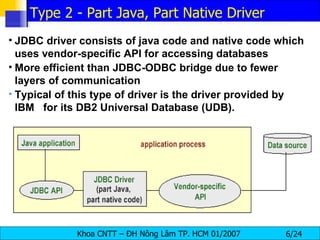
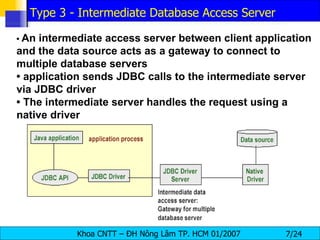
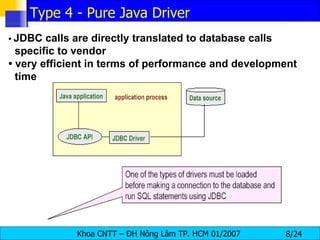
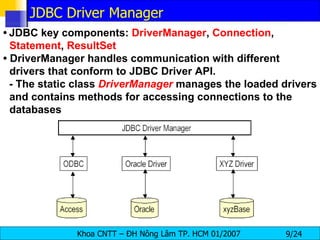
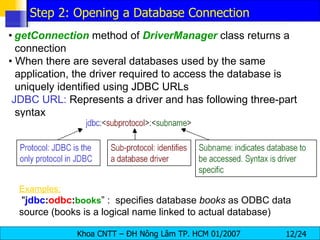
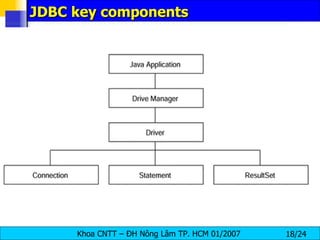
JDBC provides a standard interface for connecting to and interacting with relational databases in Java. It uses drivers specific to each database vendor to translate JDBC calls to calls native to that database. The key components of JDBC include the DriverManager for loading drivers, Connection for establishing a connection, Statement for executing SQL queries, and ResultSet for accessing the results.










![Basic Database operations public static void main(String[] args) { String url = "jdbc:odbc:sach" ; String userName = "ltmang" ; String password = "ltmang" ; try { Class. forName ( "sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver" ); Connection connection = DriverManager. getConnection (url,userName,password); Statement statement = connection.createStatement(); String sql = "select * from sach" ; ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(sql); while (rs.next()) { System. out .println(rs.getString( "tens" )); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdbc-091011080051-phpapp02/85/Jdbc-23-320.jpg)
