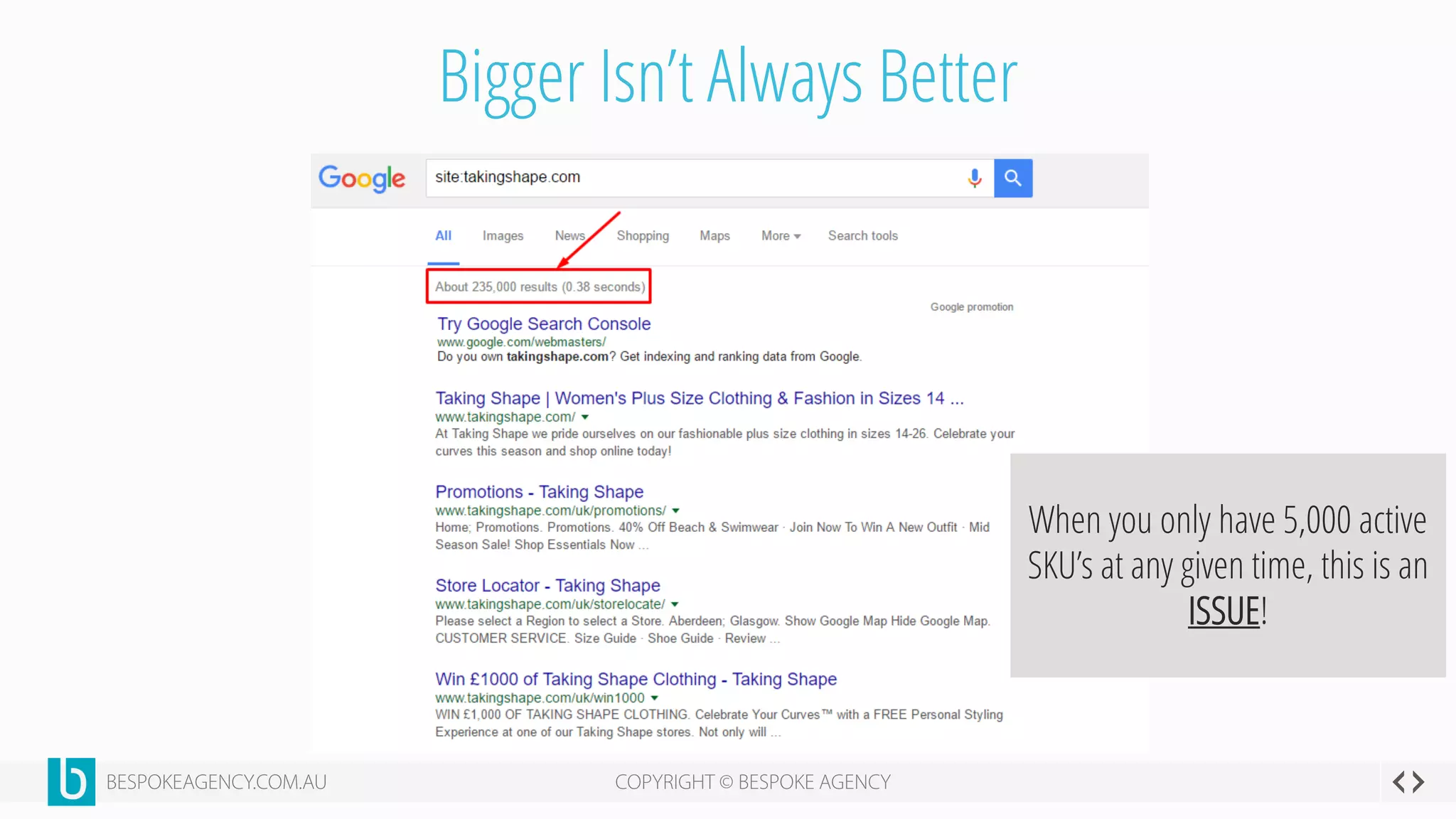
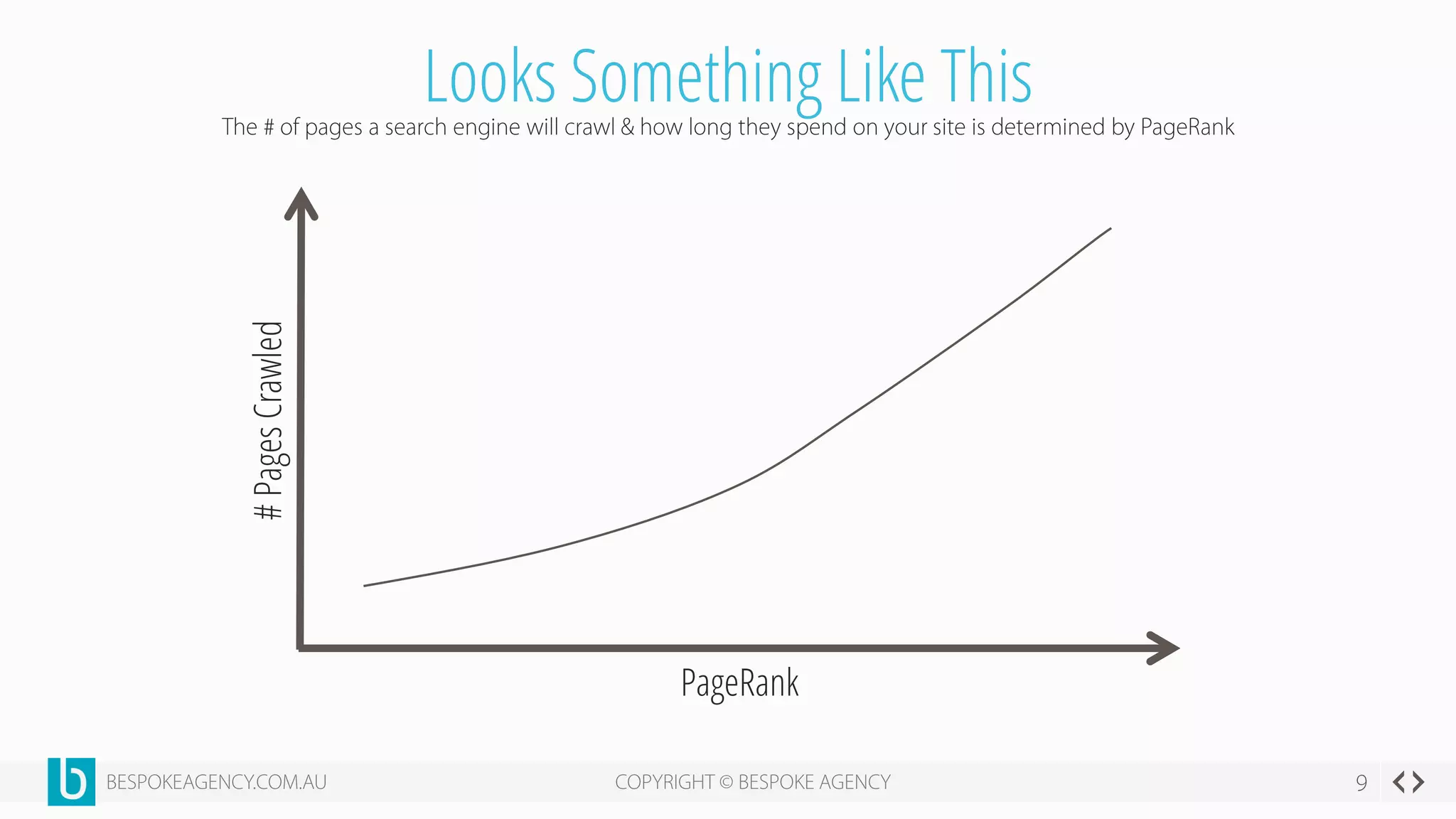
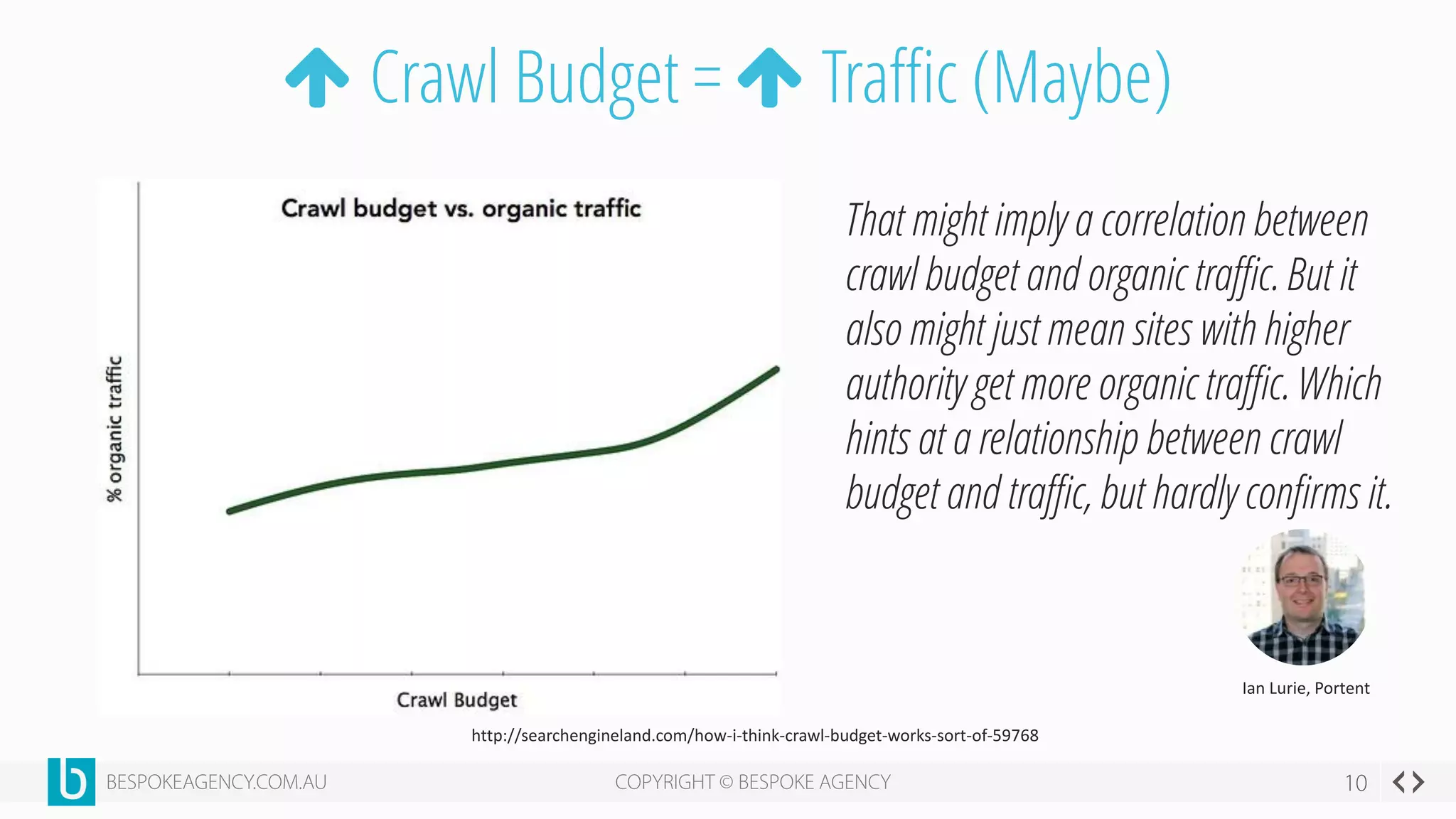
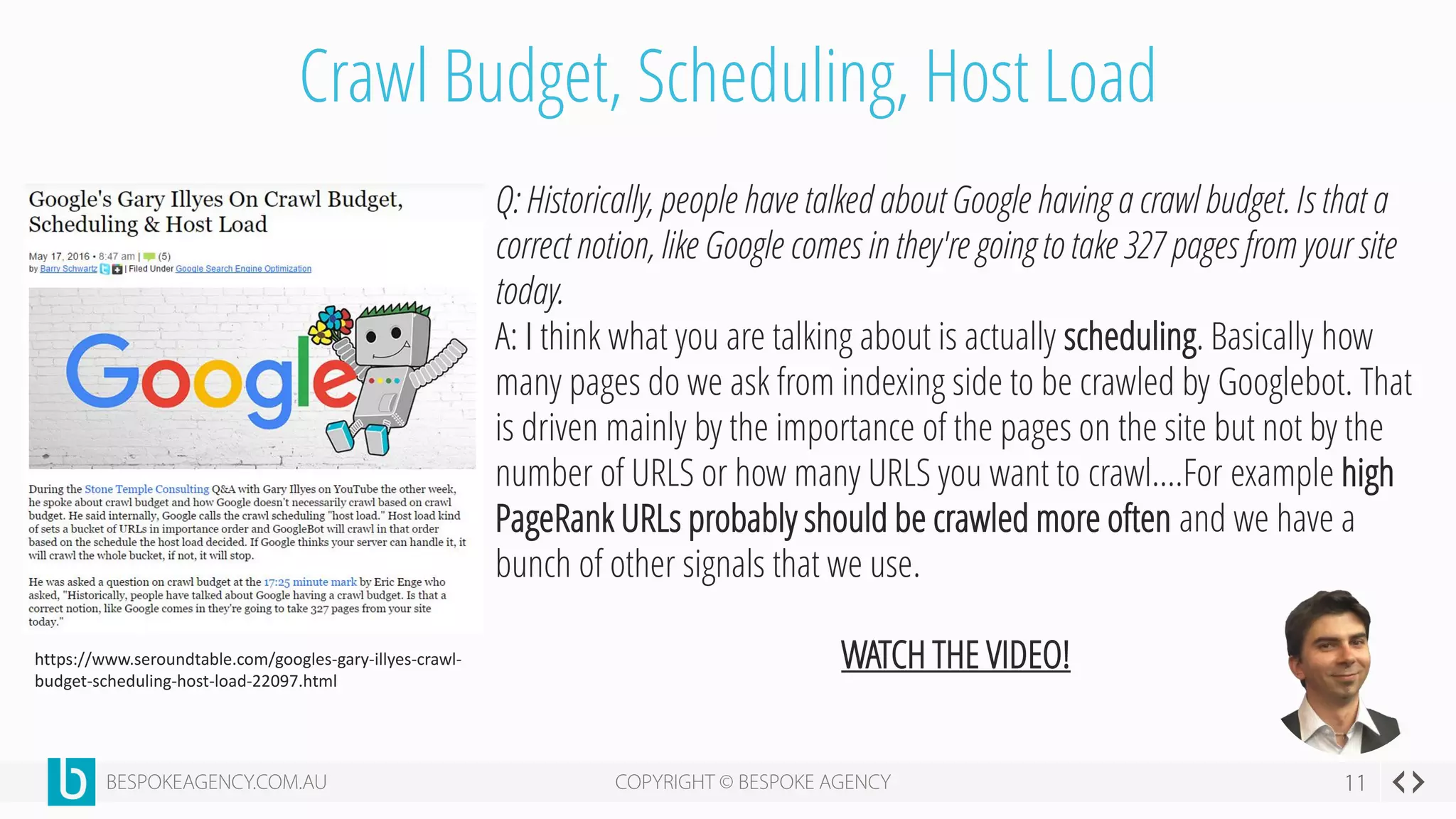
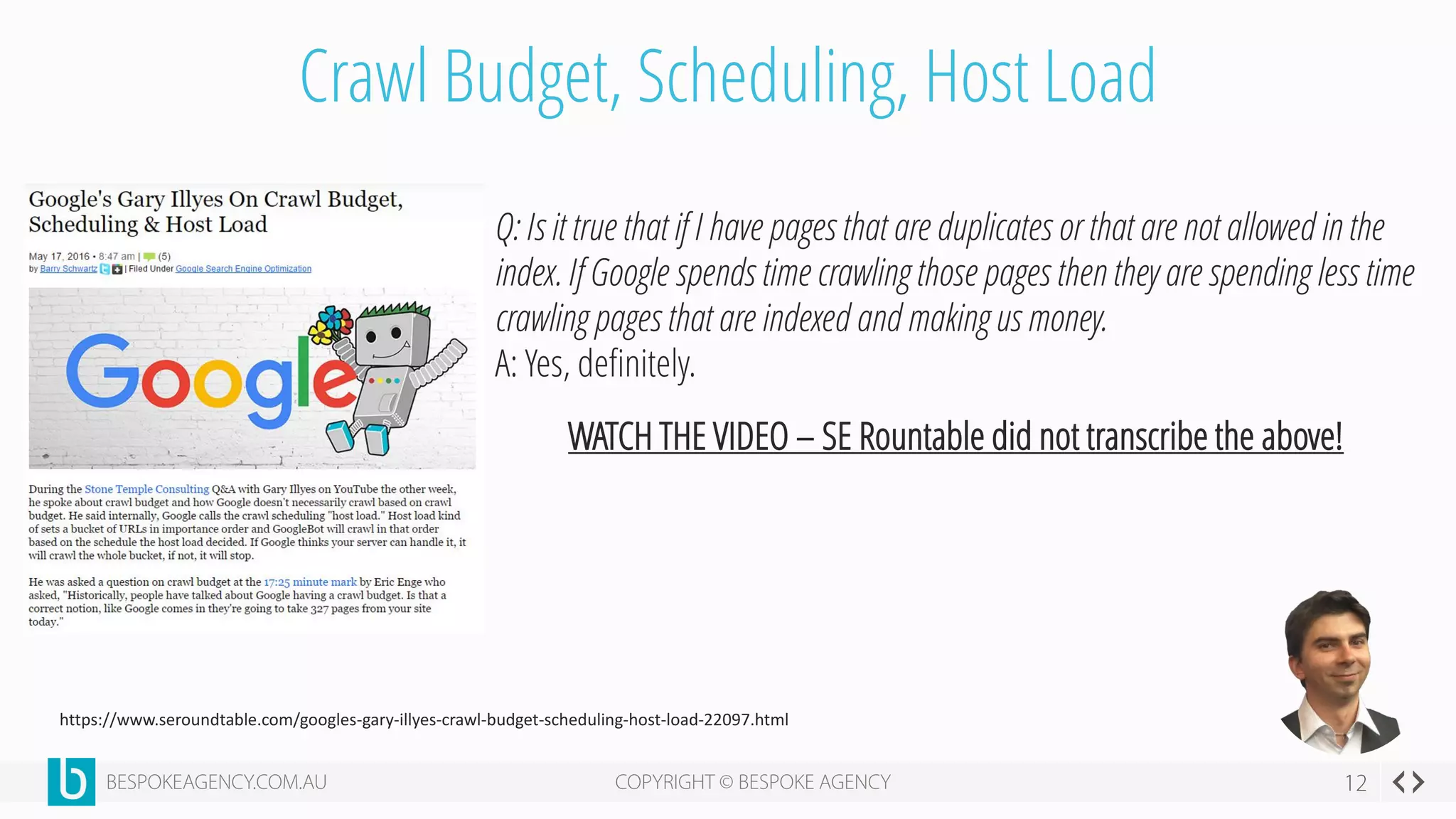
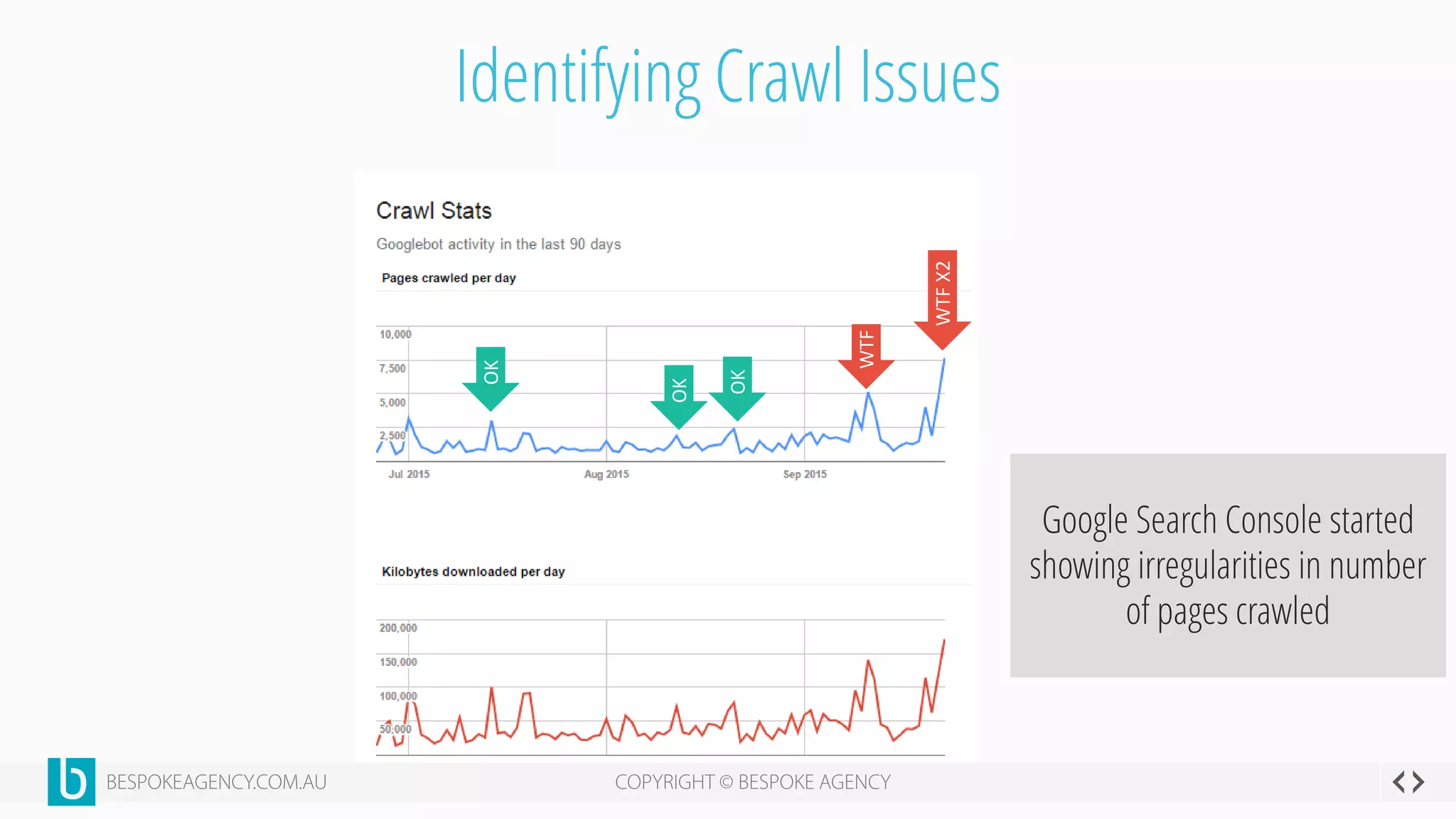
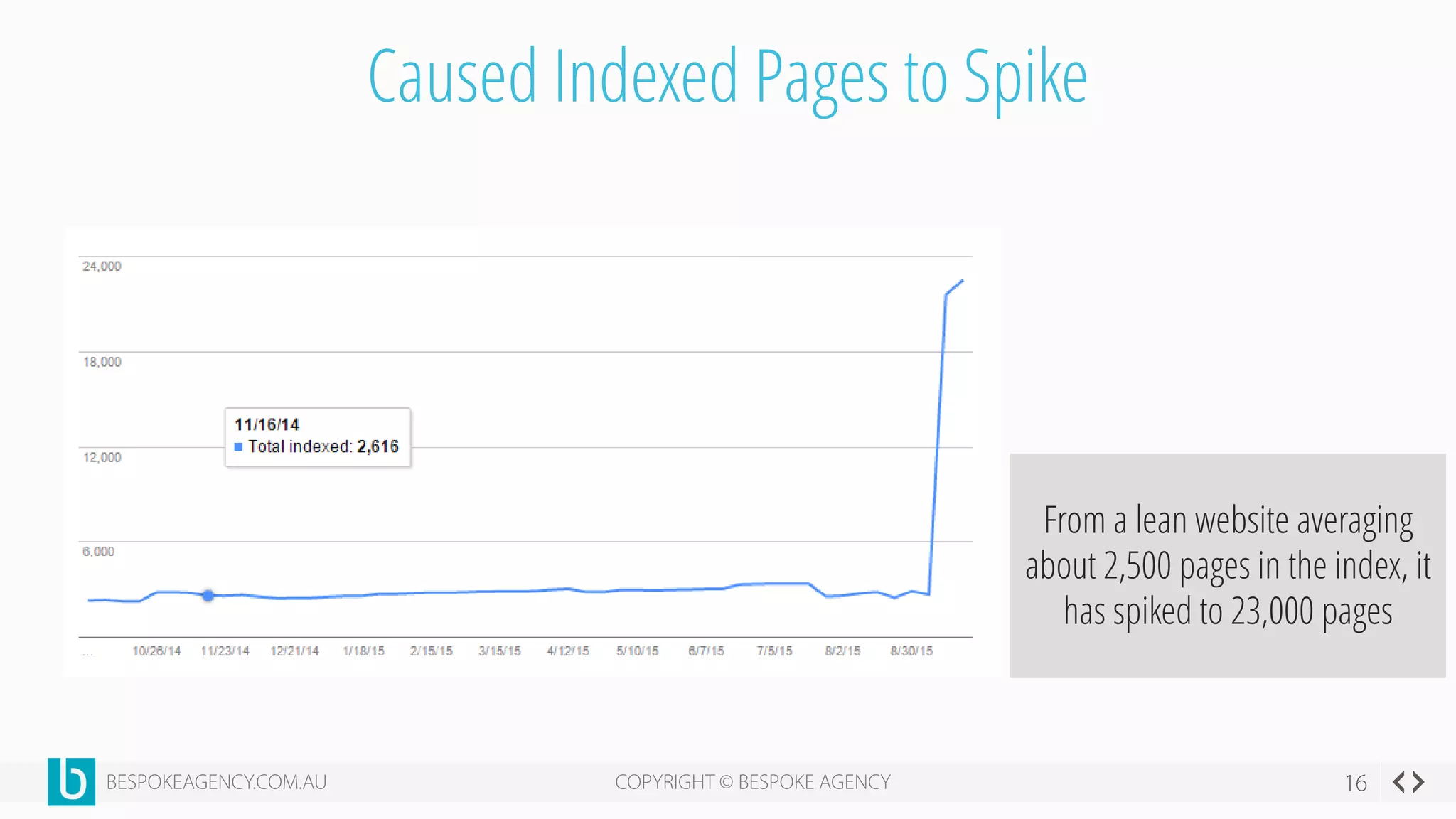
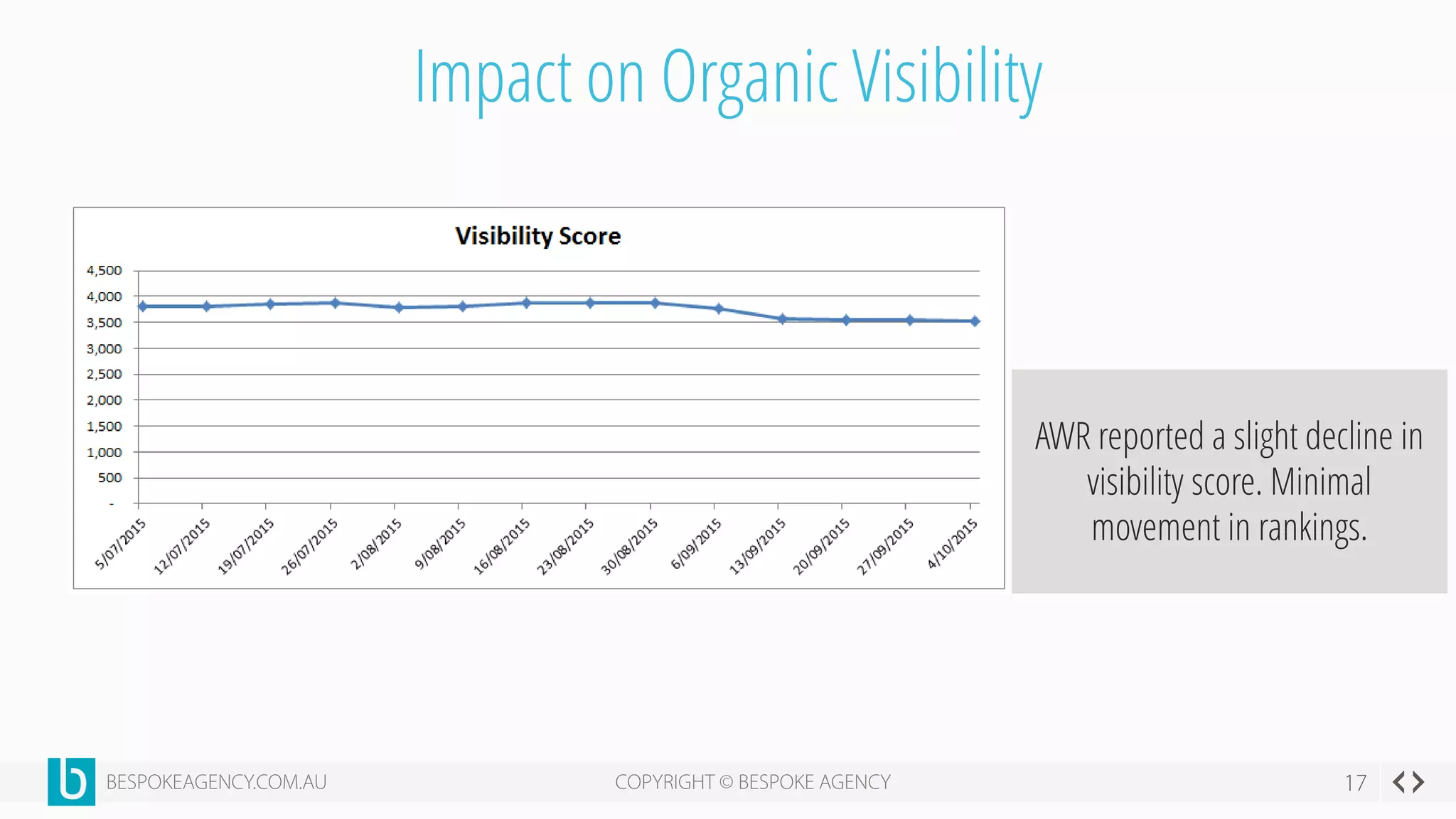
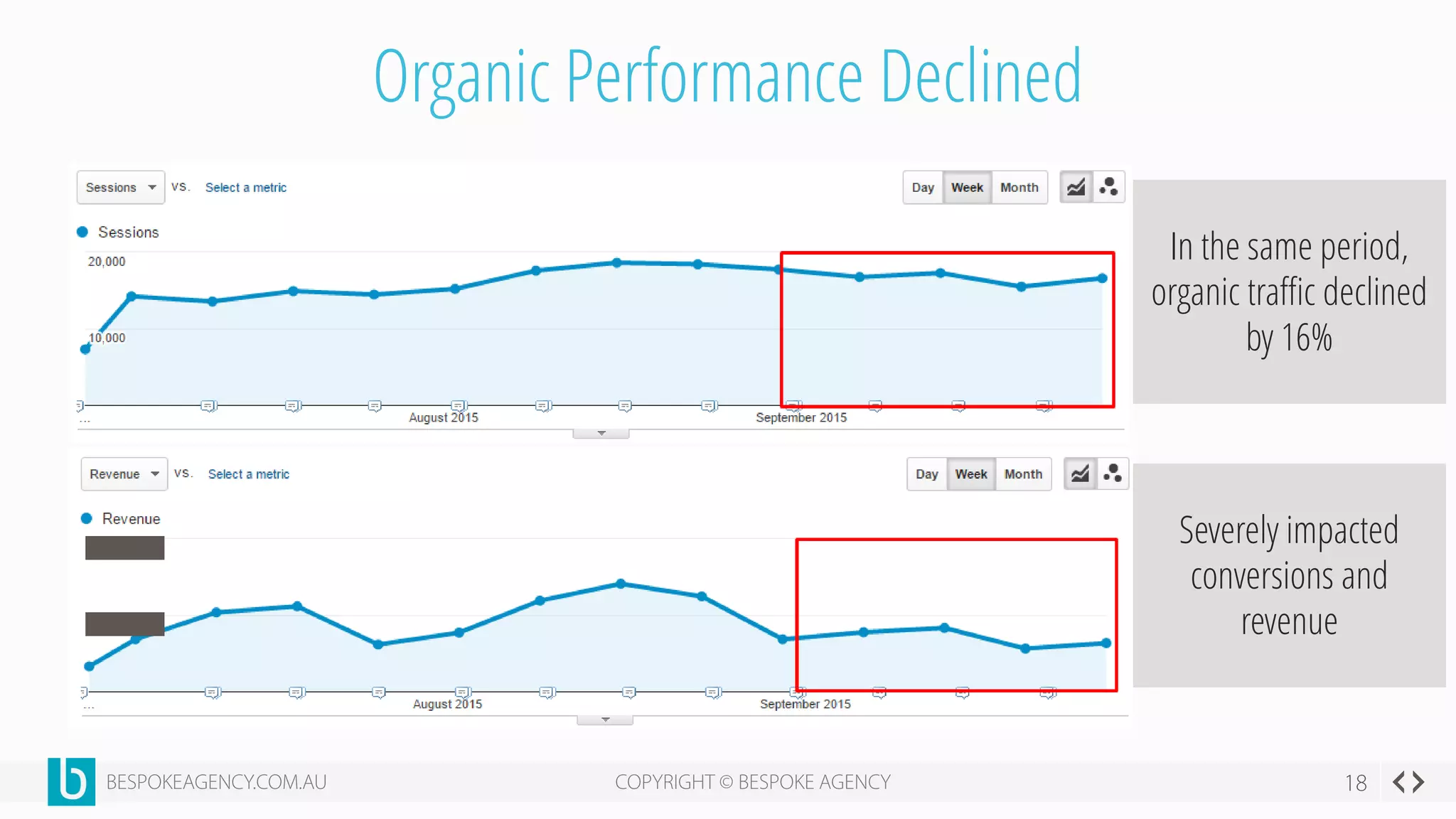
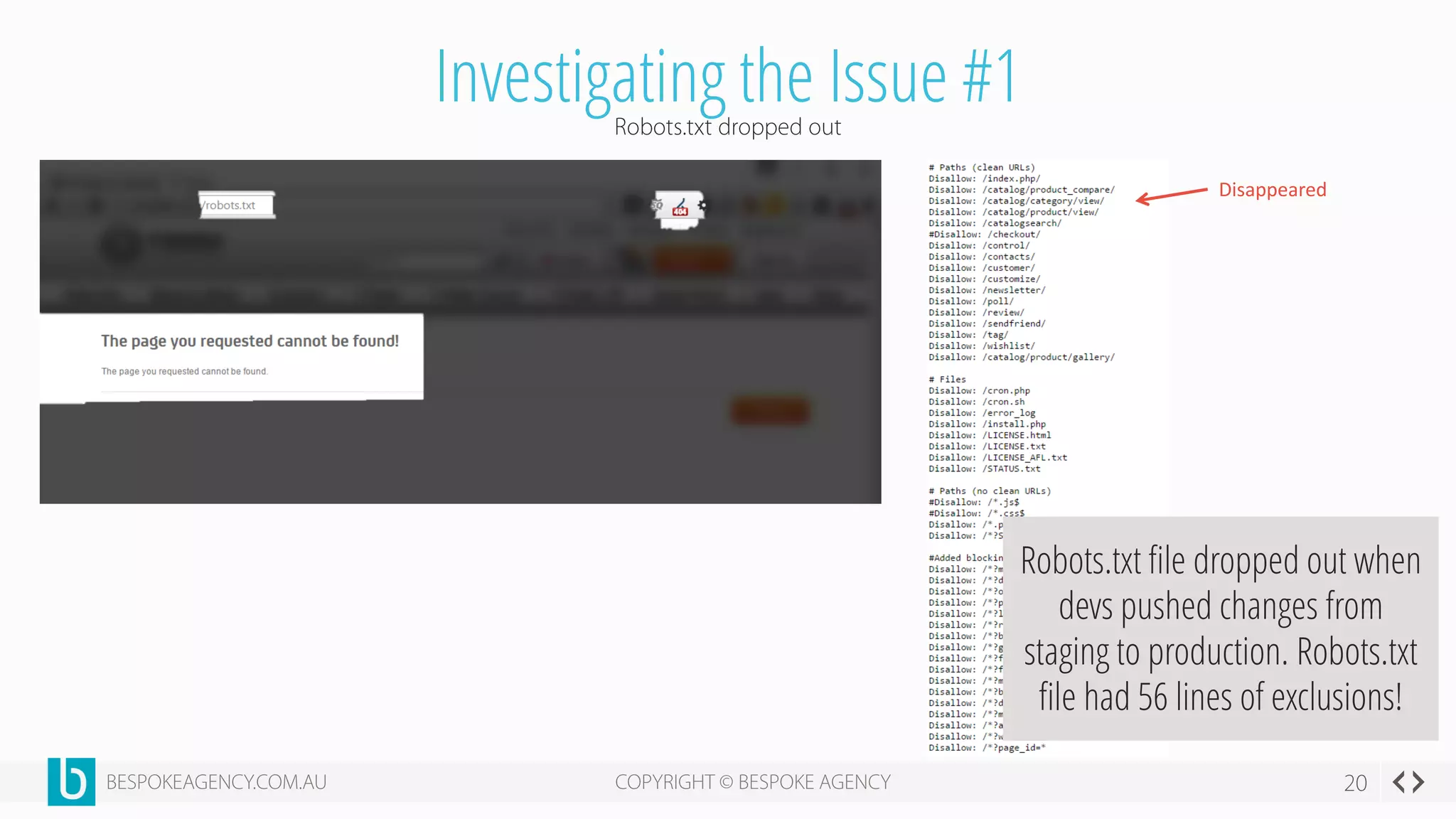
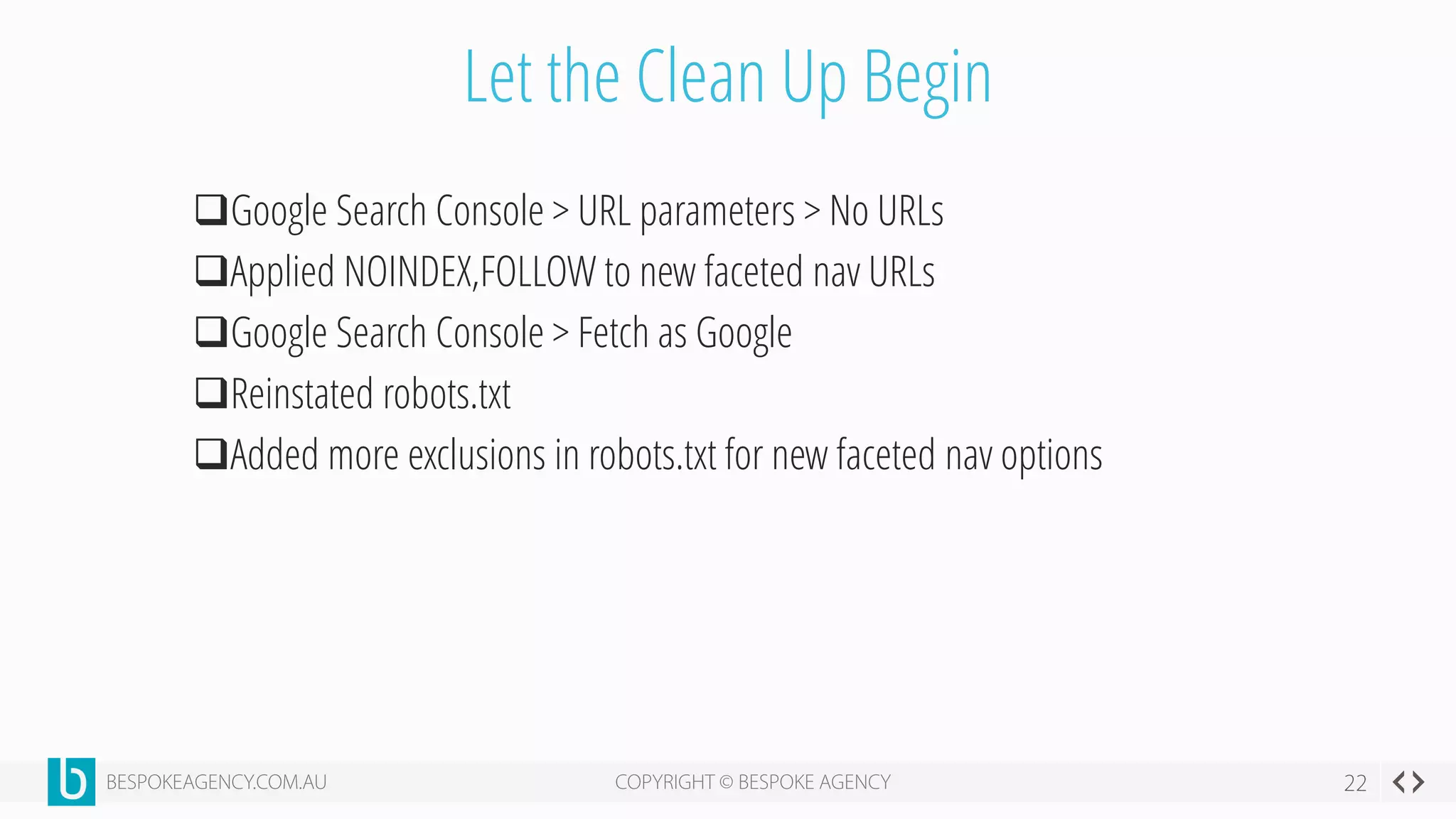
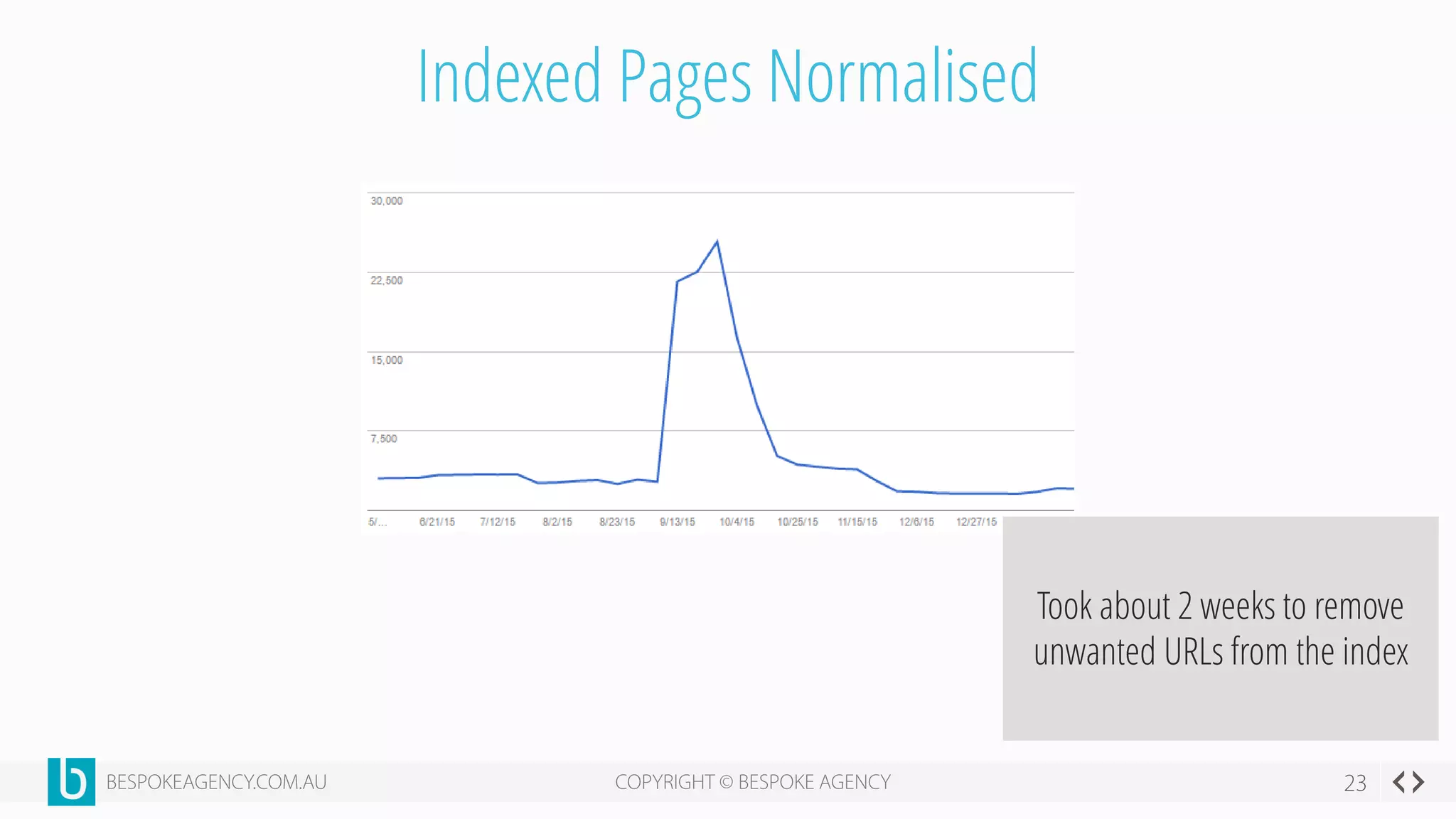
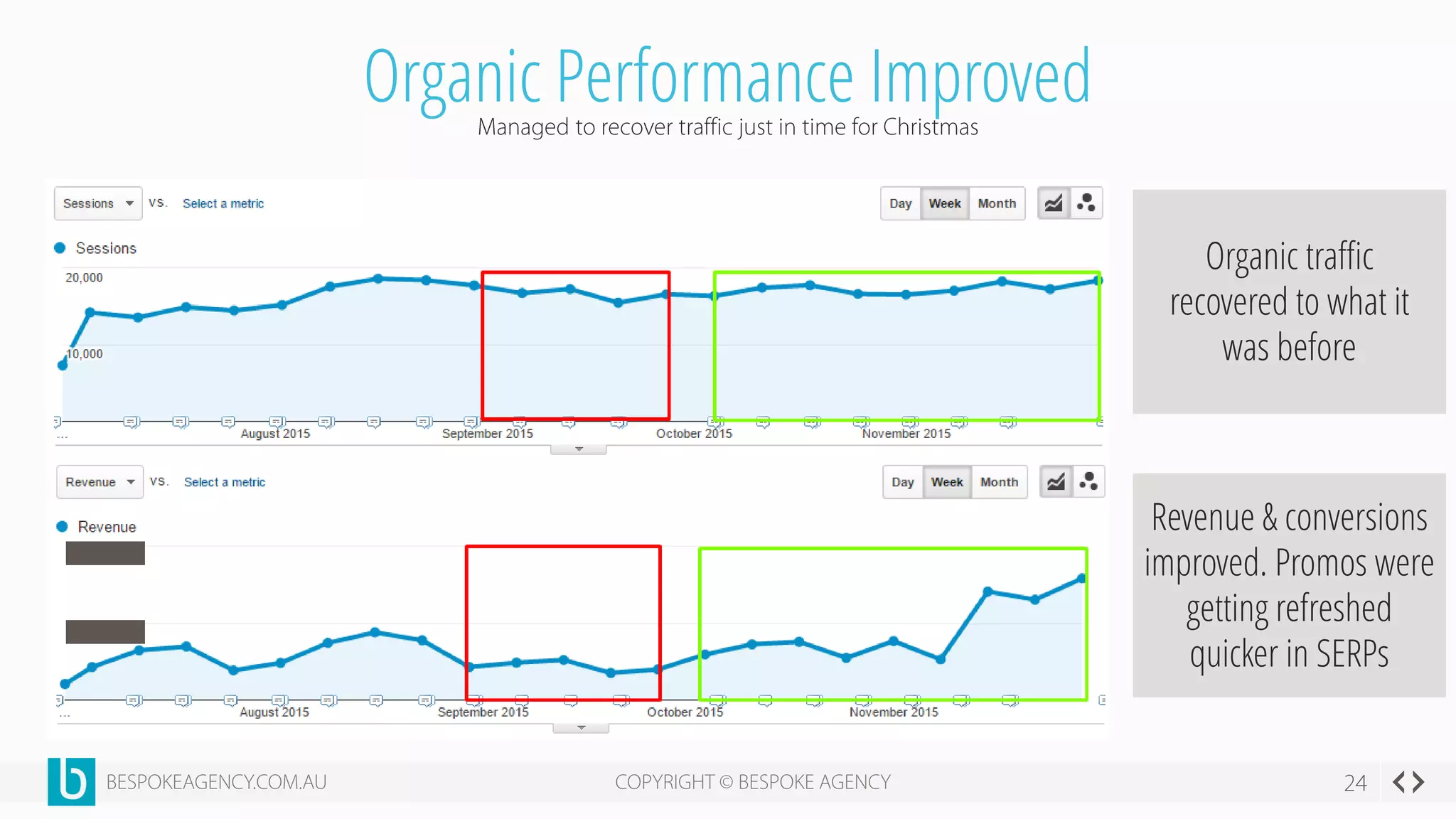
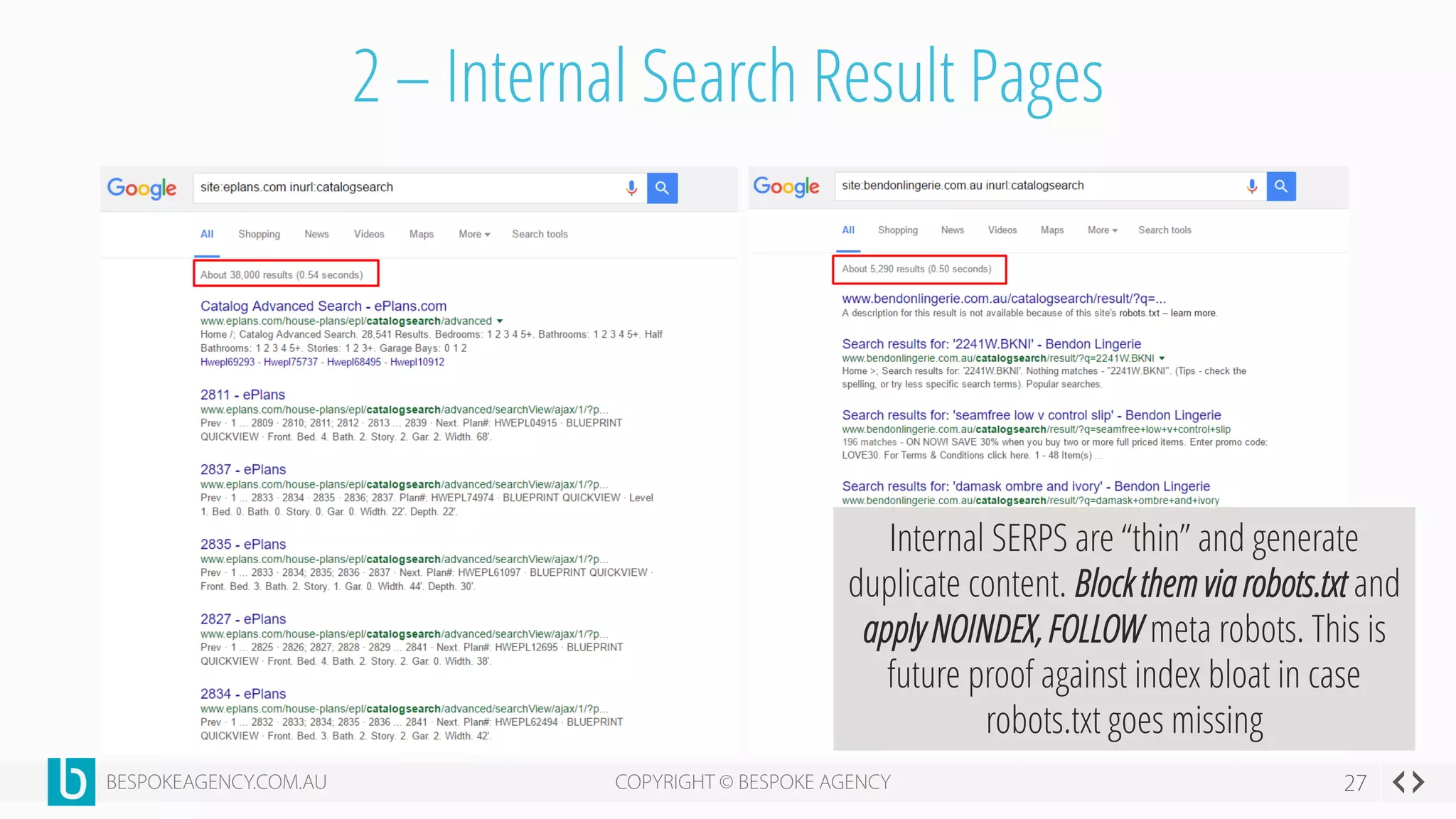
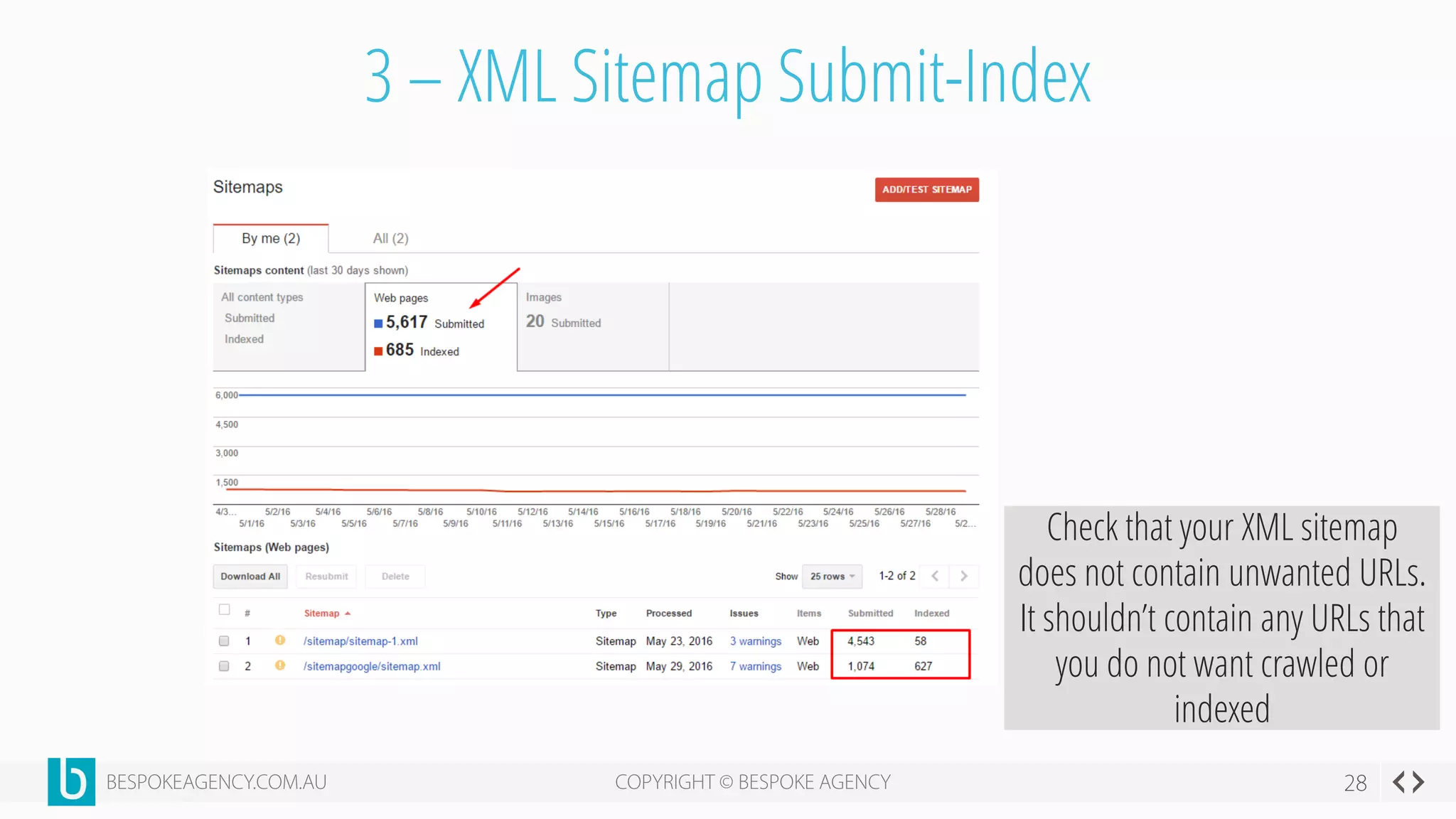
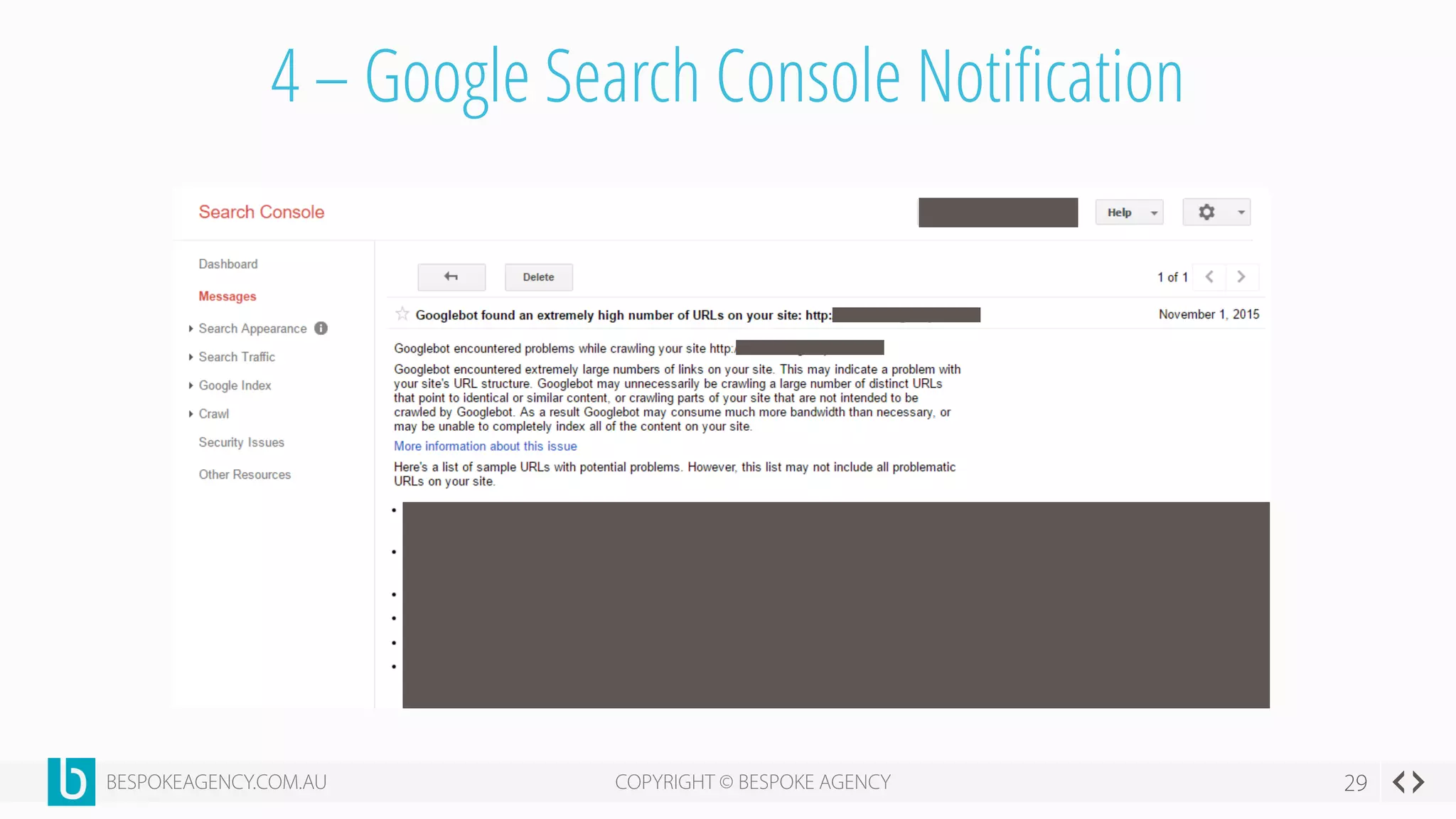
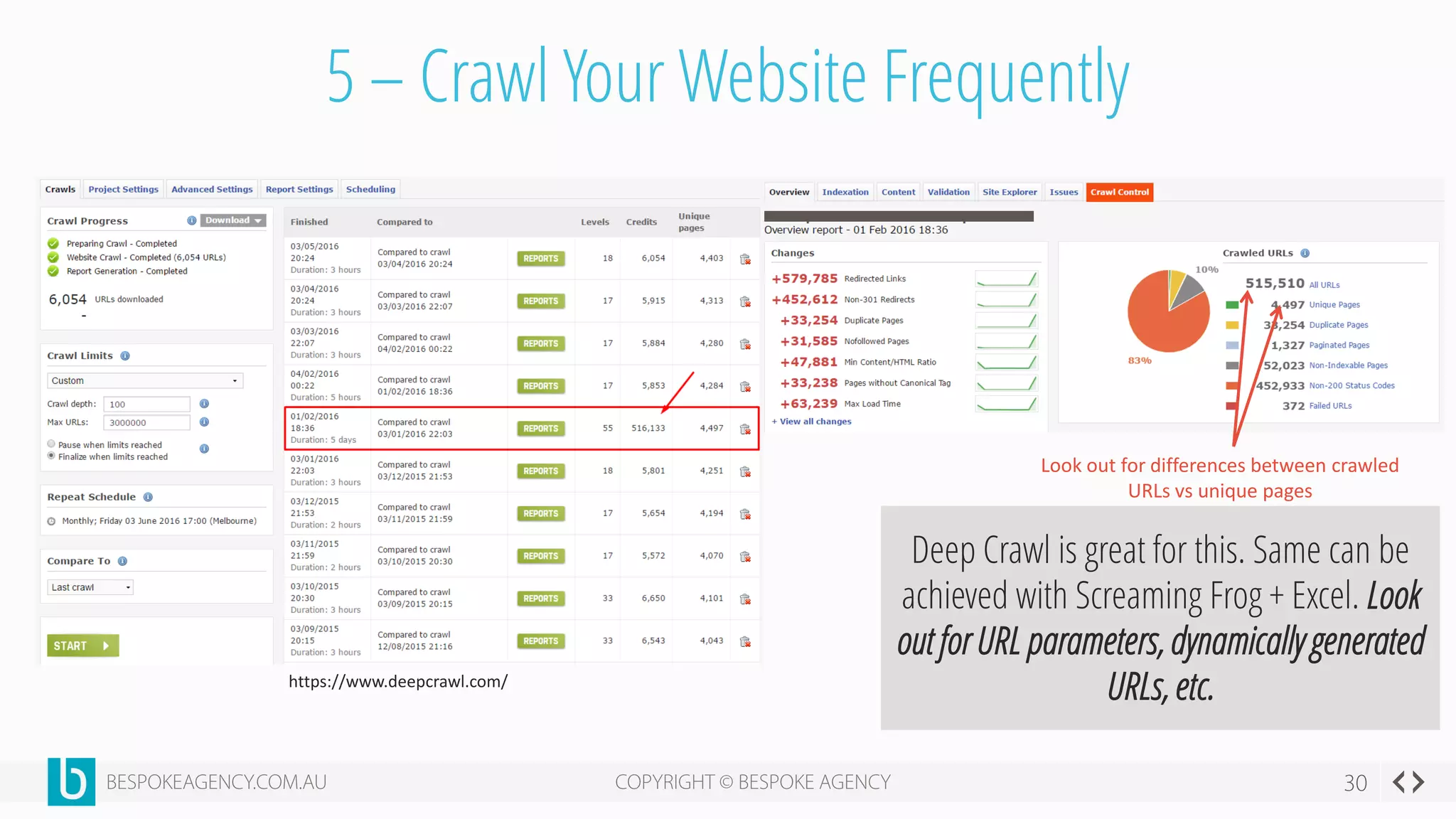
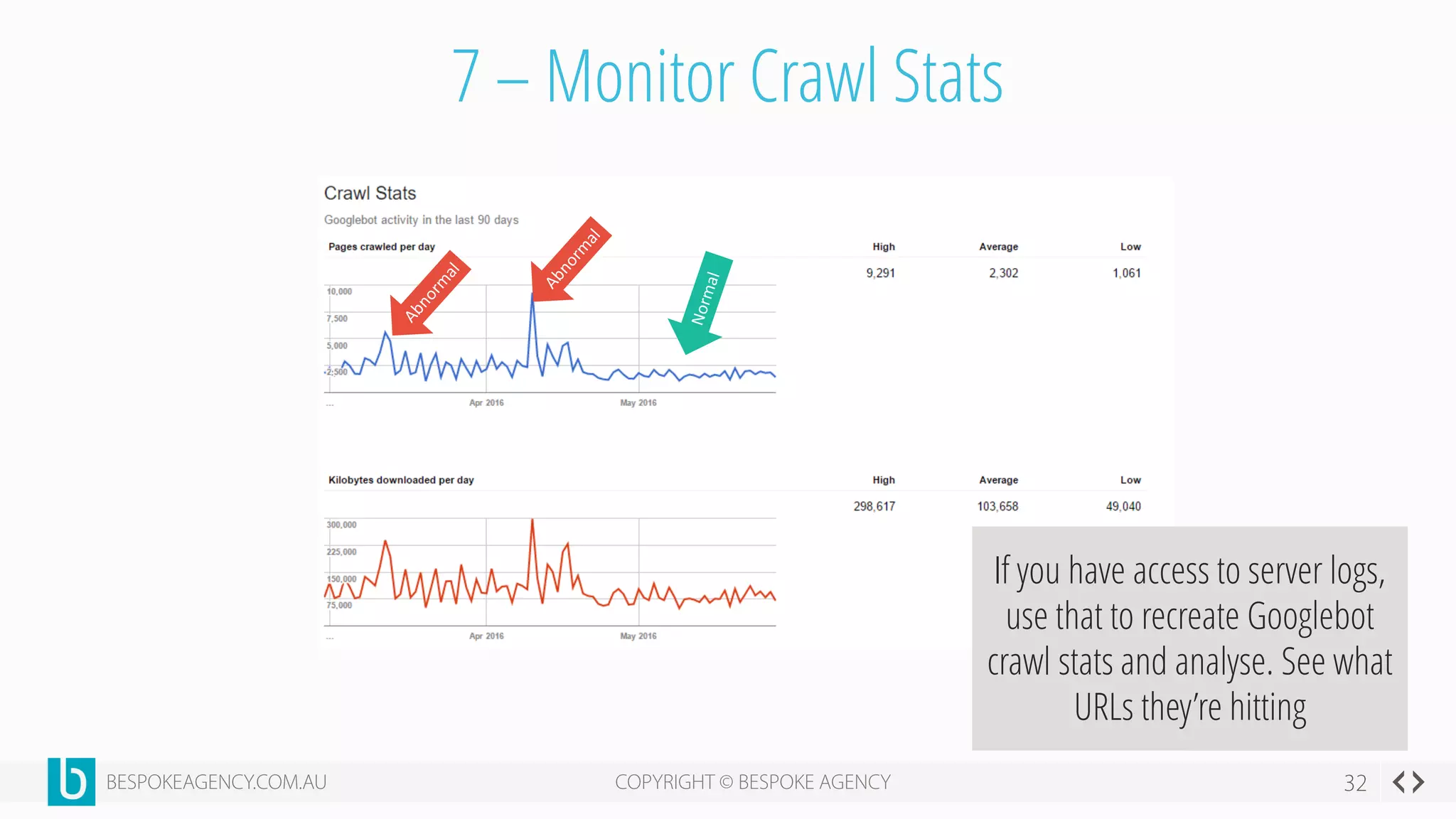
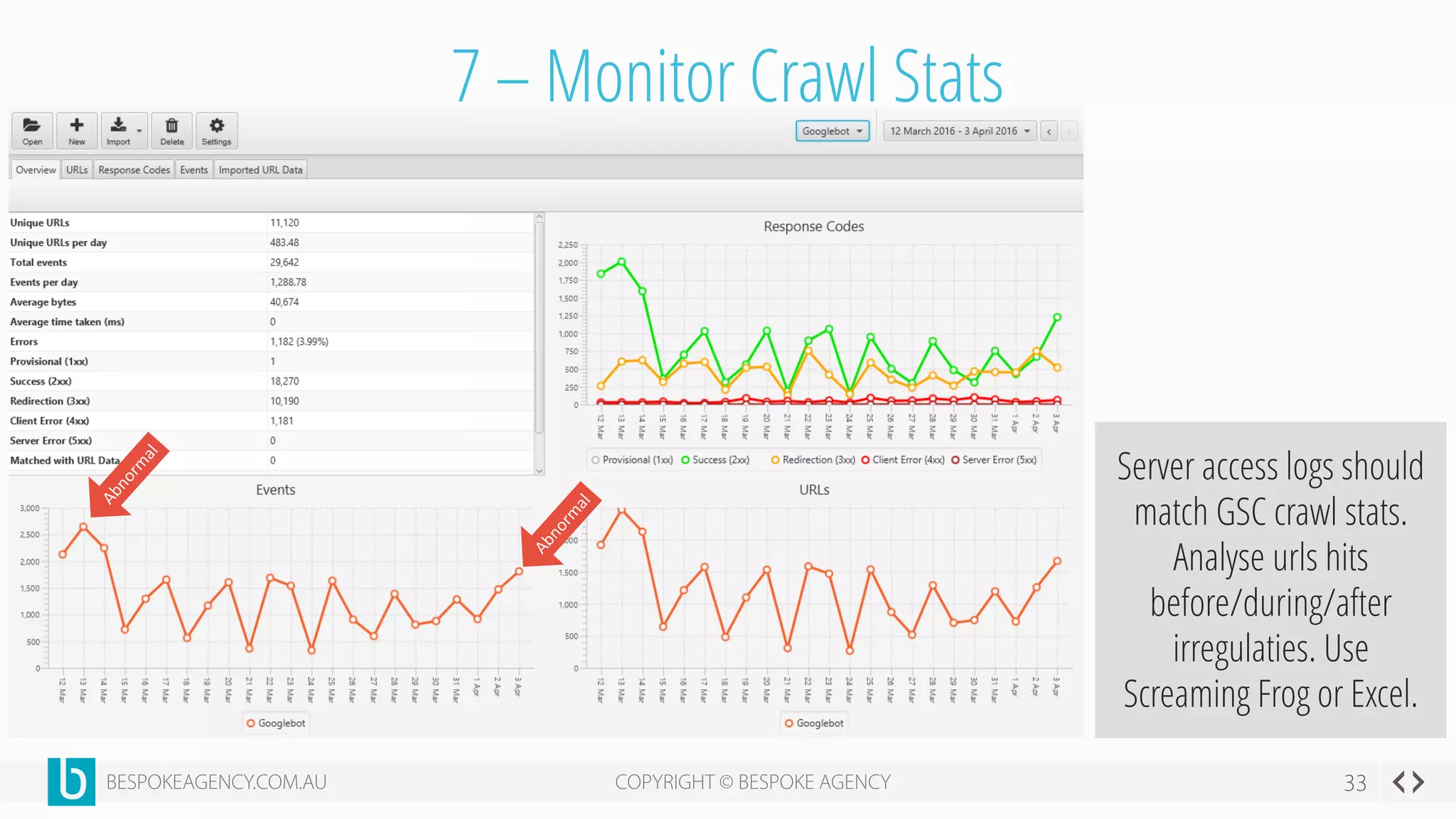
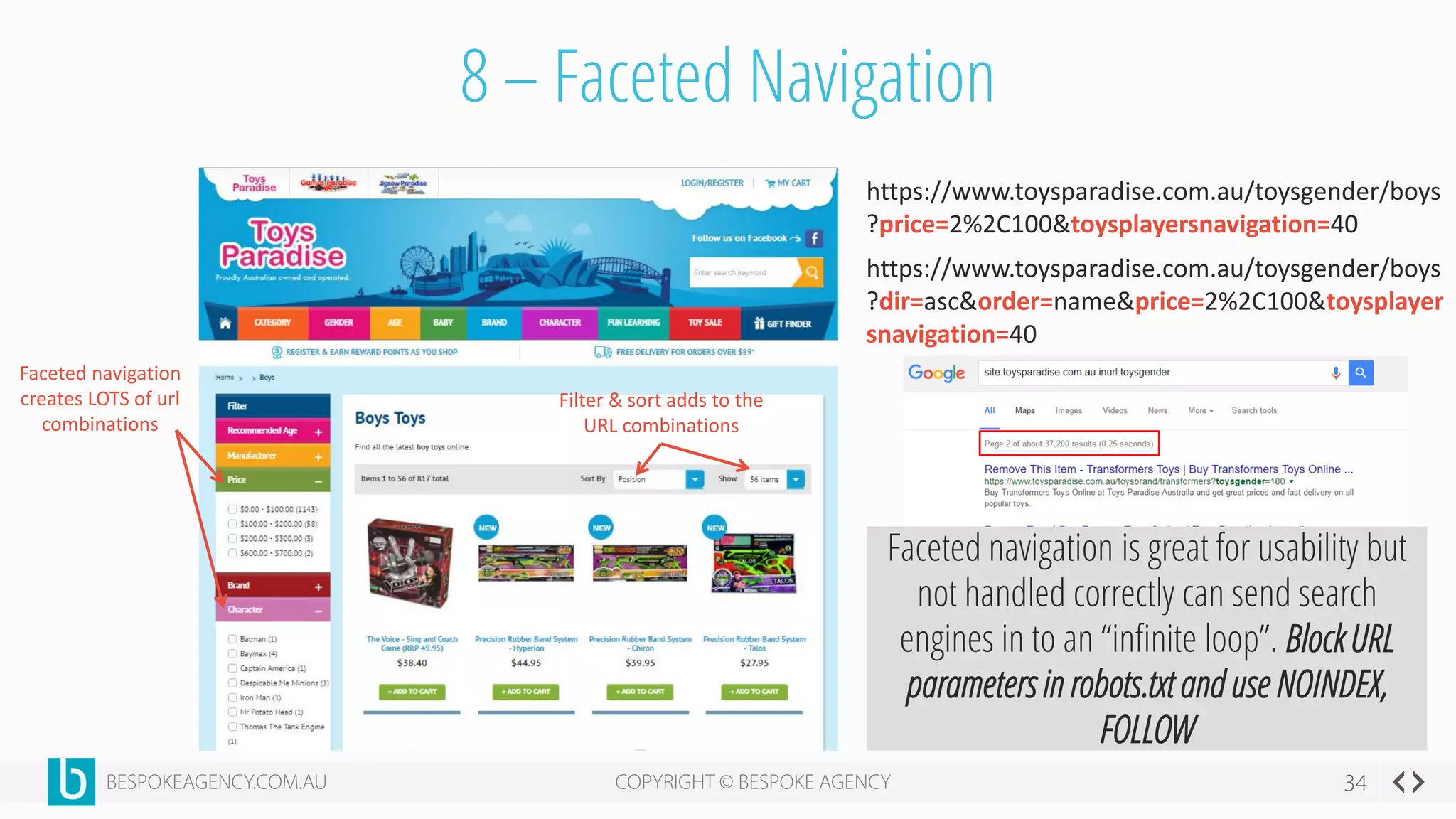
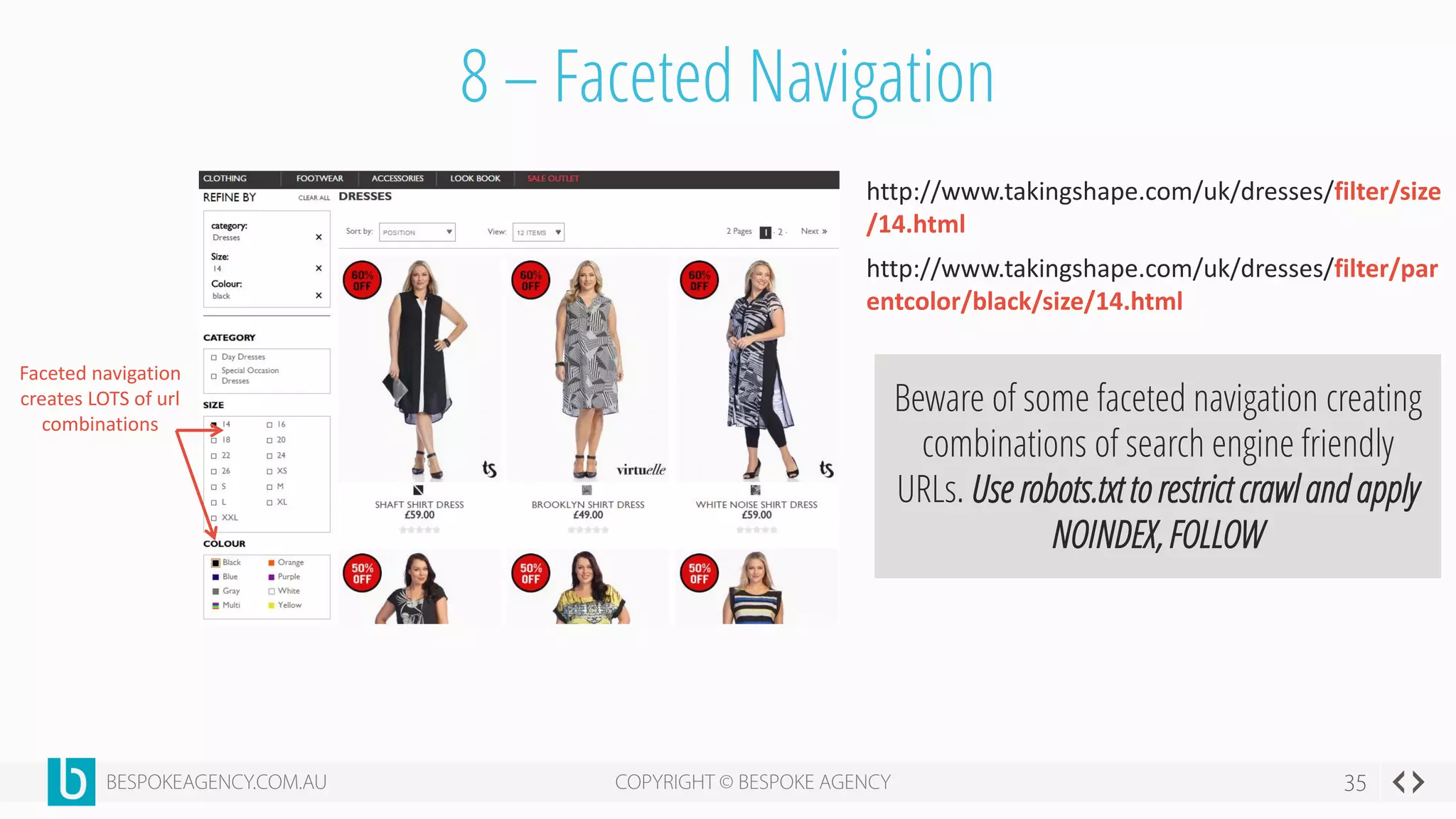
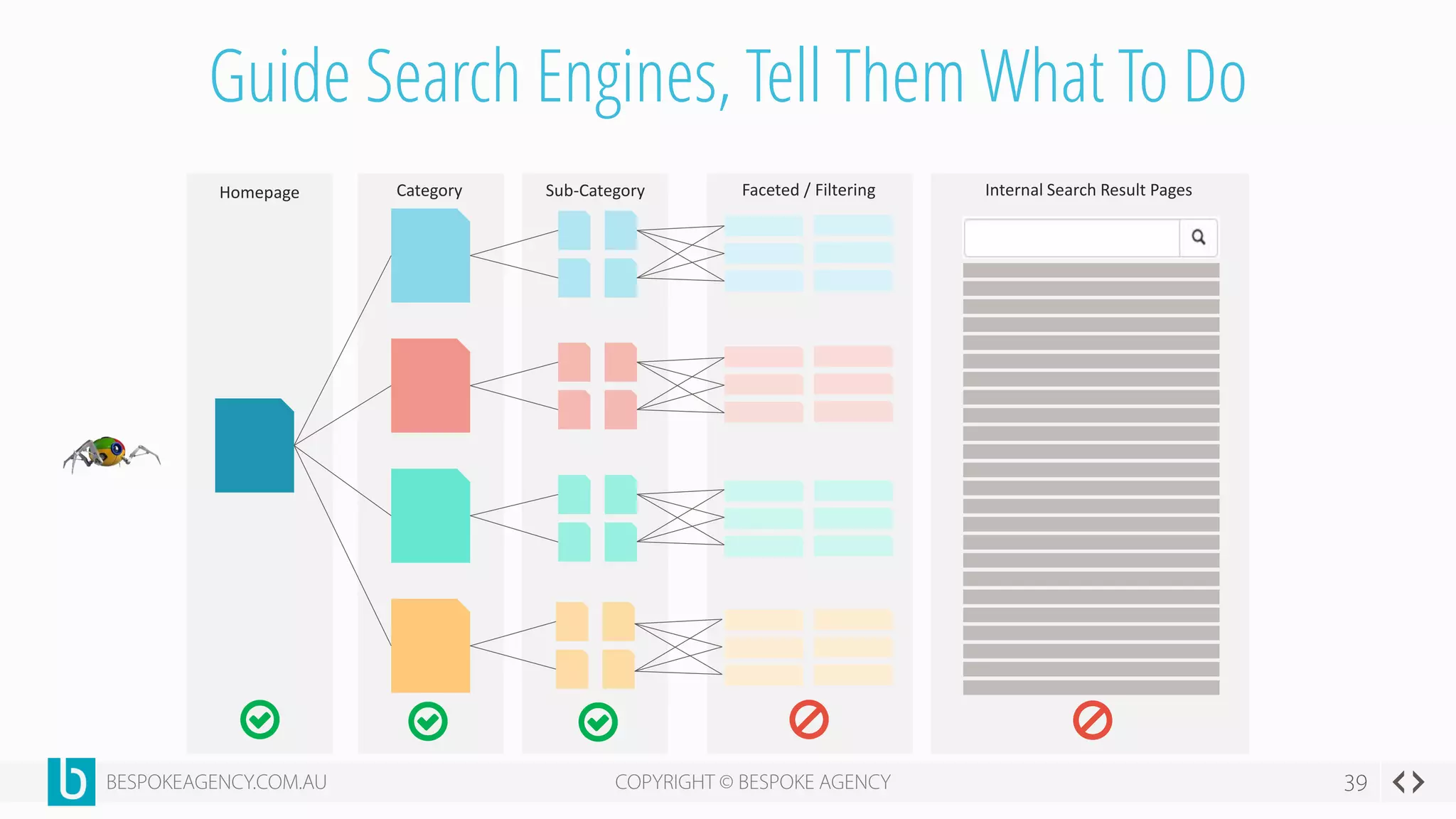
This document discusses crawl optimization and how to manage a website's crawl budget. It defines crawl optimization as controlling what content search engines can and cannot crawl and index. The document explains that a site's crawl budget is related to its PageRank, with higher ranked pages receiving more frequent crawls. It then presents a case study where an ecommerce site saw a spike in crawled and indexed pages that hurt organic performance. Investigating found the robots.txt file was missing, allowing unnecessary pages to be crawled. The document outlines various ways to identify and prevent crawl wastage like faceted navigation parameters and internal search results pages.