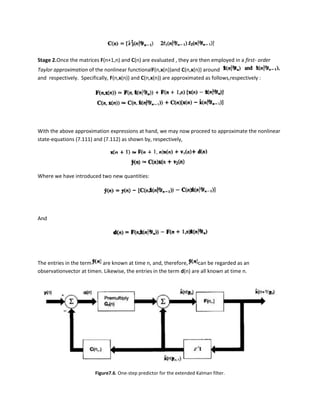
The document discusses the extended Kalman filter (EKF), which extends the standard Kalman filter to nonlinear systems through linearization. The EKF linearizes the system equations at each time step by taking the derivative of the nonlinear functions around the current state estimate. This results in an approximate linear system that can then be processed using the standard Kalman filter equations. The key steps of the EKF algorithm are to 1) compute the linearized system matrices using derivatives, 2) use these in a first-order Taylor approximation to linearize the system equations, and 3) apply the standard Kalman filter equations to this approximate linear system to recursively estimate the state.
![THE EXTENDED KALMAN FILTER
The Kalman filtering problem considered up to this point has addressed the estimation of as state vector
in a linear model of a dynamical system. If, however, the model is nonlinear, we may extend the use of
Kalman filteringthrough a linearizationprocedure. The resulting filter is naturally referred to as extended
Kalman filter (EFK). Such an extension is feasible by virtue of fact that Kalman filters described in terms
of differential equations (in the case of continuous–time systems) or difference equations (in the case of
discrete-time systems). This is in contrast to Wiener filter that is limited to linearsystems,since the
notion of an impulse response (on which the Wiener filter is based ) is meaningful only in the context of
linear systems . Hereis another important advantage of Kalman filter over the Wiener filter.
To set the stage for development of the extended Kalman filter in the discrete-time domain, consider
first the standard linear state –space model that we studied in the earlier part of this chapter [Eqs. (7.17)
and (7.19)], reproduced here for convenience of presentation:
Where v1(n) and v2(n) are uncorrelated zero-mean white-noise processes with correlation matrices
Q1(n) and Q2(n), respectively, as defined in equations(7.18),(7.20), and (7.21). thecorresponding Kalman
filter equations are summarized in Table. In this section, however we will rewrite these equations in a
slightly modified form that is more convenient for our present discussion. Specifically,the update of the
sate estimate is performed in two steps . The first step updates this update
equation is simply (7.59).The second step updates and is obtained by substituting Eq.
(7.45)into Eq. (7.60),and by defining a new gain matrix:
We may thus write
We next make the following observation. Suppose thatinstead of the state equations (7.99) and (7.100),
weare given the alternative state vector model](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theextendedkalmanfilter-120311234933-phpapp02/85/The-extended-kalman-filter-1-320.jpg)