goal is to achieve bony union in proper alignment within 6 months to provide a painless, stable leg.