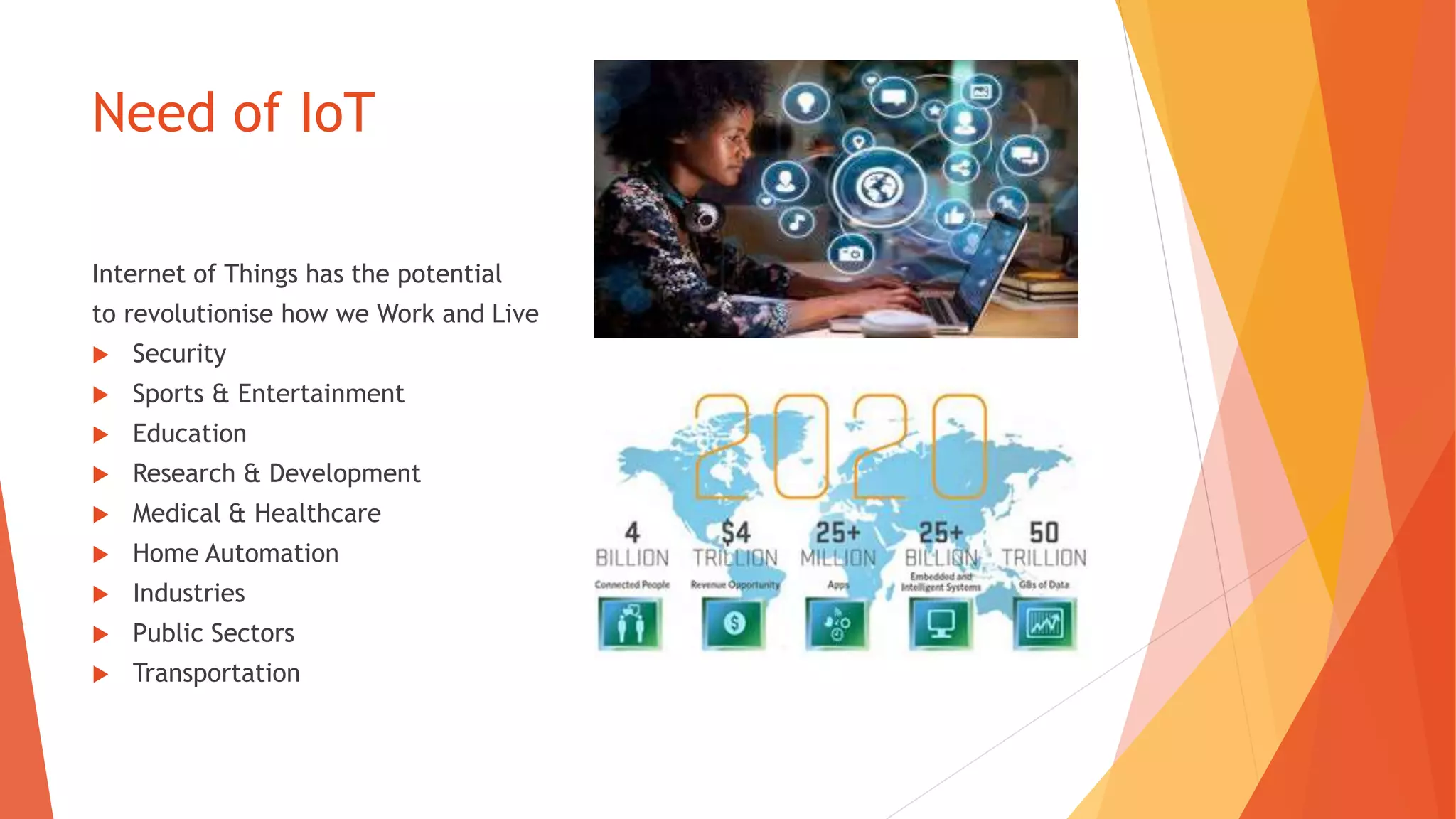
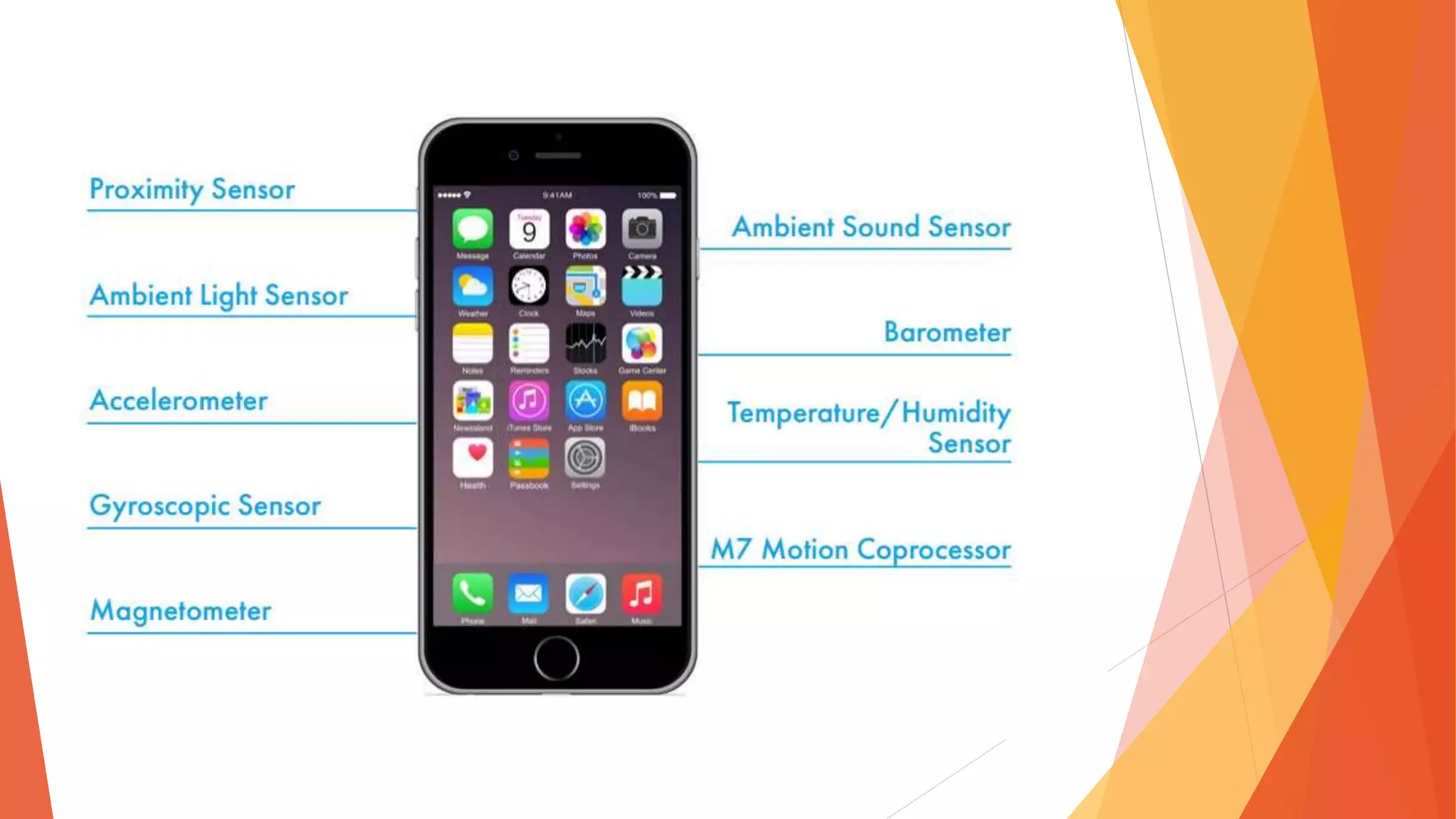
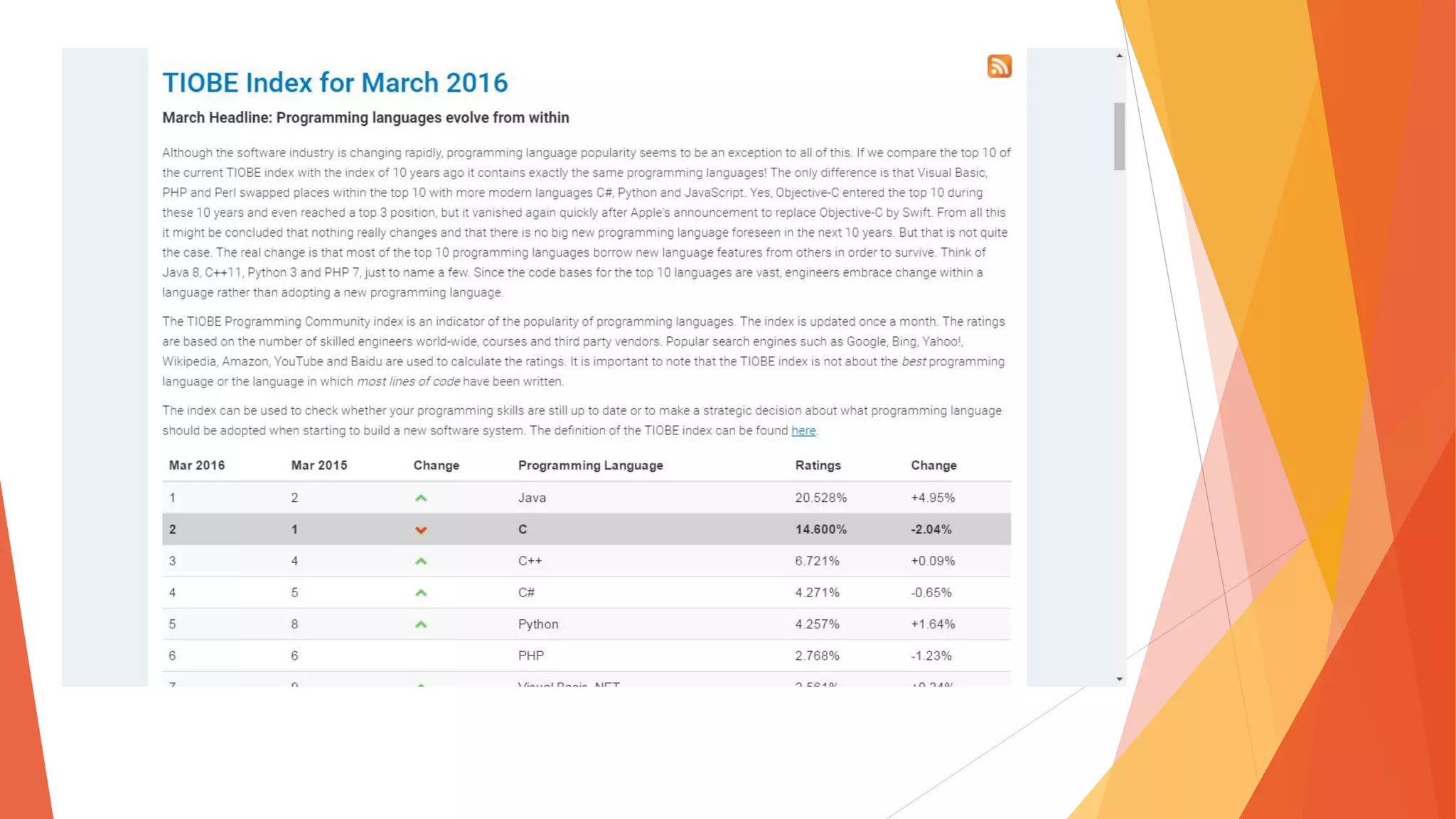
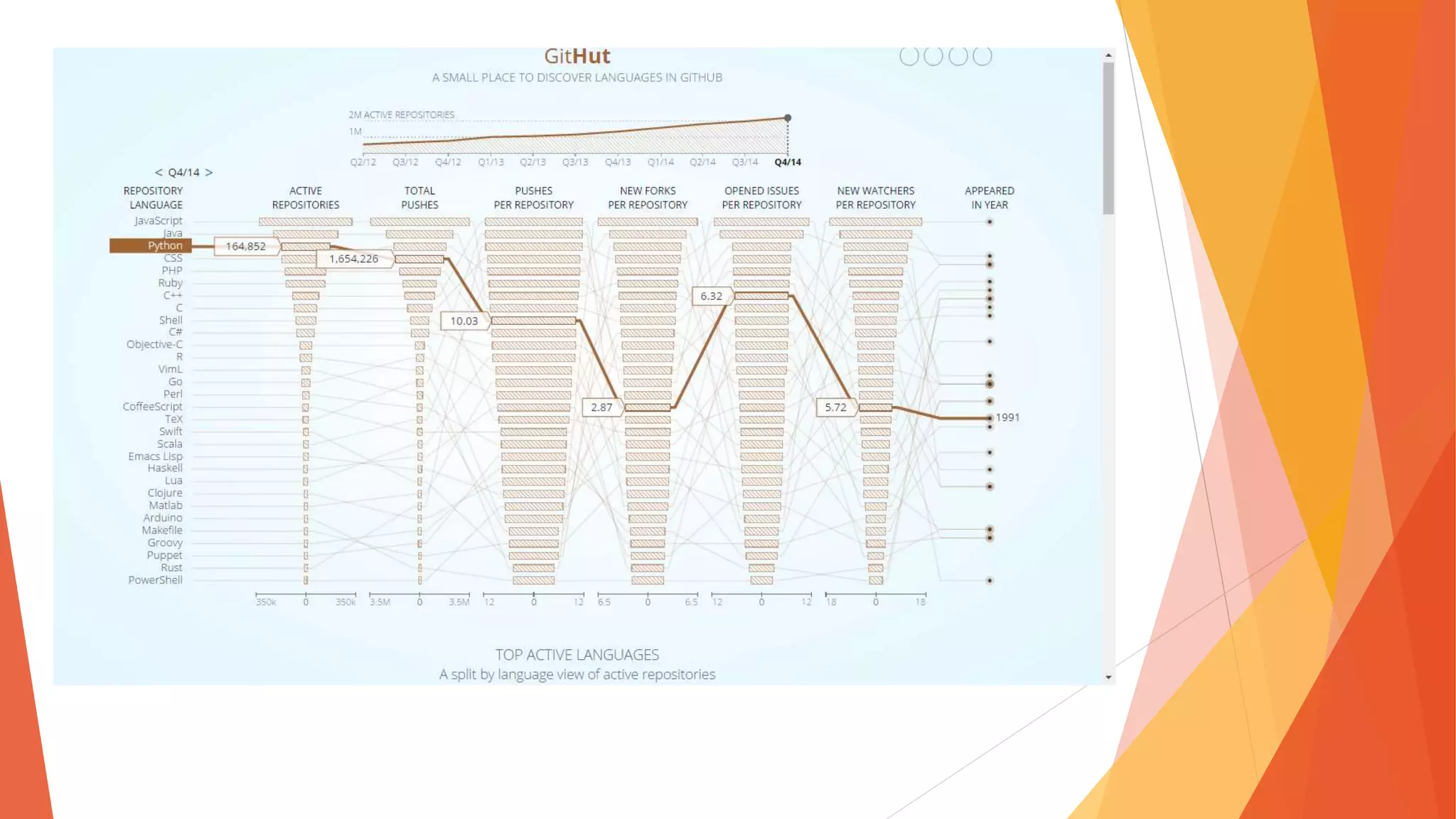
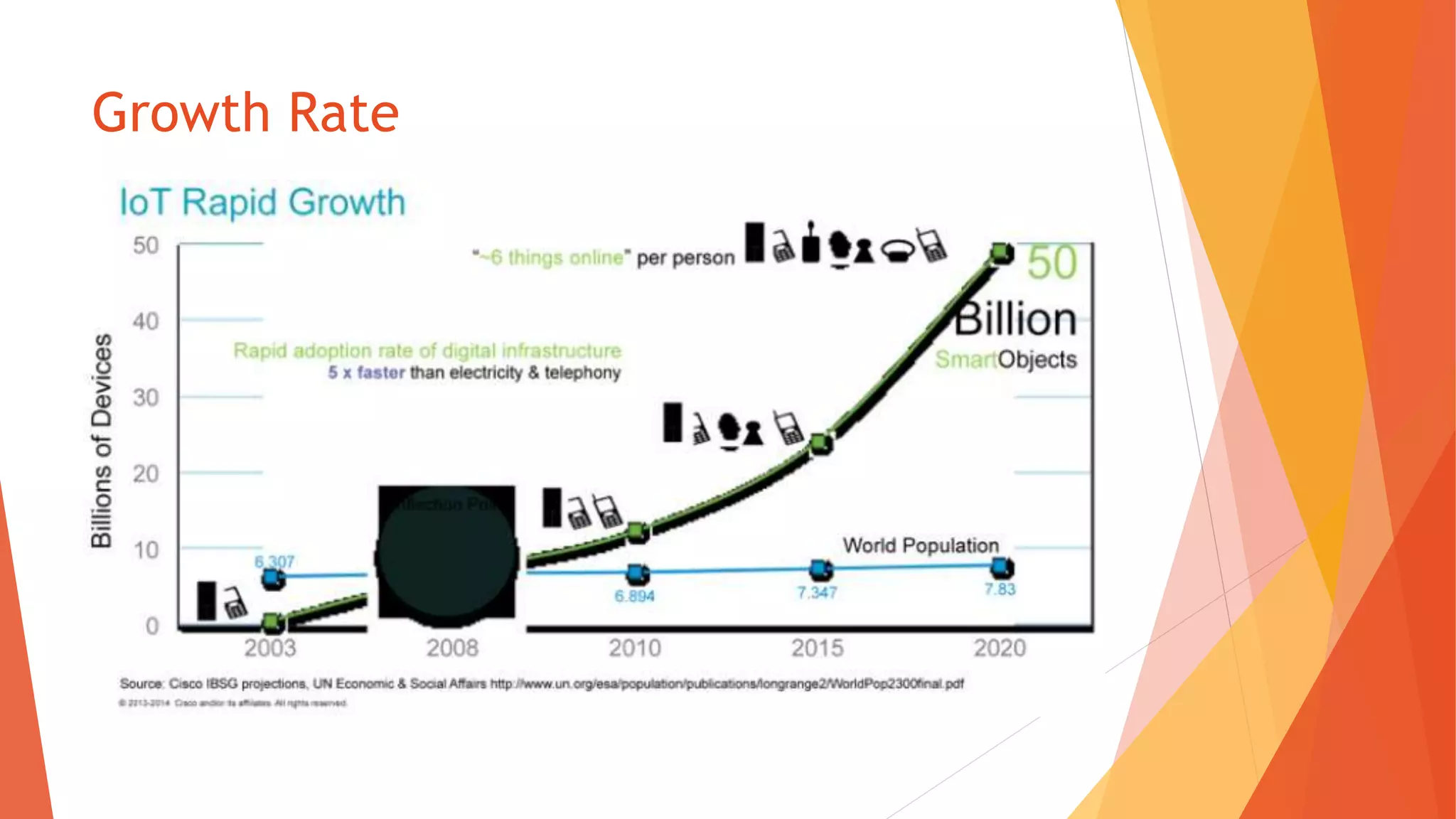
The document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT), describing it as the interconnection of physical devices embedded with technology to collect and exchange data across various sectors including healthcare, education, and industry. It highlights the skills needed for IoT development, the importance of cost-effectiveness, privacy, and security implications, as well as the necessity for interoperability among devices. Major companies such as Microsoft, IBM, and Apple are noted for their investments in advancing IoT technology.