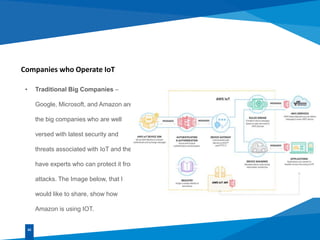
This document discusses IoT security threats and challenges. It begins by defining IoT as the network of physical objects embedded with electronics, software and sensors that enables them to connect and exchange data. It then discusses common IoT devices and associated security challenges in protecting embedded chips from remote attackers. It outlines common threats like vulnerable perimeters, data breaches, and malware/botnet attacks. Finally, it summarizes the top 10 IoT vulnerabilities introduced by OWASP like insecure interfaces, authentication, encryption and software/firmware issues.