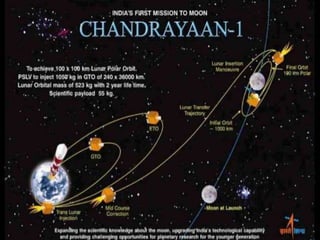
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is India's space agency, established in 1969 with a vision to use space technology for national development. ISRO has launched many satellites using its family of launch vehicles like PSLV and GSLV. Notable missions include India's first satellite Aryabhata launched in 1975, INSAT for telecommunications, and Indian Remote Sensing satellites which form the largest civilian remote sensing constellation. Current and future missions include Chandrayaan-2 to the moon, Aditya-1 solar mission, and development of reusable launch vehicles. ISRO has achieved numerous firsts for India including successful Mars and moon missions.