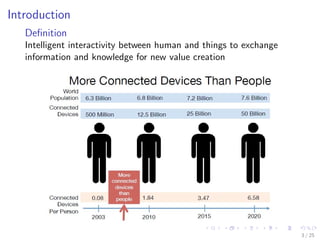
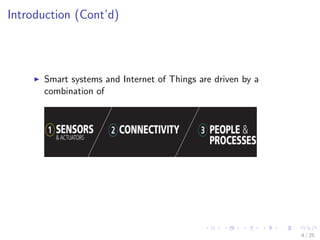
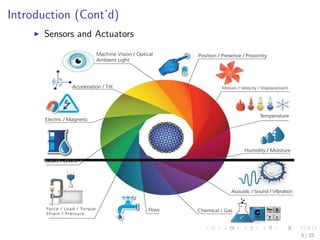
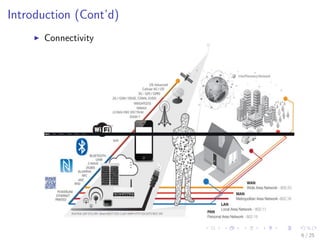
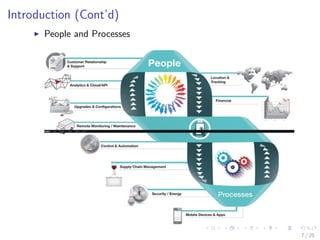
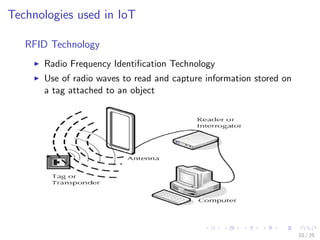
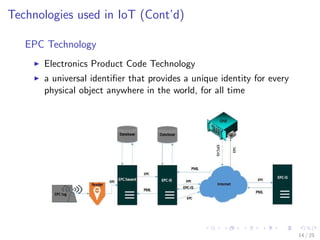
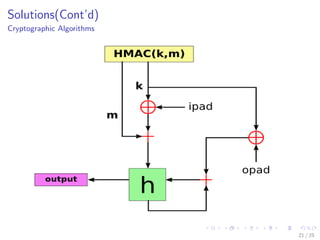
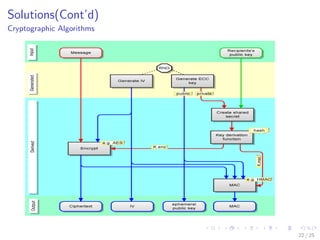
The document discusses the security challenges associated with the Internet of Things (IoT), highlighting issues such as access control, confidentiality, integrity, and privacy. It outlines technologies used in IoT like RFID and EPC, as well as suggesting solutions including cryptographic algorithms such as ECC and HMAC for better security. The conclusion emphasizes the need for stronger security measures in the design of IoT devices to prevent vulnerabilities.