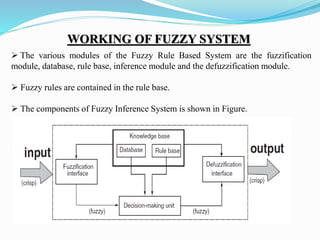
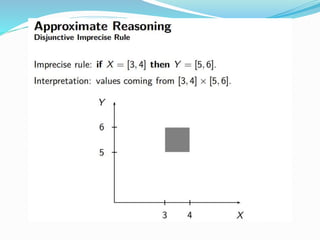
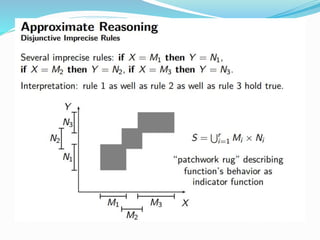
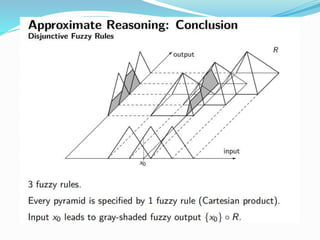
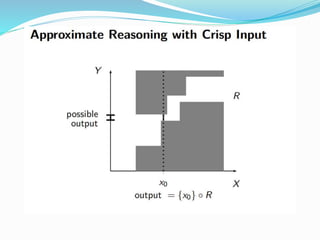
This document discusses fuzzy rule-based classification systems. There are three types of rules that can be formed: assignment statements, conditional statements, and unconditional statements. A fuzzy inference system uses a rule base of fuzzy rules to perform fuzzy reasoning and mapping of fuzzy inputs to outputs. The key components of a fuzzy inference system are fuzzification of inputs, a rule base, an inference engine, and defuzzification of outputs. Fuzzy rule-based systems find application in decision making problems.