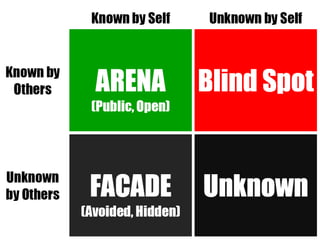
The document discusses interpersonal awareness and feedback processes, highlighting the Johari Window model, which enhances understanding and communication within groups. It outlines the four areas of the Johari Window: open area, blind spot, facade, and unknown, along with applications in improving interpersonal relationships. Additionally, the document describes strategies for giving and receiving feedback effectively to foster self-awareness and trust in interpersonal interactions.