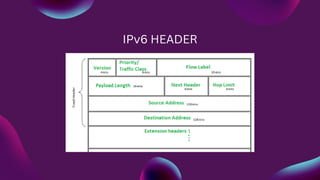
IPv6 was designed by IETF to replace IPv4 due to the exponentially growing number of internet users. IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses compared to IPv4's 32-bit addresses, providing trillions more available addresses to meet future demand. IPv6 protocols were upgraded from IPv4, such as OSPF becoming OSPF3 and ARP being replaced by NDP. IPv6 addresses can be written in abbreviated or unabbreviated hexadecimal format, and use prefix lengths to identify the network portion similar to IPv4 subnet masks.