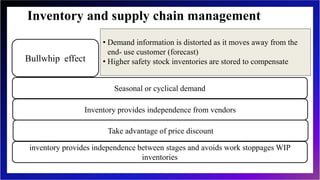
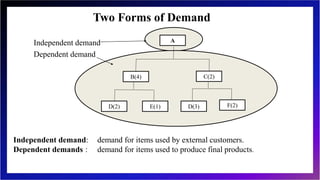
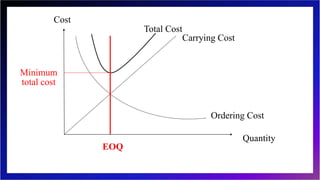
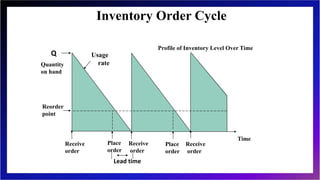
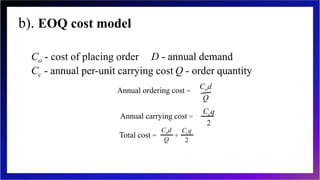
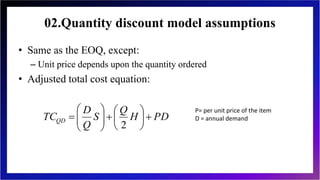
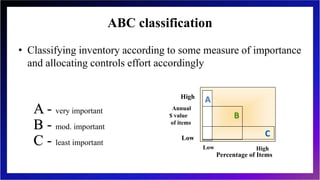
This document discusses inventory management and inventory management models. It begins by defining inventory and listing reasons for holding inventory. The objectives of inventory management are then discussed, including maximizing turnover and minimizing costs. Several inventory management models are described, including the economic order quantity model, quantity discount model, reorder point model, and single period model. The document also discusses inventory costs, valuation methods, and the ABC classification approach.