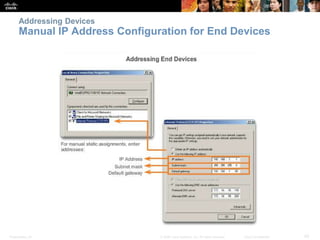
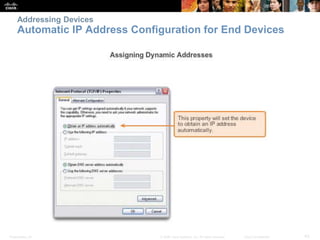
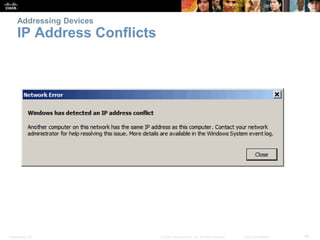
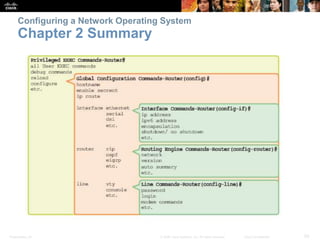
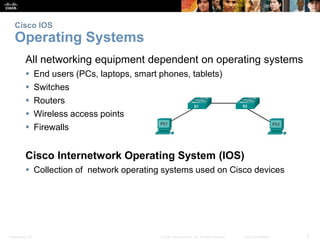
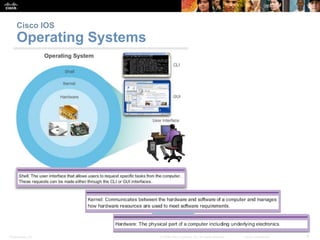
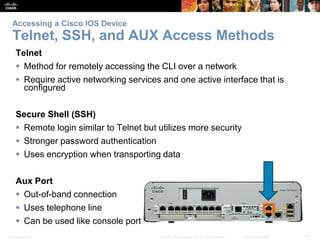
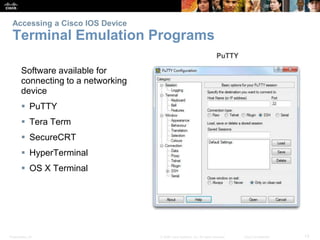
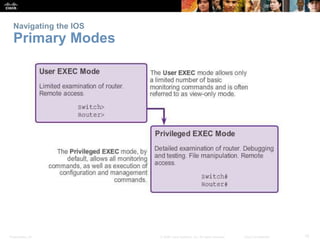
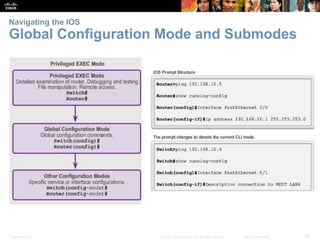
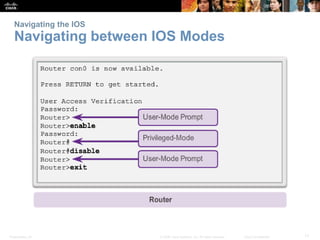
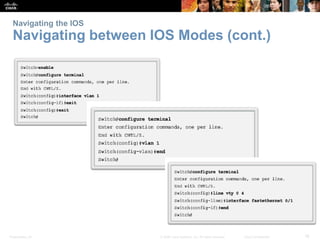
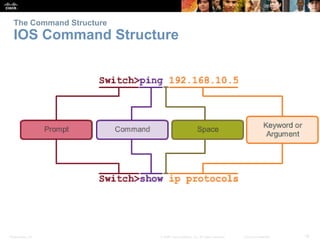
This chapter discusses configuring a network operating system using Cisco IOS. It covers accessing and navigating the Cisco IOS using the command line interface, setting hostnames and IP addresses, securing device access, and verifying basic network connectivity. Key topics include how to configure a switch hostname, set passwords to limit access, assign IP addresses to devices and interfaces, and use ping and show commands to test connectivity.




















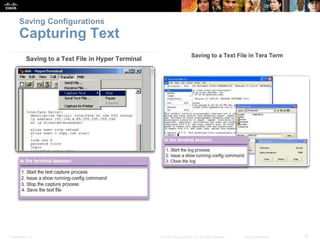
![Saving Configurations
Configuration Files
Switch# reload
System configuration has
been modified. Save?
[yes/no]: n
Proceed with reload?
[confirm]
Startup configuration is
removed by using
the erase startup-config
Switch# erase startup-config
On a switch you must
also issue the delete
vlan.dat
Switch# delete vlan.dat
Delete filename [vlan.dat]?
Delete flash:vlan.dat?
[confirm]
Presentation_ID © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Confidential 36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itninstructorpptchapter2-140924015728-phpapp01/85/CCNA-RS_ITN-Chapter-2-36-320.jpg)