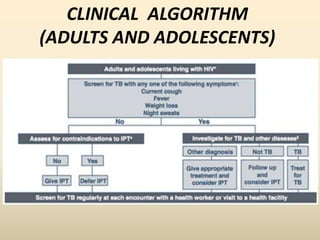
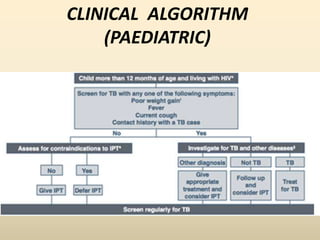
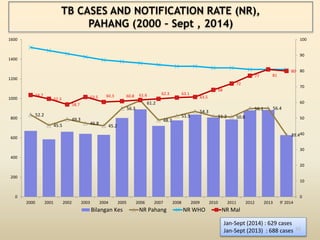
The document discusses Malaysia's intensified case finding (ICF) program for tuberculosis (TB) detection. It provides an overview of the 3 main components of ICF: intensified case finding, isoniazid preventive therapy, and infection control. It emphasizes finding TB cases early through screening high-risk groups like people living with HIV and in institutional settings like prisons. The goal is to reduce TB transmission in communities and improve TB treatment outcomes.