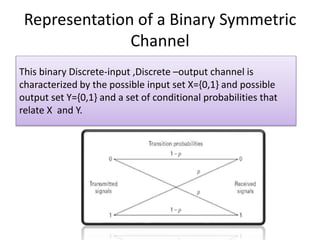
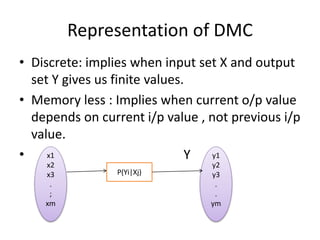
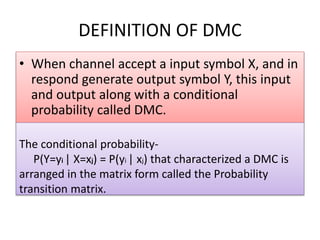
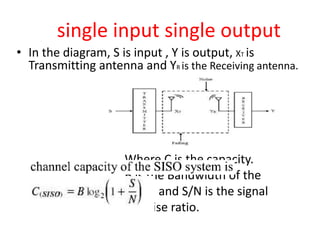
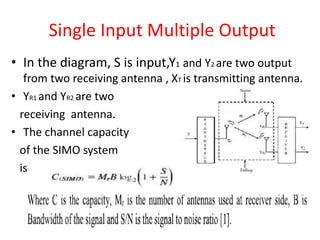
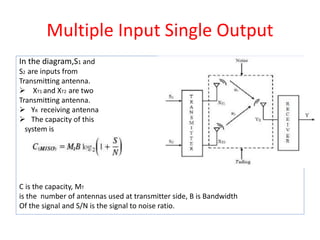
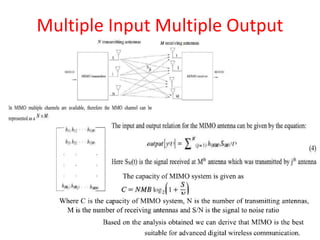
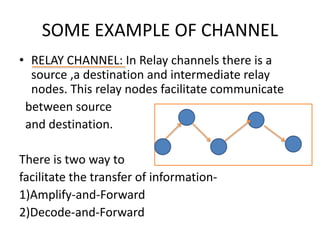
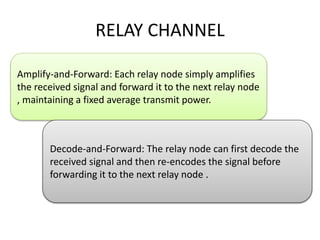
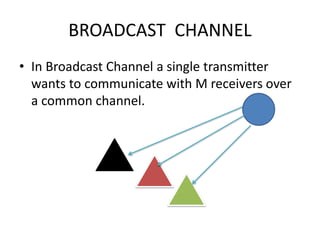
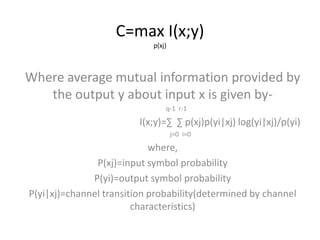
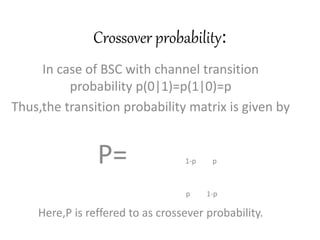
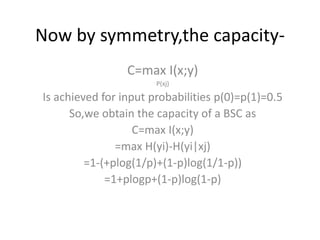
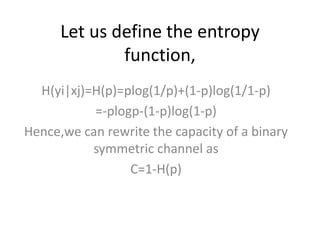
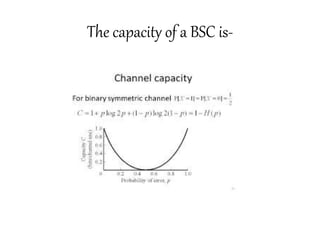
This document introduces channel models and channel capacity. It defines a binary symmetric channel (BSC) as a channel with input and output sets of {0,1} and a crossover probability p that an input bit is flipped. A discrete memoryless channel is characterized by a conditional probability matrix relating discrete inputs to outputs. Channel types include single-input single-output, single-input multiple-output, multiple-input single-output, and multiple-input multiple-output. Channel capacity is the maximum mutual information between input and output, achieved by optimizing the input distribution. Capacity examples include relay channels and multiple access channels. The BSC capacity is 1-H(p) where H(p) is the entropy function