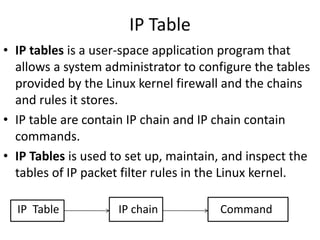
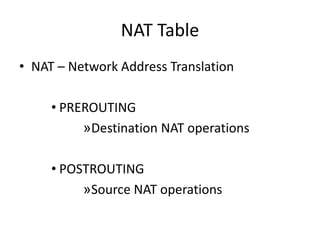
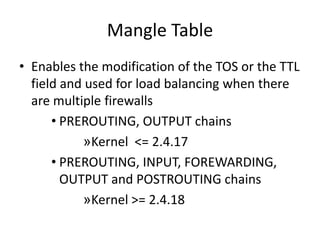
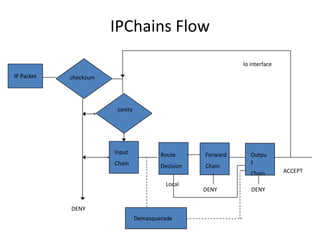
This document discusses IP routing and firewall configuration in Linux. It covers IP forwarding, the routing cache, routing tables, and rule-based routing. It then discusses IP tables, which contain three tables (filter, NAT, mangle) and chains. Each table contains chains and rules to filter, translate, or modify packets. IP chains are used to divert and return packets between the tables. The document provides examples of IPTables and IPChains commands used to manage rules and packet flow.