Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX




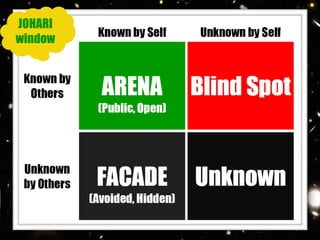




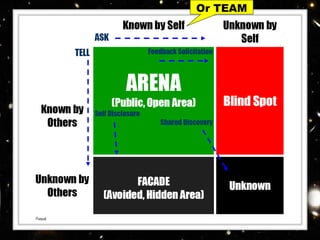






















The Johari Window model is a psychological tool created in 1955 to help people understand interpersonal communication and relationships. It uses four "panes" or categories to classify information about a person: Open Self, Blind Spot, Hidden Self, and Unknown. The goal is to increase the Open Self by disclosing more information and receiving feedback, and decrease the Unknown through greater self-awareness and understanding between individuals. The model was developed by Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham through their research on group dynamics and interpersonal relations. It remains a useful framework today for improving cooperation, empathy, and development within teams and organizations.































