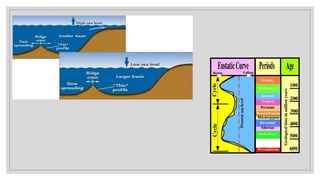
Sea level change can occur through two main processes: isostatic and eustatic. Isostatic changes are local and caused by land height changes, while eustatic changes are global and caused by ocean water volume changes. During ice ages, water is stored in glaciers causing eustatic sea levels to drop; melting then causes levels to rise. Coastlines can emerge from isostatic uplift or submerge through subsidence. Emergent coasts may have raised beaches and cliffs, while rias and fjords form in submerged areas. Sea level changes impact coastal ecosystems and infrastructure through flooding and erosion.