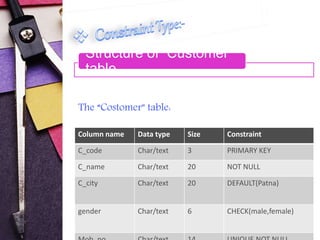
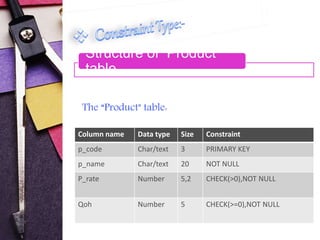
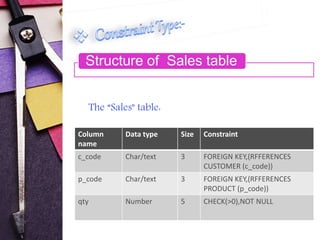
This document discusses different types of constraints in SQL including not null, unique key, primary key, foreign key, check key, and default key. It provides the syntax for creating constraints and examples of each constraint type. The examples show the creation of tables for customers, products, and sales with the appropriate constraints defined. Integrity constraints are used to prohibit illegal data and ensure referential integrity between tables.




![Syntax For Create Constraint
Sql> CREATE TABLE <table name>(
<attribute name> DATA TYPE (<size>) [constraint],
<attribute name> DATA TYPE (<size>) [constraint],
<attribute name> DATA TYPE (<size>) [constraint],
…………………….
……………………
);
NOTE: [ ]->Optional,( )->Required, < >->Required & depend
on programmer;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/entigrityconstraint-140919110204-phpapp01/85/Entigrity-constraint-5-320.jpg)