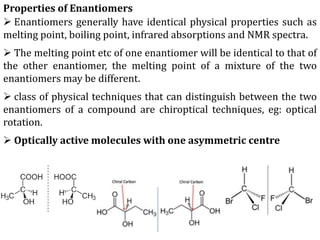
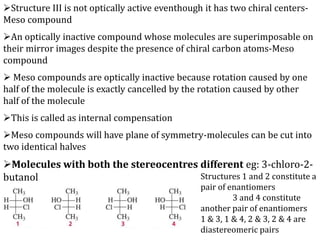
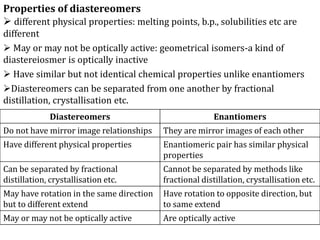
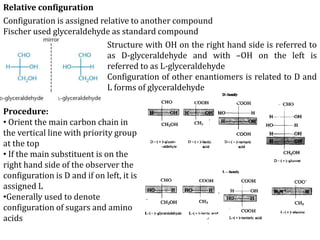
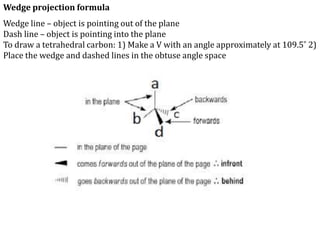
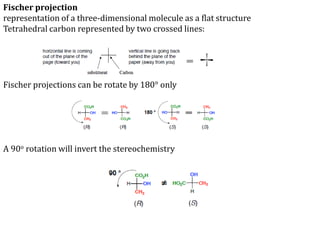
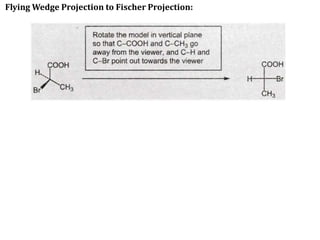
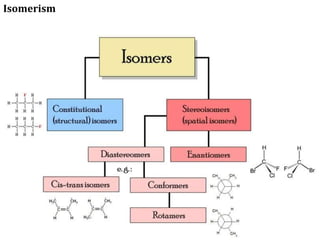
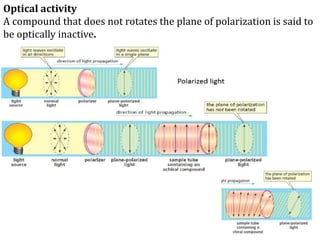
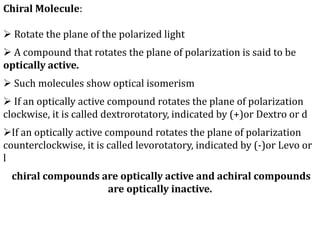
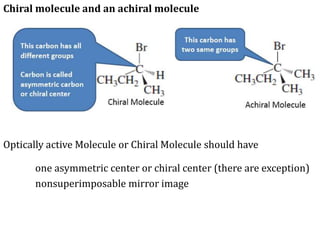
This document discusses stereochemistry and isomerism in organic compounds. It defines stereoisomers as isomers that have the same connectivity of atoms but differ in their spatial arrangements. Optical isomers are stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images and can rotate the plane of polarized light in opposite directions. Chiral molecules have an asymmetric carbon atom and are optically active, while achiral molecules are optically inactive. Enantiomers are a pair of chiral molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. Diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror images. Absolute configuration defines the actual spatial arrangement of atoms, while relative configuration relates a compound's configuration to a


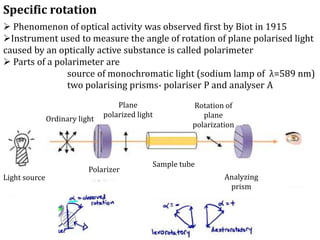

![The specific rotation αD is given by
Where α is the observed rotation, l is the length of the polarimeter in
dm and c is the concentration of the substance in grams per ml
Thus specific rotation can be defined as the observed angle of
optical rotation α when plane polarized light is passed through a
sample of pathlength one decimeter and concentration of 1gm per
ml.
Molecular rotation is the product of molecular mass and specific
rotation.
The specific rotation of sucrose solution at 20oC using sodium light is
[α]D
20= +66.5o
The sign + denotes that sucrose is dextrorotatory or it rotates plane
polarized light in clockwise direction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stereochemistrysem3core-200929140034/85/Stereochemistry-9-320.jpg)