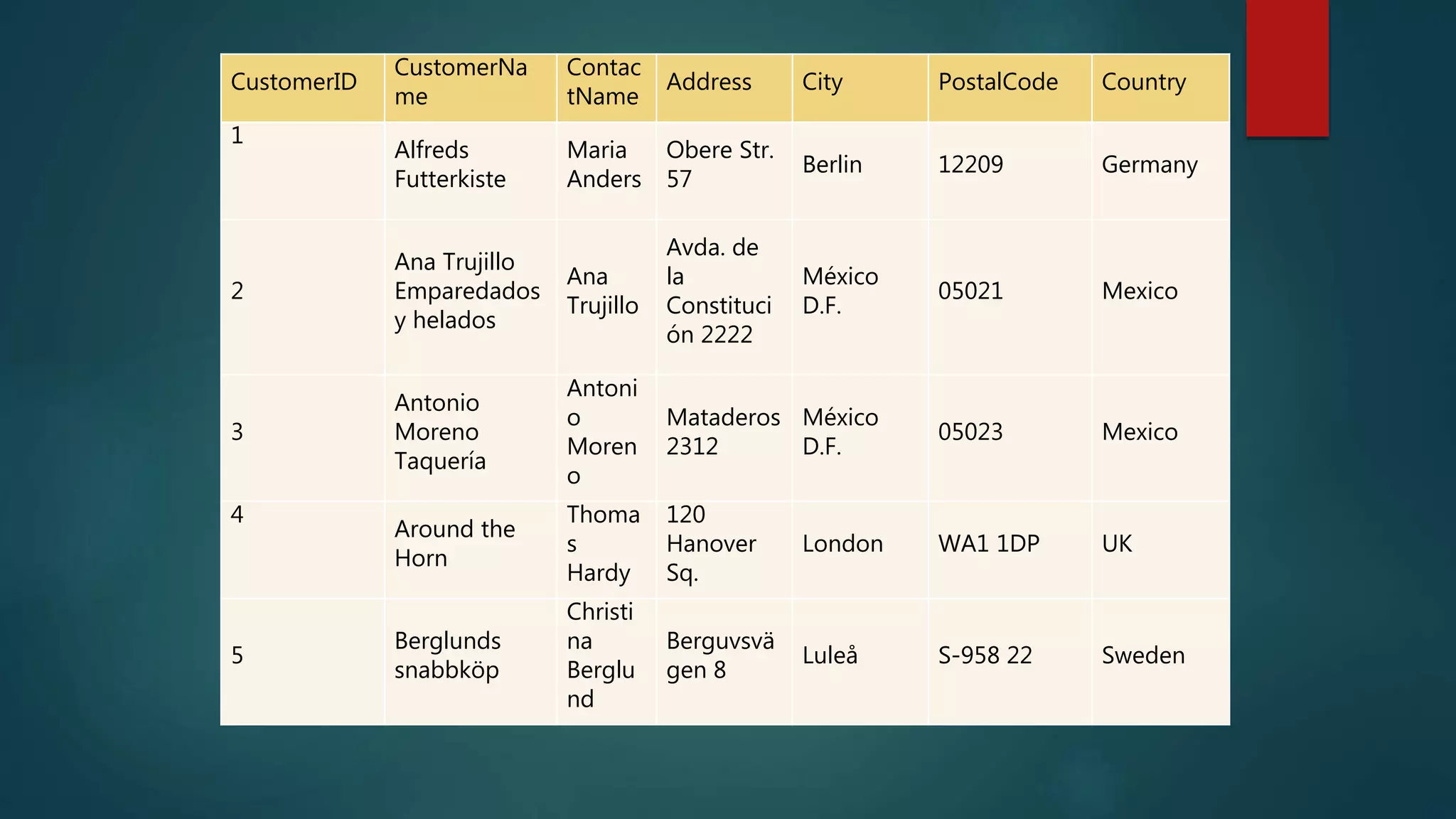
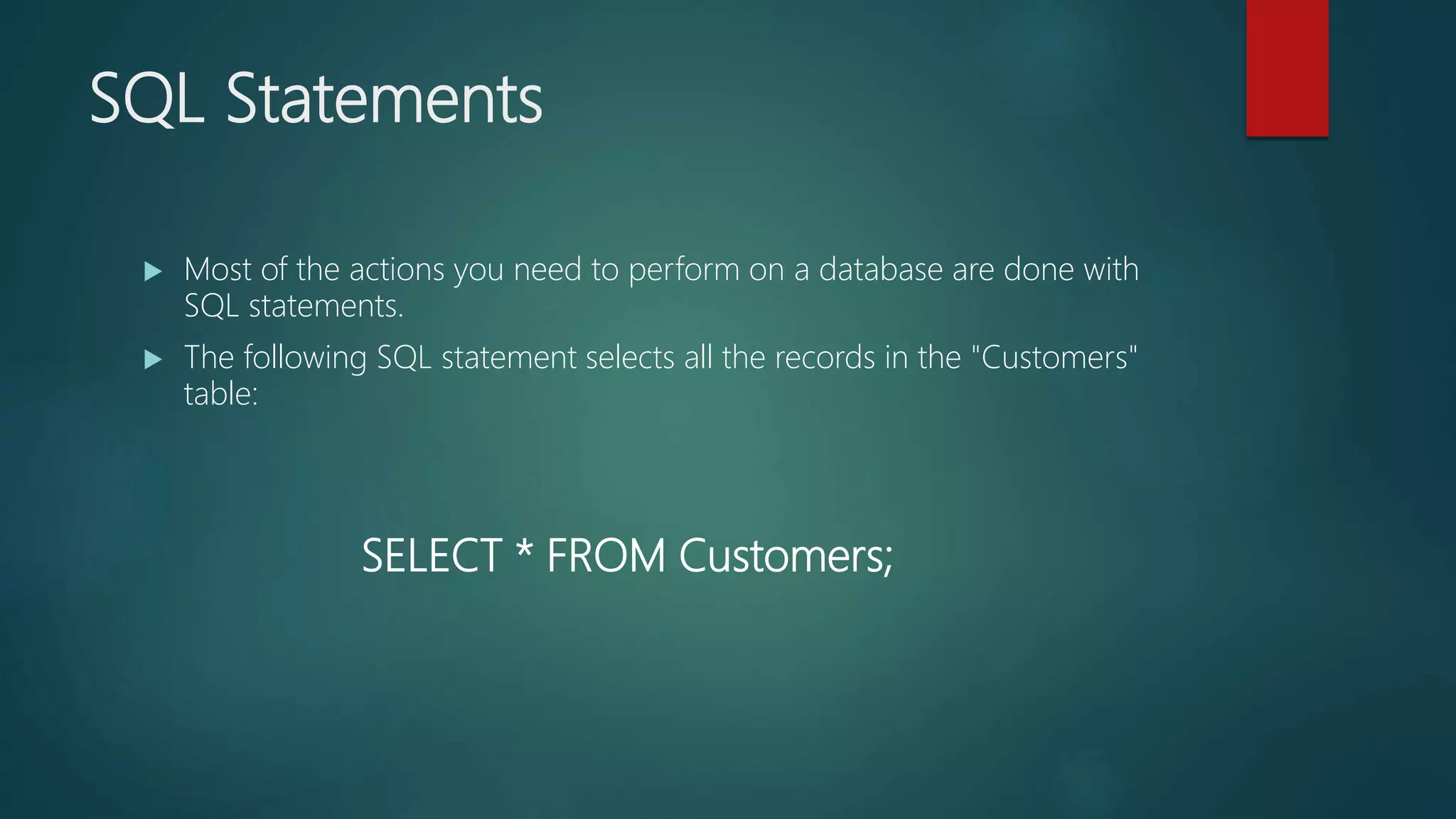
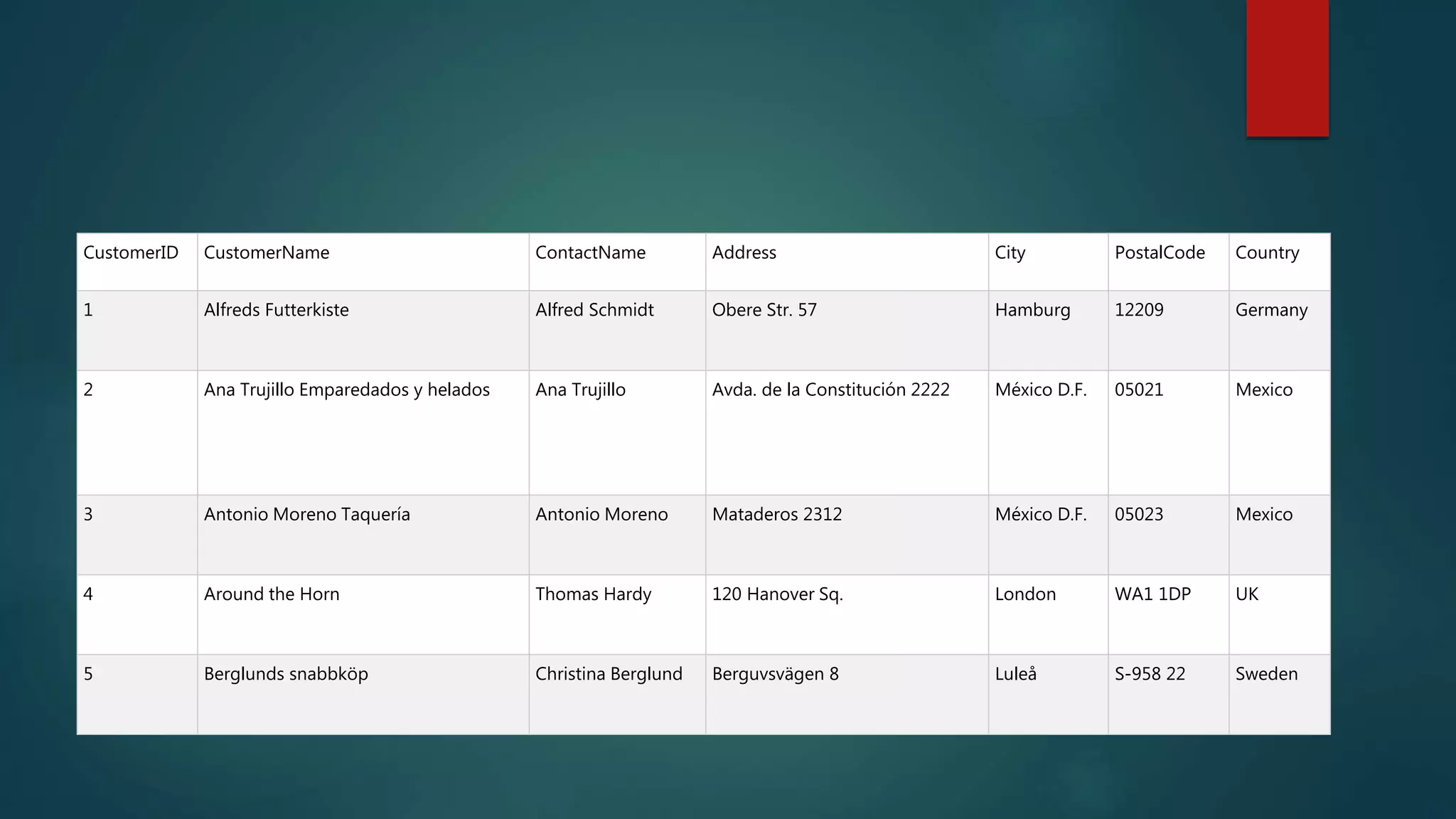
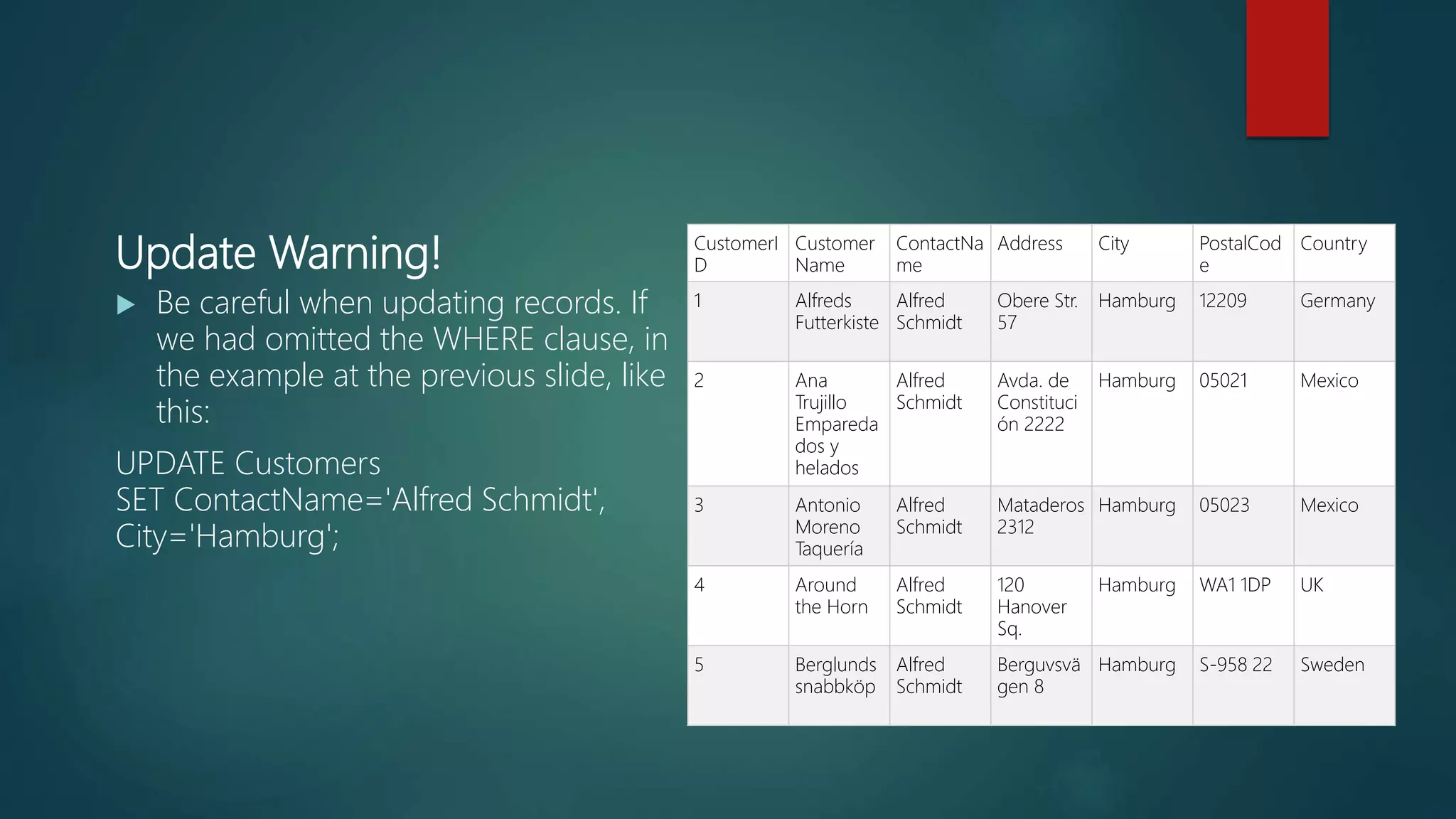
SQL is a standard language for accessing and manipulating databases. It allows users to retrieve, insert, update, and delete data as well as create new databases and tables. Common SQL statements include SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT. SQL uses clauses, operators, and wildcards to filter records based on conditions. Some key points are that SQL is an ANSI standard but different versions exist, it allows querying and modifying data in databases, and is essential for interacting with relational database systems.

















![SQL Wildcards
A wildcard character can be used to substitute for any other character(s)
in a string.
Wildcard Description
% A substitute for zero or more characters
_ A substitute for a single character
[charlist] Sets and ranges of characters to match
[^charlist]
or
[!charlist]
Matches only a character NOT specified
within the brackets](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql-161018025538/75/SQL-24-2048.jpg)


![SQL [charlist] Wildcard
The following SQL statement selects all customers with a City starting with
"b", "s", or "p":
SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE City LIKE '[bsp]%';
The following SQL statement selects all customers with a City starting with
"a", "b", or "c":
SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE City LIKE '[a-c]%';
The following SQL statement selects all customers with a City NOT starting
with "b", "s", or "p":
SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE City LIKE '[!bsp]%';
or
SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE City NOT LIKE '[bsp]%';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql-161018025538/75/SQL-27-2048.jpg)




