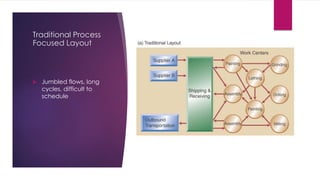
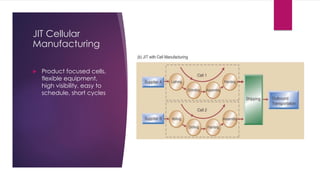
JIT is a system that aims to supply goods as close as possible to when they are needed to reduce inventory costs and waste. It originated in Japan in the 1960s at Toyota and focuses on just-in-time delivery, continuous improvement, quality at the source, and respect for people. Key aspects of JIT include eliminating waste, visual controls, flexible workflows, strong supplier partnerships, and respect for employees through consensus-based problem solving. JIT implementation requires organizational changes, setup time reductions, and a switch to pull-based production.