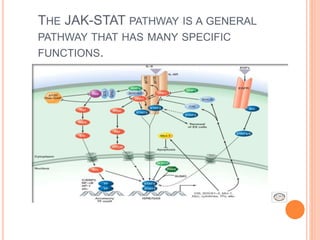
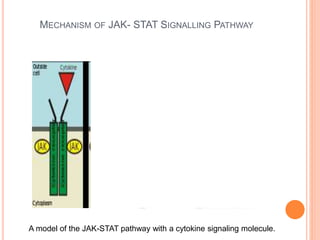
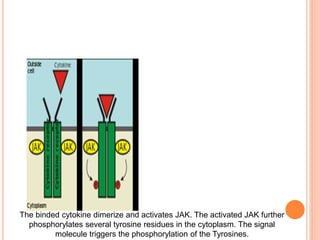
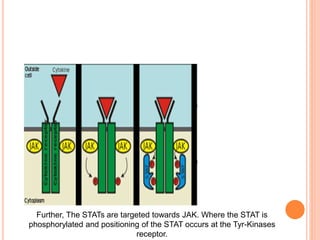
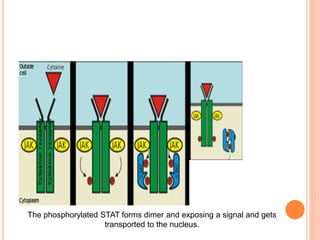
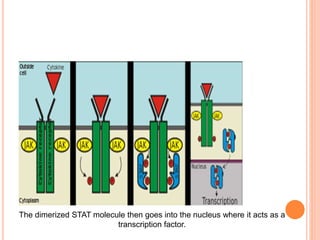
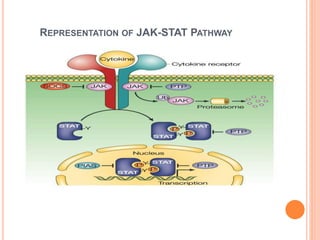
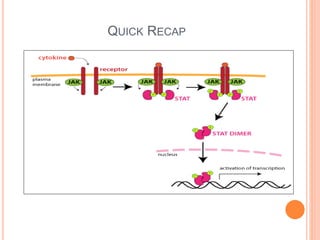
This document summarizes the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. It describes that the pathway involves Janus kinases (JAKs) and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins that communicate chemical signals from outside the cell to the cell's nucleus. The JAK-STAT pathway is involved in processes like immunity, cell division, cell death, and tumor formation. Disruptions to the pathway can lead to diseases affecting the skin, immune system, and cancers. The document outlines the key steps of the pathway including cytokine binding, JAK phosphorylation, STAT phosphorylation and dimerization, STAT transport to the nucleus to act as a transcription factor.