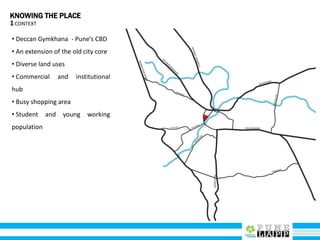
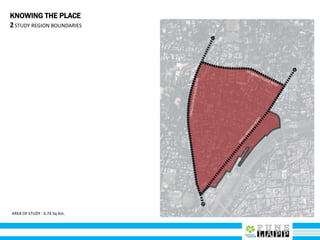
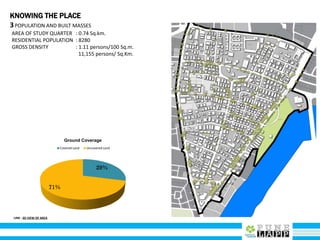
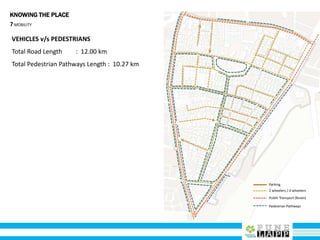
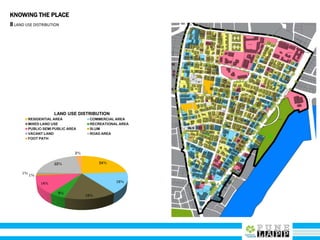
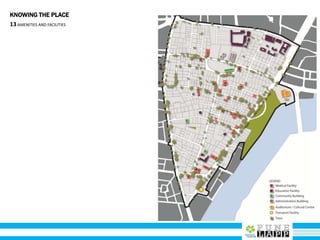
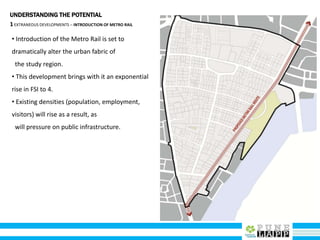
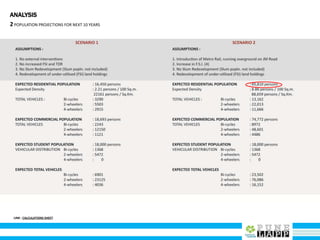
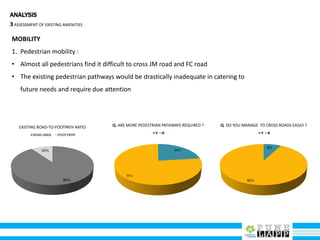
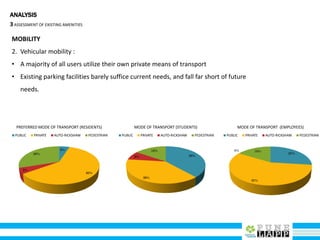
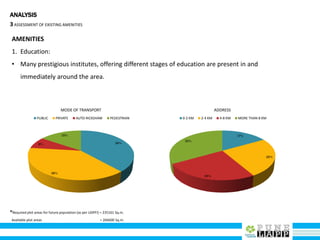
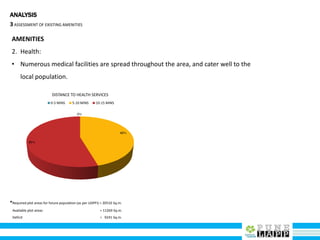
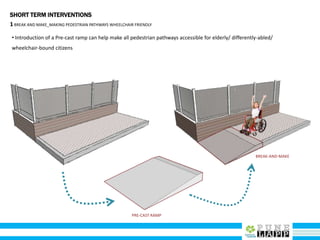
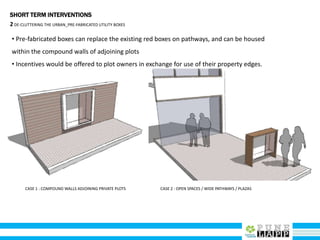
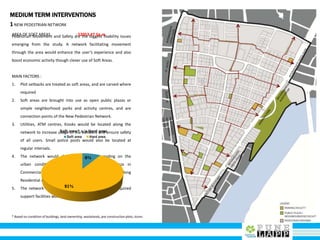
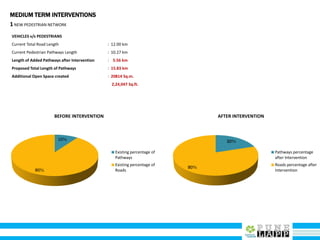
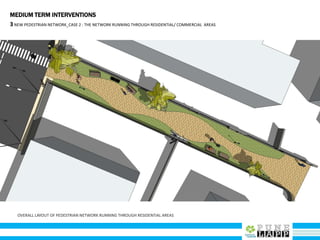
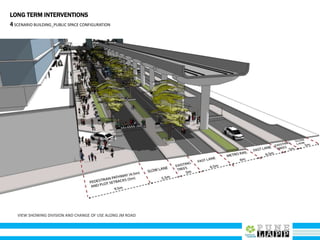
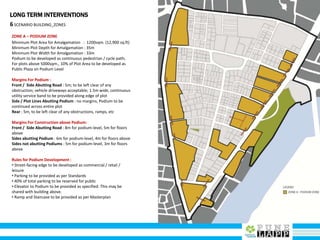
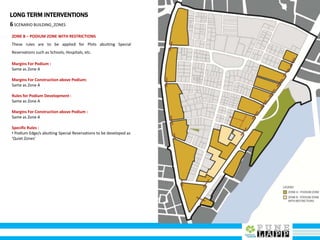
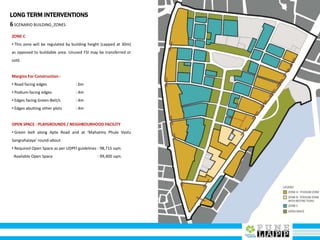
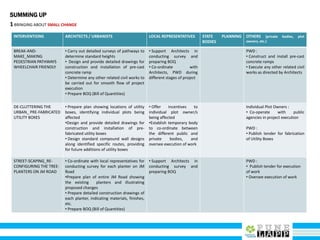
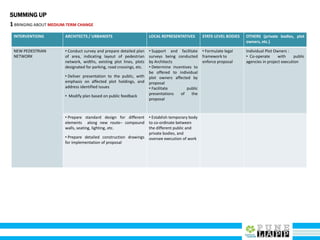
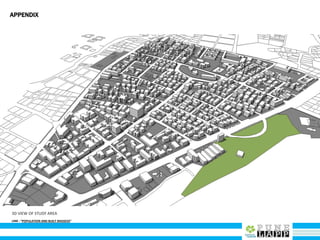
This document provides an analysis of Deccan Gymkhana, Pune's central business district. It summarizes the existing conditions, including land use, population density, transportation networks, and amenities. The analysis finds that while the area has many strengths like a mix of land uses and major institutions, it also faces issues like inadequate pedestrian infrastructure and parking. The document proposes short, medium, and long-term interventions to address these problems by creating a more connected pedestrian network, improving crossings, adding street furniture, and reconfiguring public spaces to accommodate future growth brought by a new metro rail project. The goal is to enhance mobility, accessibility, and quality of public spaces as the area undergoes significant changes.