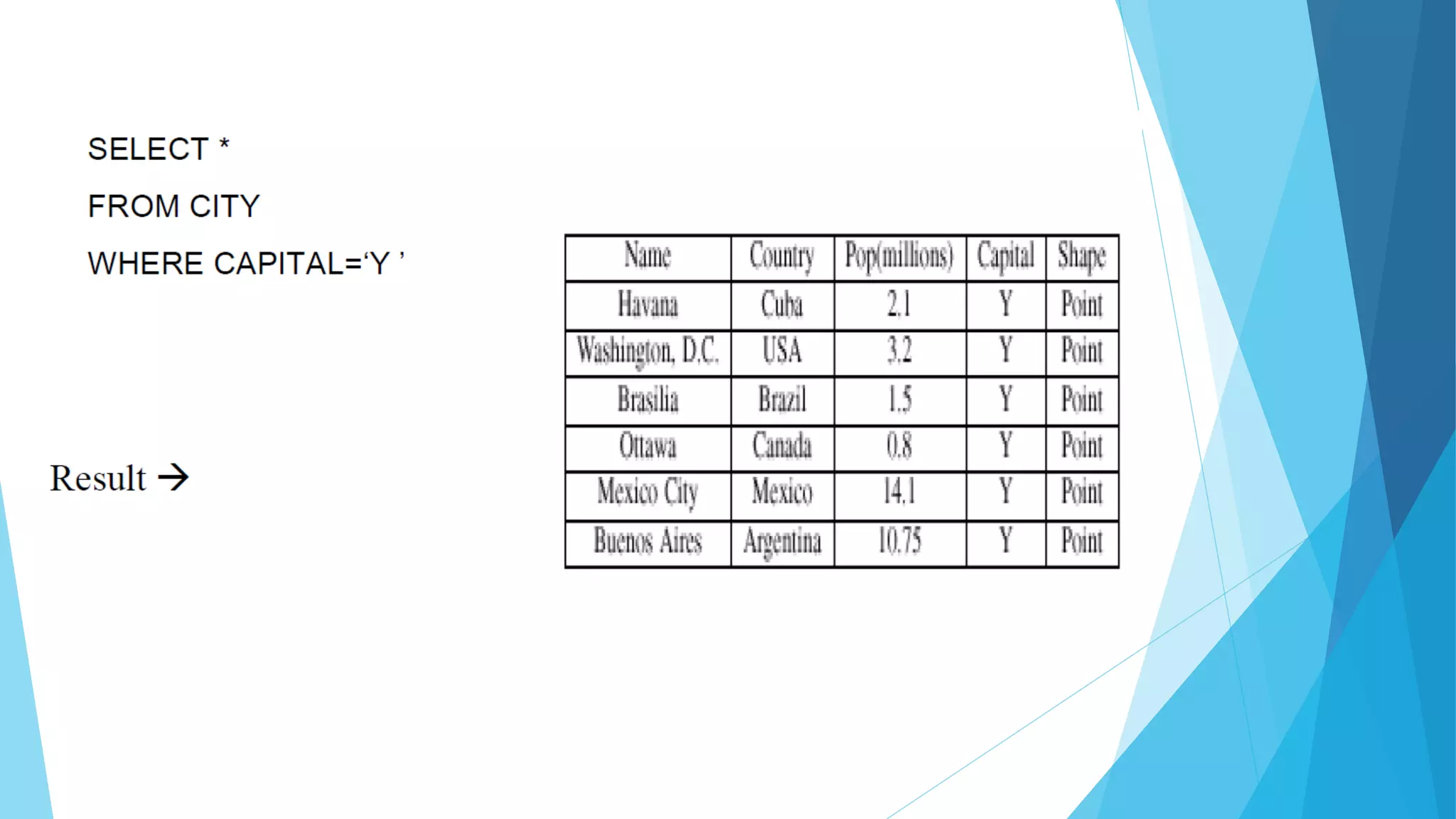
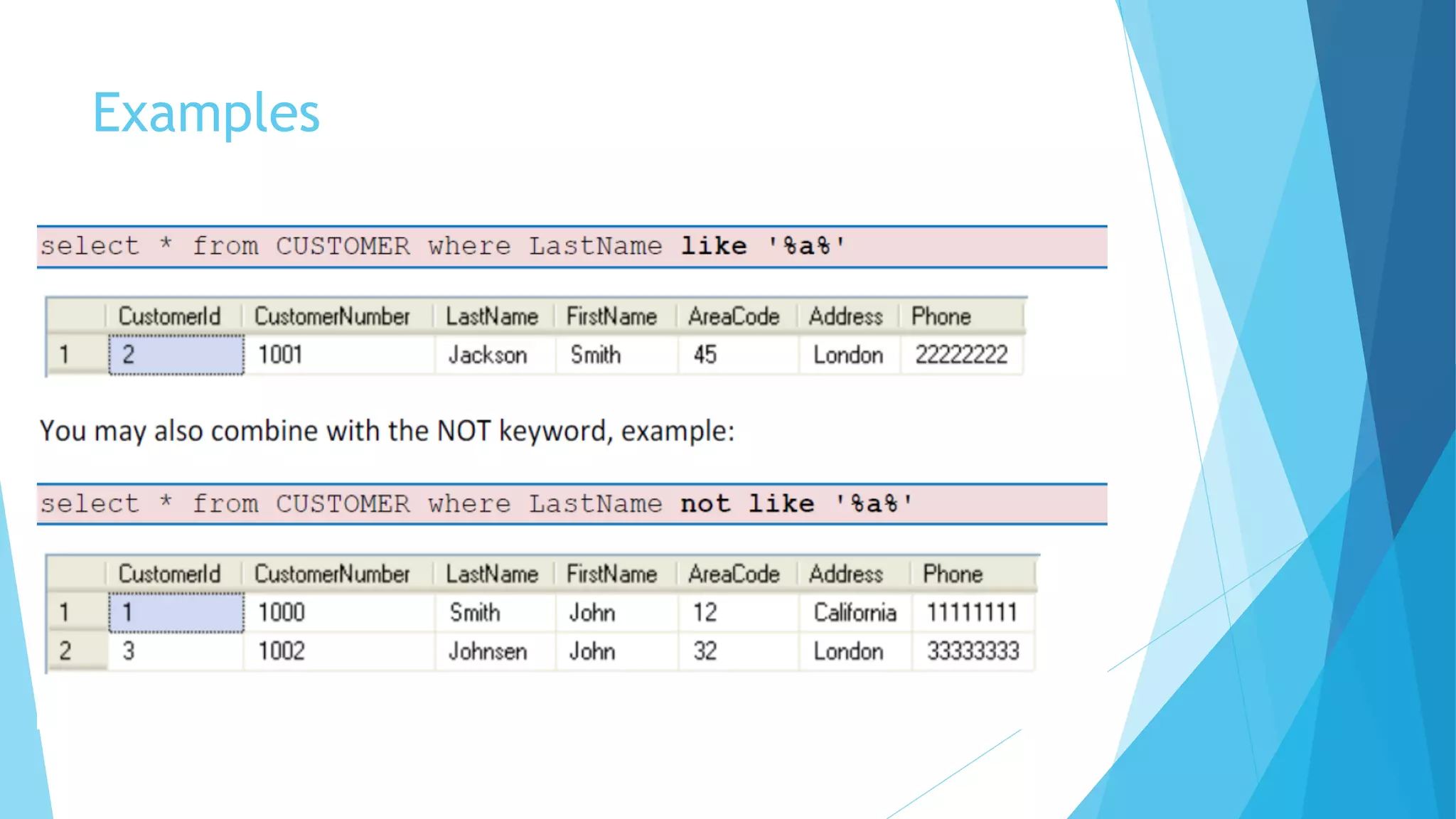
This document provides an introduction to structured query language (SQL). It describes SQL's use for communicating with databases and its basis in set theory and relational operations. Examples are provided to demonstrate basic SQL statements like SELECT, FROM, WHERE, DISTINCT, ORDER BY, LIKE, IN, BETWEEN and how to retrieve, filter and sort data from database tables. Keywords, operators and syntax are defined for core SQL clauses and functions.