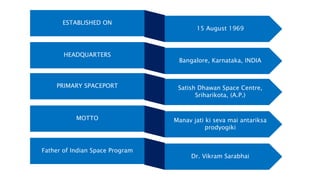
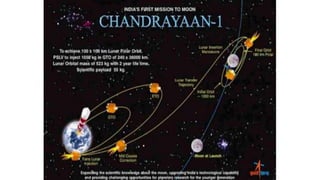
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is the space agency of India. ISRO was established in 1969 with a vision to use space technology for national development and pursue space science research. Since then, ISRO has launched many satellites and developed launch vehicles like PSLV and GSLV. Notable missions include Chandrayaan-1, which discovered water on the Moon, and Mangalyaan, which made India the first nation to reach Mars orbit on its first attempt. ISRO continues to work on future projects like human spaceflight and a space station.