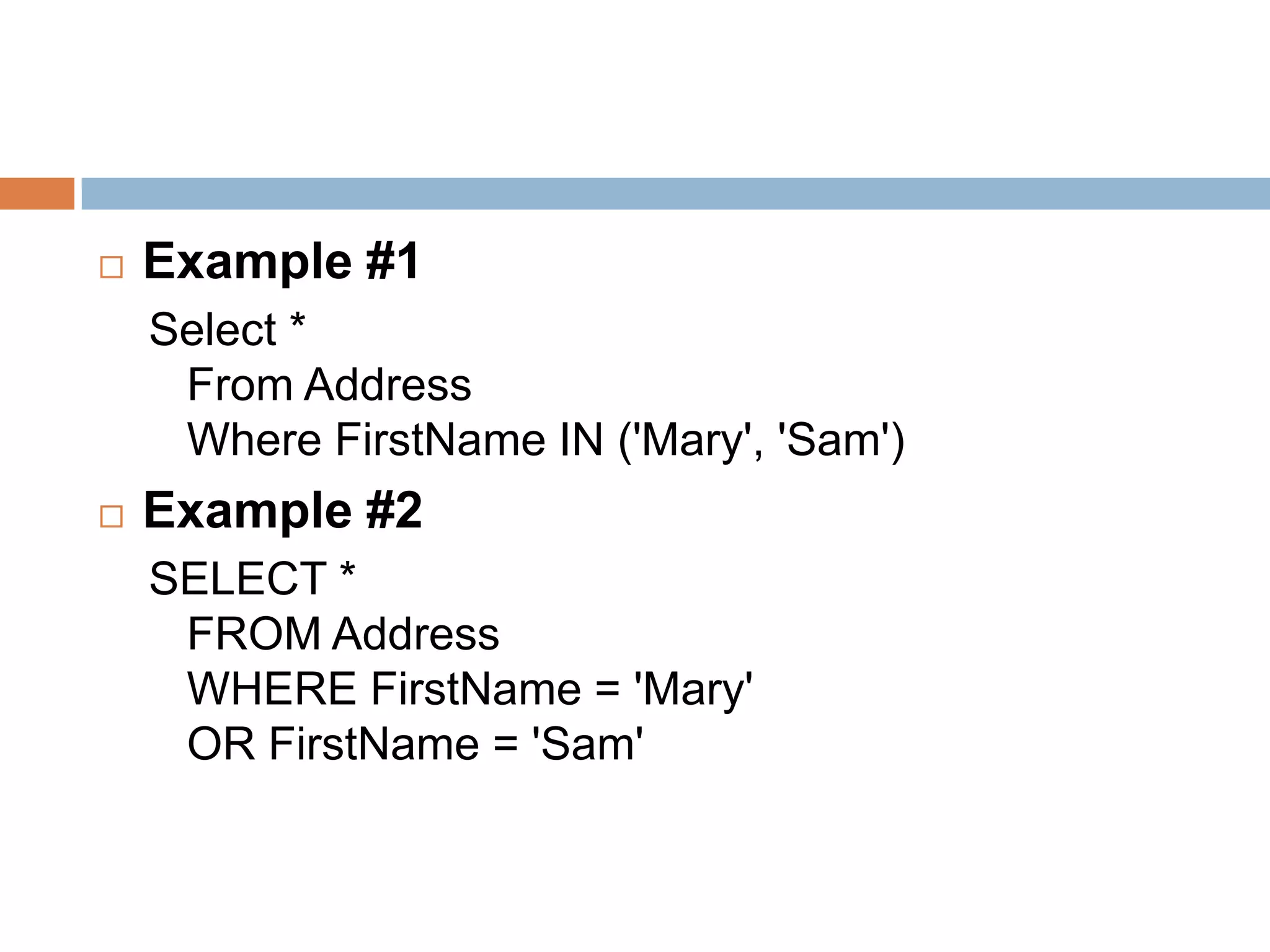
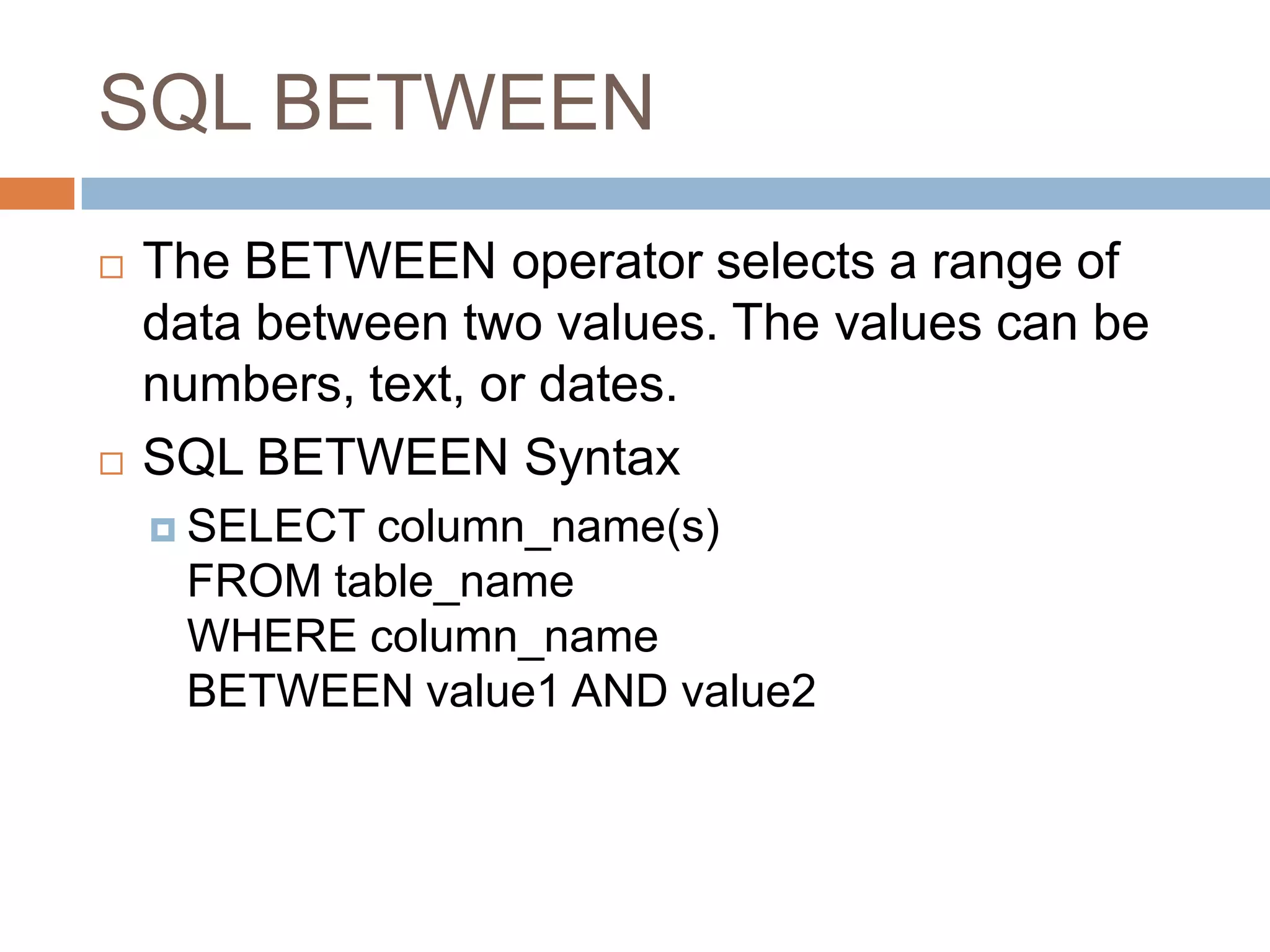
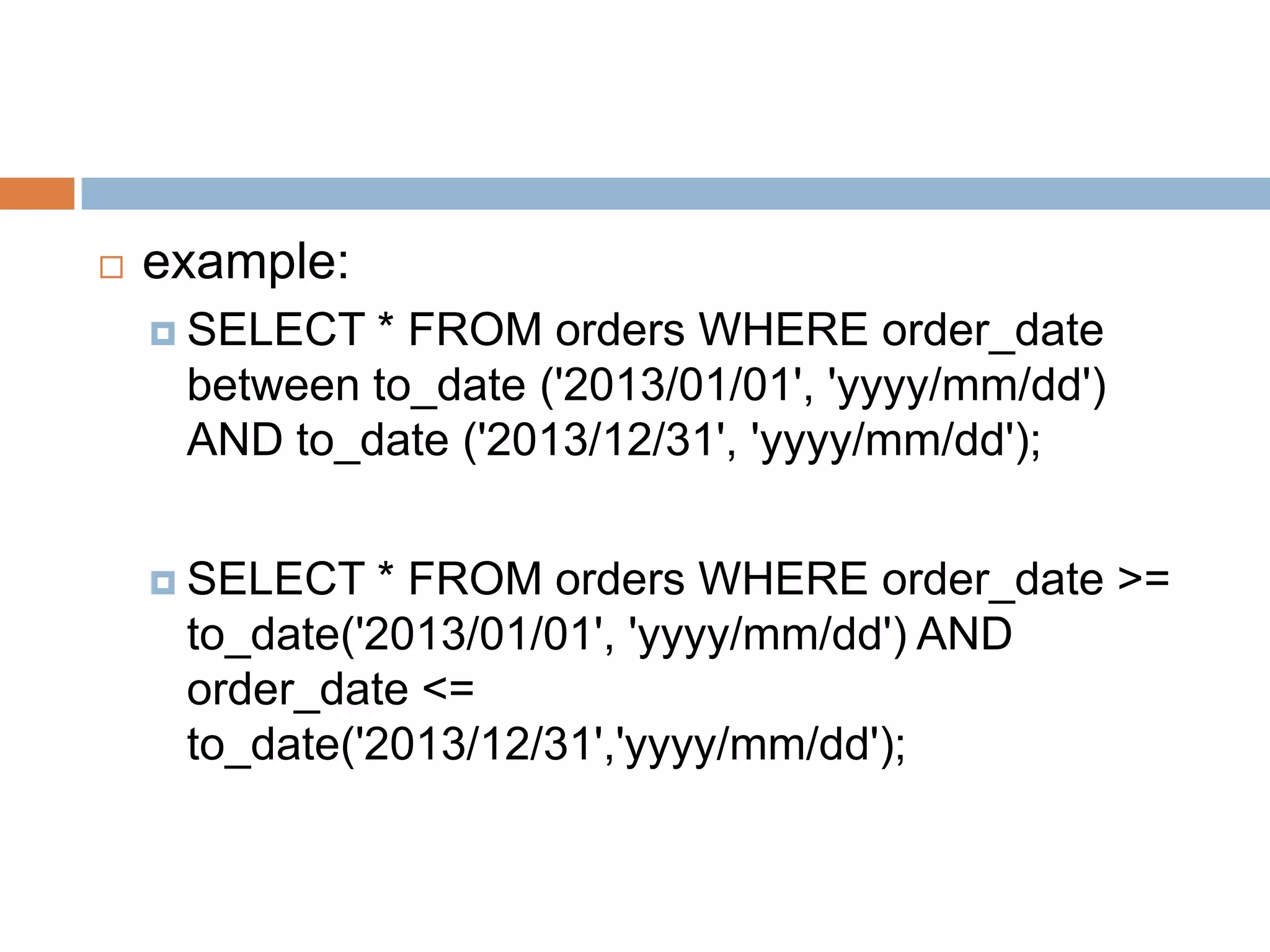
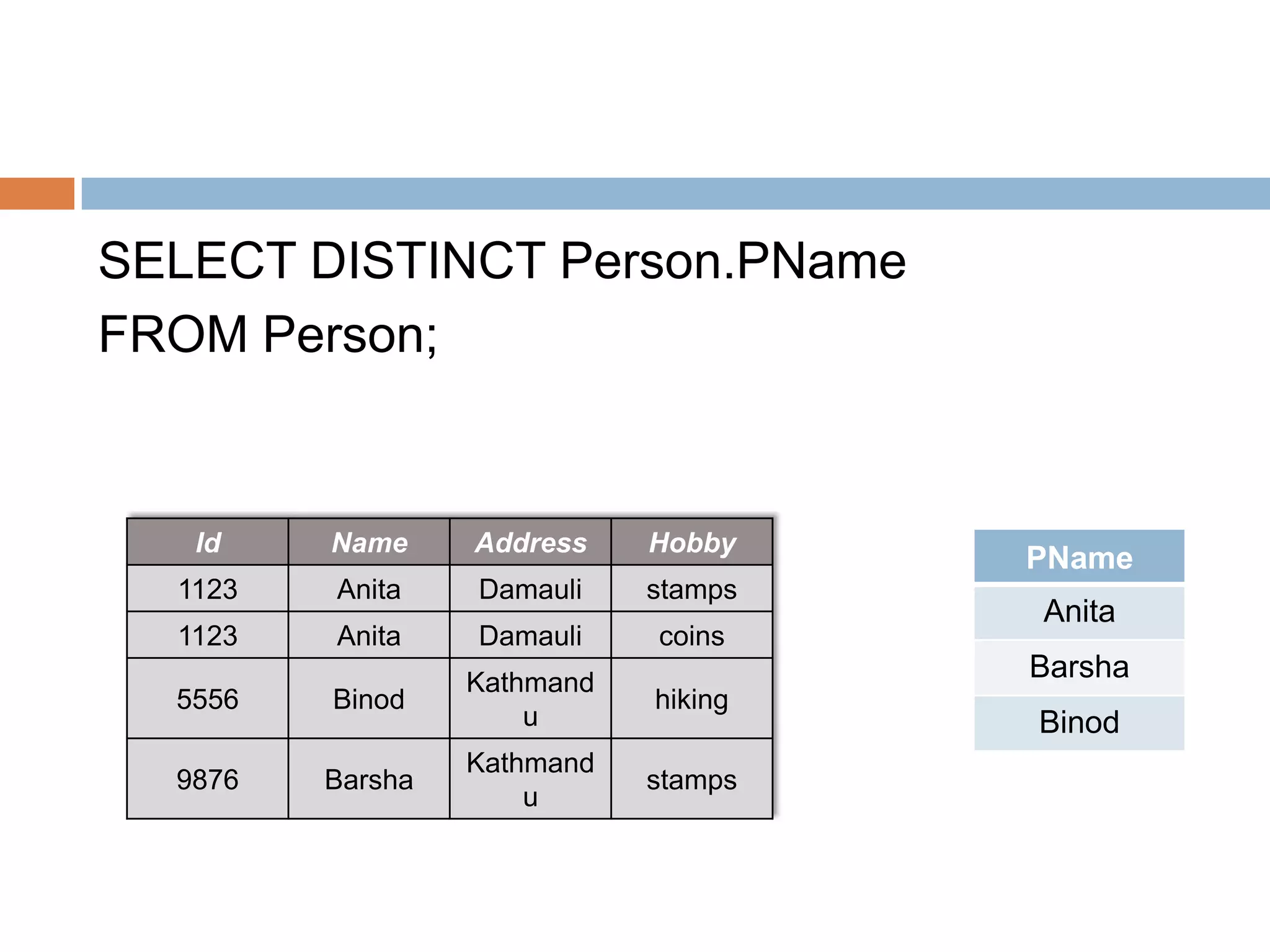
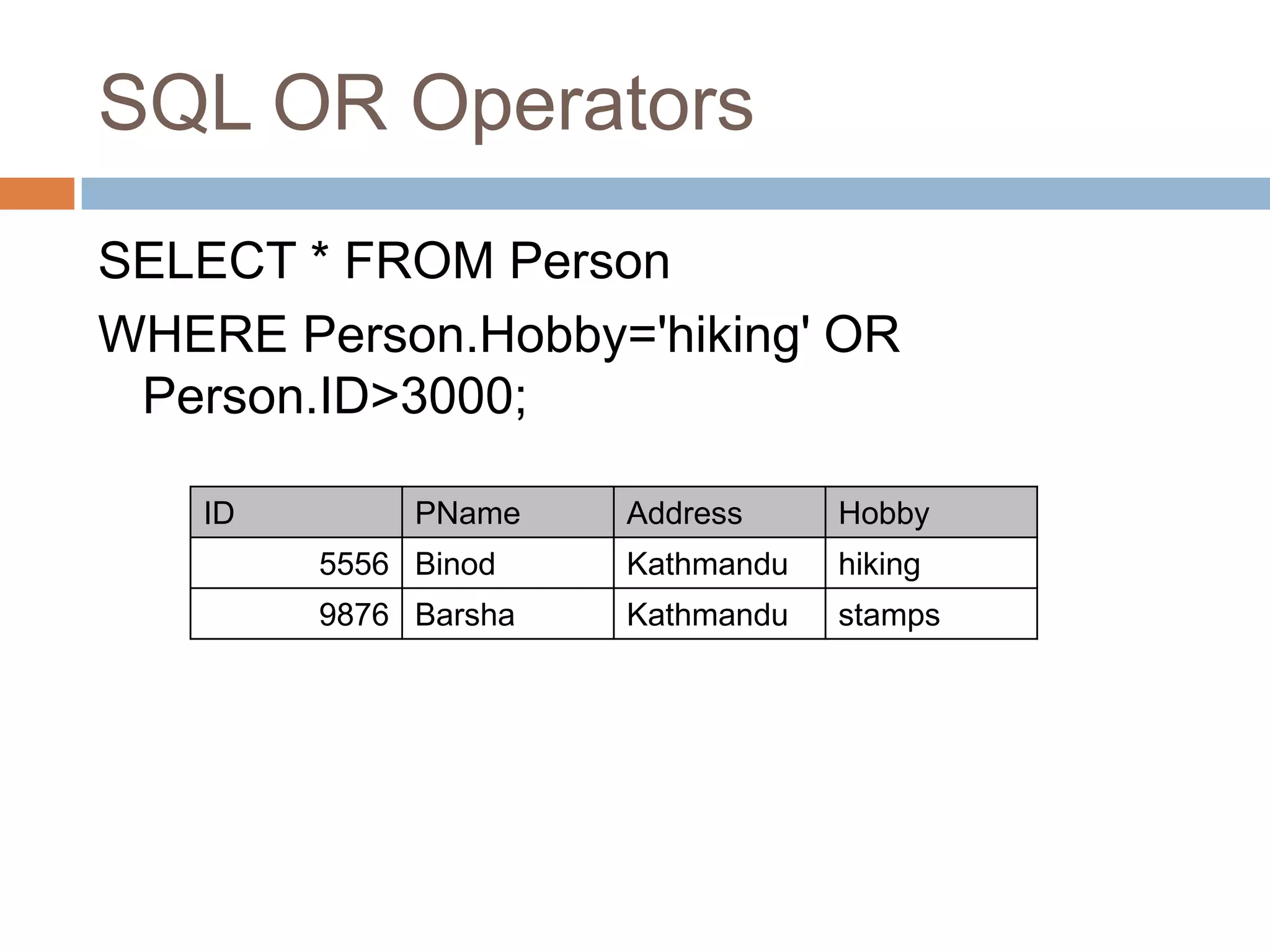
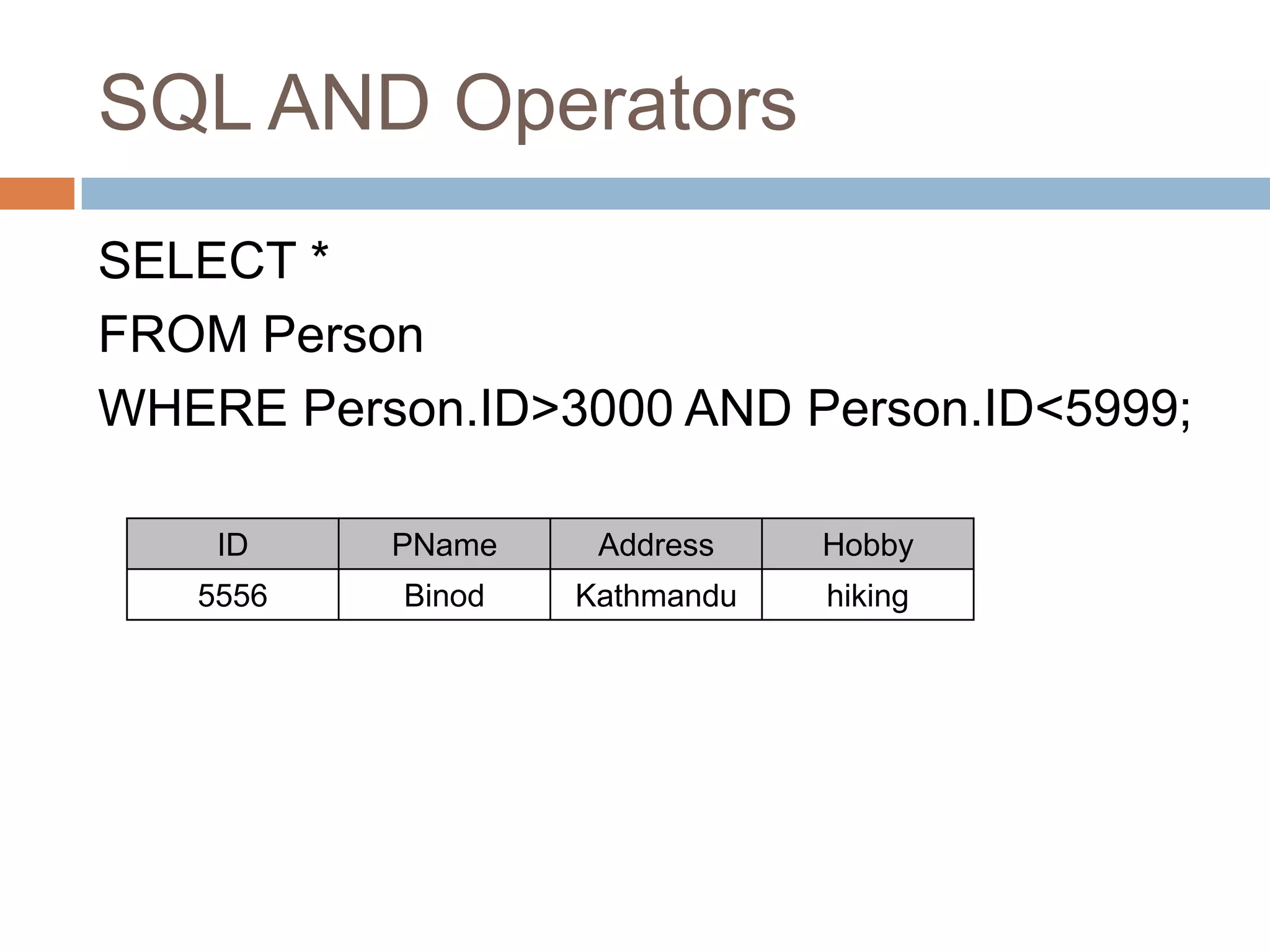
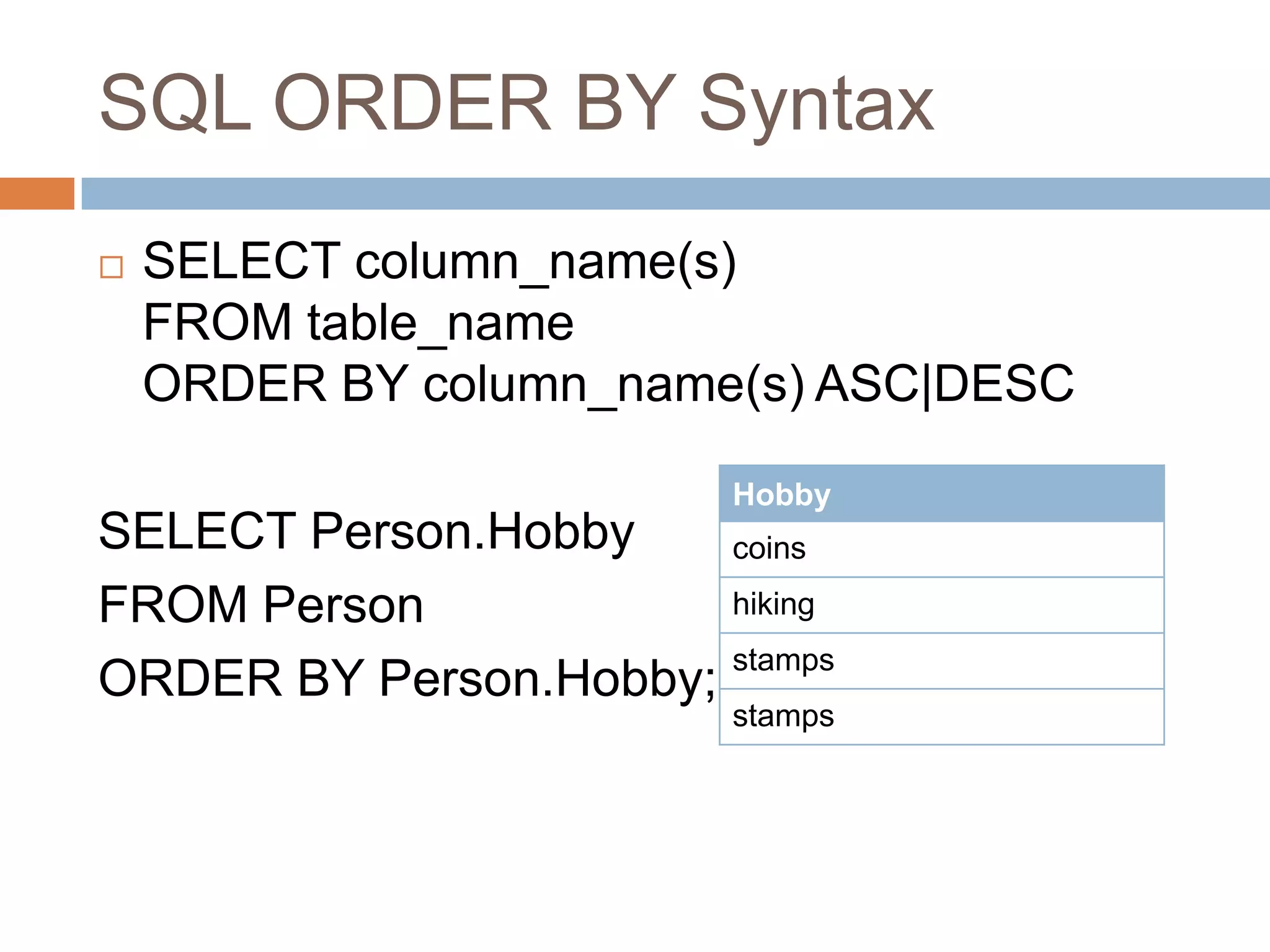
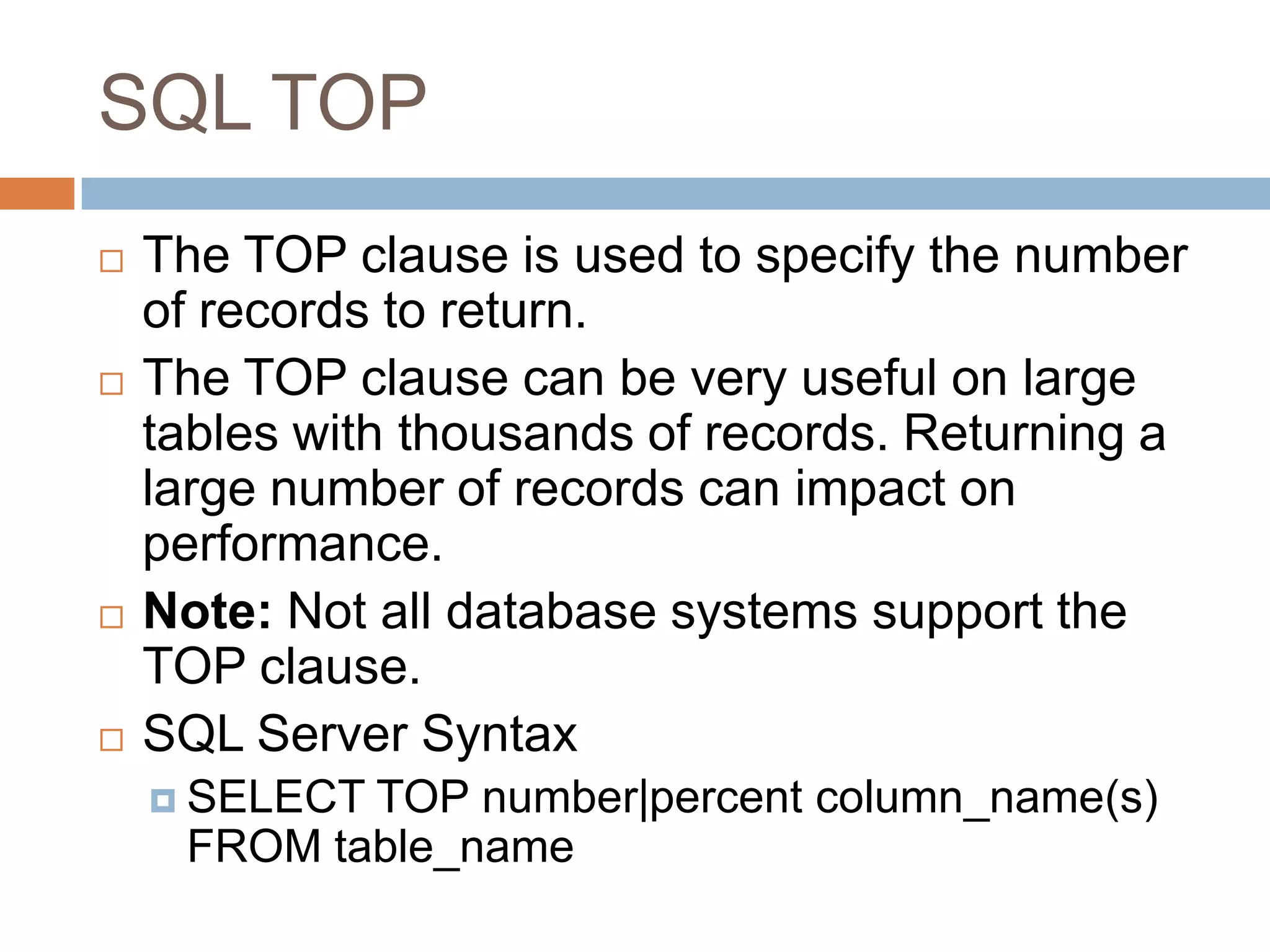
The document provides information about various SQL clauses and operators used to select, filter, sort and manipulate data in database tables. It explains clauses like SELECT, DISTINCT, WHERE, ORDER BY, INSERT INTO, UPDATE, DELETE, TOP, LIKE, IN and BETWEEN and provides syntax and examples for each.











![SQL Wildcards
Wildcard Description
% A substitute for zero or more characters
_ A substitute for exactly one character
[charlist] Any single character in charlist
[^charlist]or
[!charlist]
Any single character not in charlist
• SQL wildcards can substitute for one or more
characters when searching for data in a
database.
• SQL wildcards must be used with the SQL
LIKE operator.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06-01sqlselectdistinct-130602223228-phpapp02/75/06-01-sql-select-distinct-18-2048.jpg)