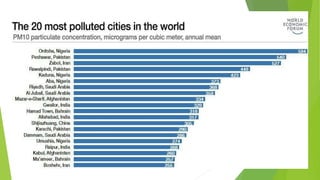
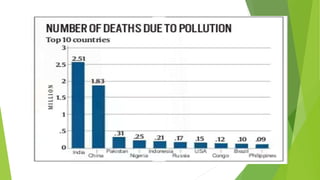
This document discusses industrial pollution, defining it as pollution that can be traced to industrial practices. It identifies the main types as air, water, soil, and noise pollution. The causes of industrial pollution include a lack of control policies, unplanned industrial growth, outdated technologies, and inefficient waste disposal. The effects include global warming, wildlife extinction, and negative impacts on human health. Controlling industrial pollution requires better policies, technology, and waste disposal practices.