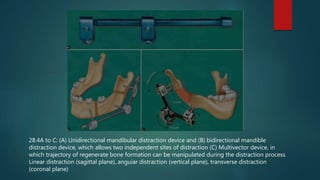
Distraction osteogenesis is a technique where bone is lengthened by slowly pulling apart the fragments of a surgically cut bone. New bone forms in the gap created. It has advantages over orthognathic surgery like being safer, decreasing hospitalization time, and allowing treatment at a younger age as it regenerates both bone and soft tissues. There are different types including monofocal, bifocal, and trifocal distraction used for various bone defects. Distraction is done in phases including latency, distraction, consolidation, and retention using both internal and external distraction devices. It is used to treat conditions like jaw hypoplasia, asymmetry, and defects from tumors or trauma.