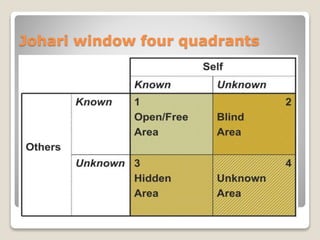
The Johari Window model is a framework for self-awareness and understanding interpersonal relationships that was created in 1955 by psychologists Joseph Luft and Harry Ingham. It divides information about a person into four categories based on what is known to the person themselves and what is known by others. The four areas are open self, blind spot, hidden self, and unknown. The model aims to increase self-awareness through feedback but has limitations if not linked to behavior change or when cultural factors impact receptiveness to feedback.