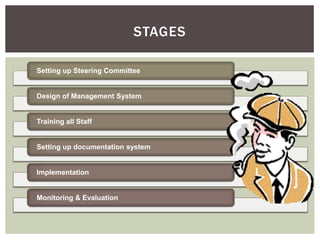
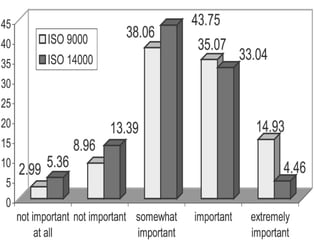
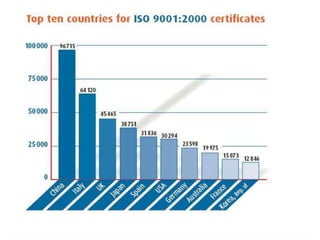
This presentation provides an overview of ISO 9000 certification. It discusses what ISO is and how it develops international standards. ISO 9000 refers to quality management standards that over a million organizations in 175 countries have implemented. The key elements of ISO 9000 certification are explained, along with the stages of achieving certification, advantages and disadvantages. Generic standards mean the same requirements can apply across industries and organizations of different sizes. The focus is on managing processes to ensure quality products and services, rather than setting product standards. Certification involves an external audit to verify conformance with ISO 9000 standards.