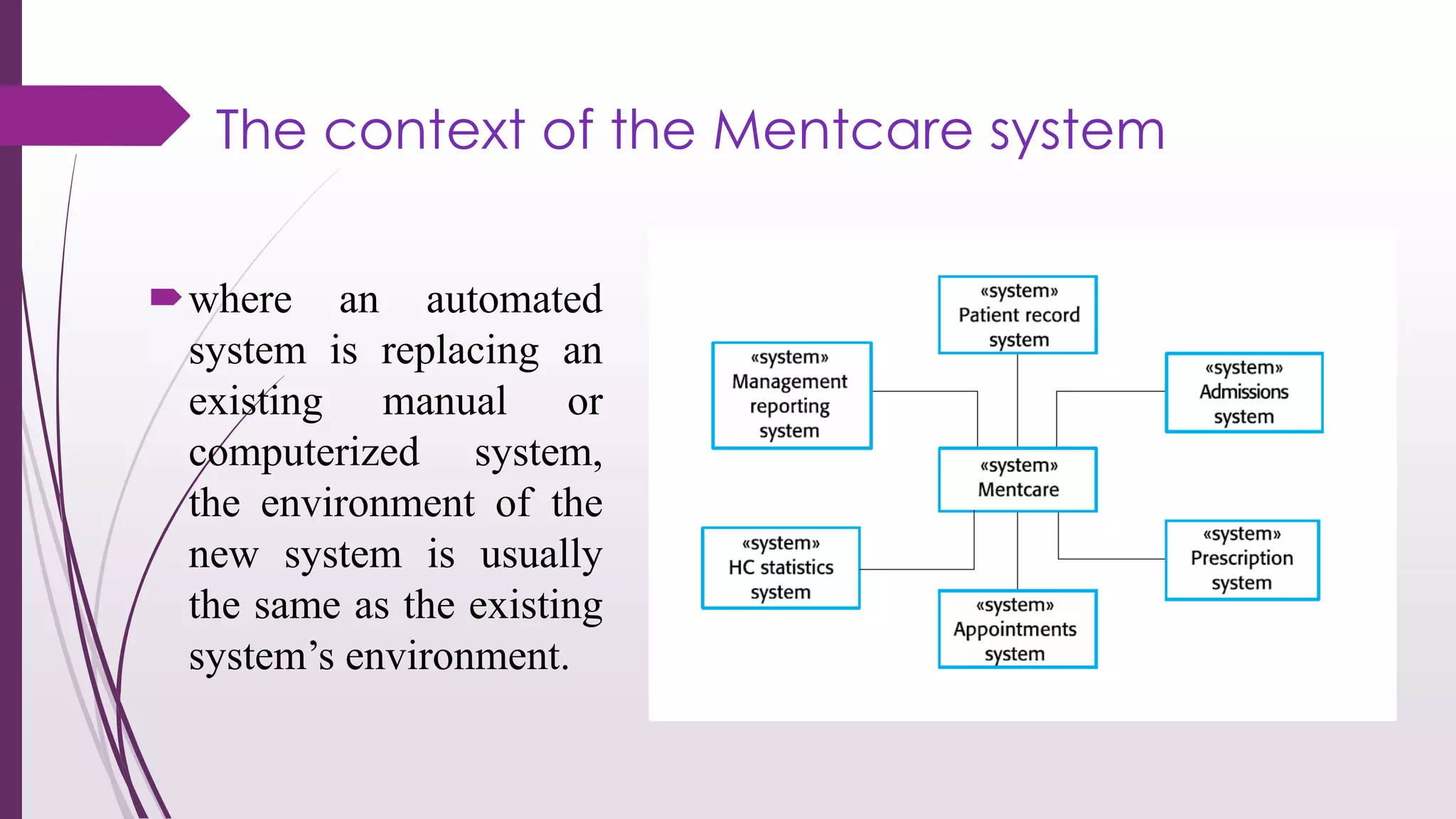
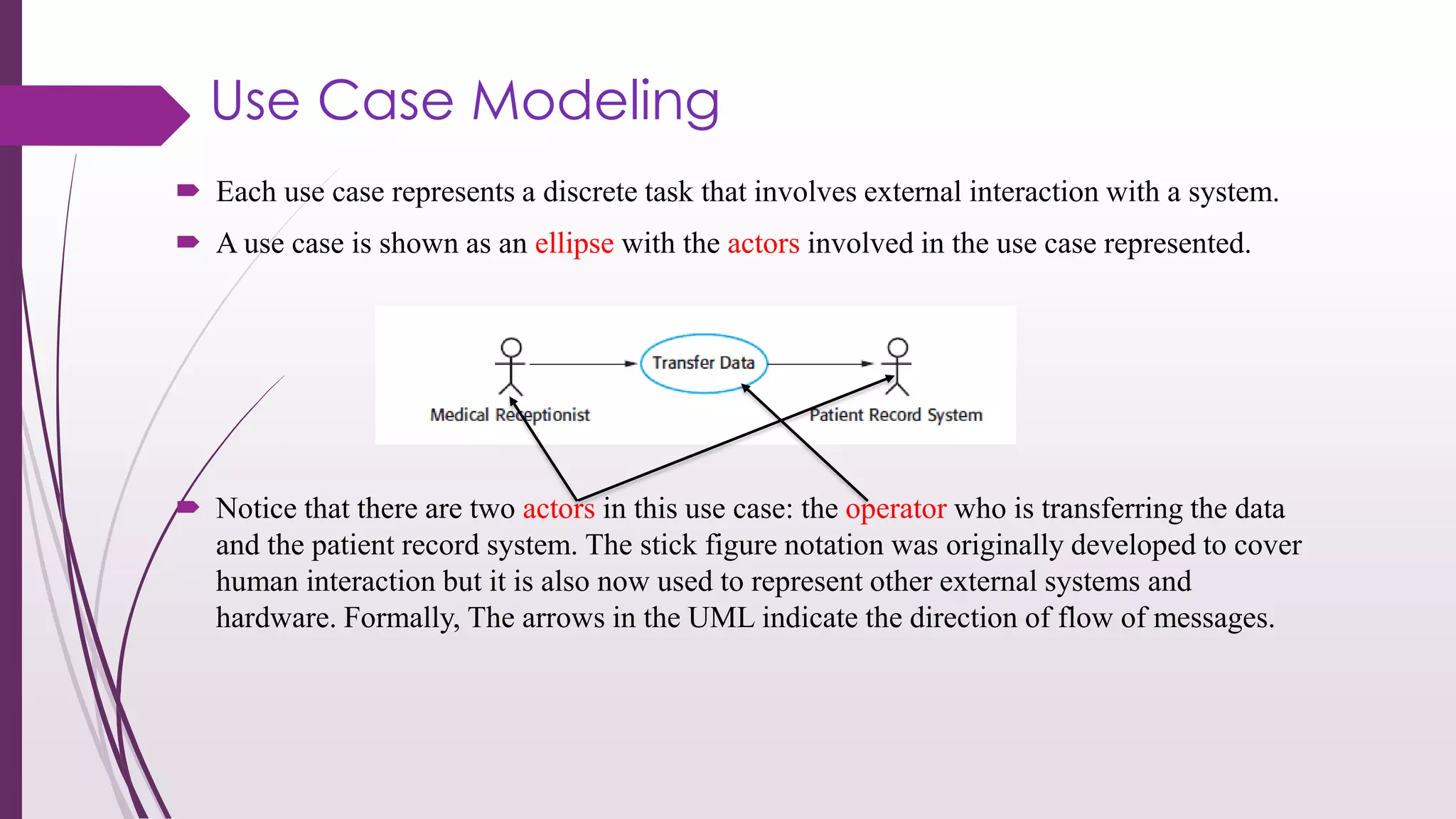
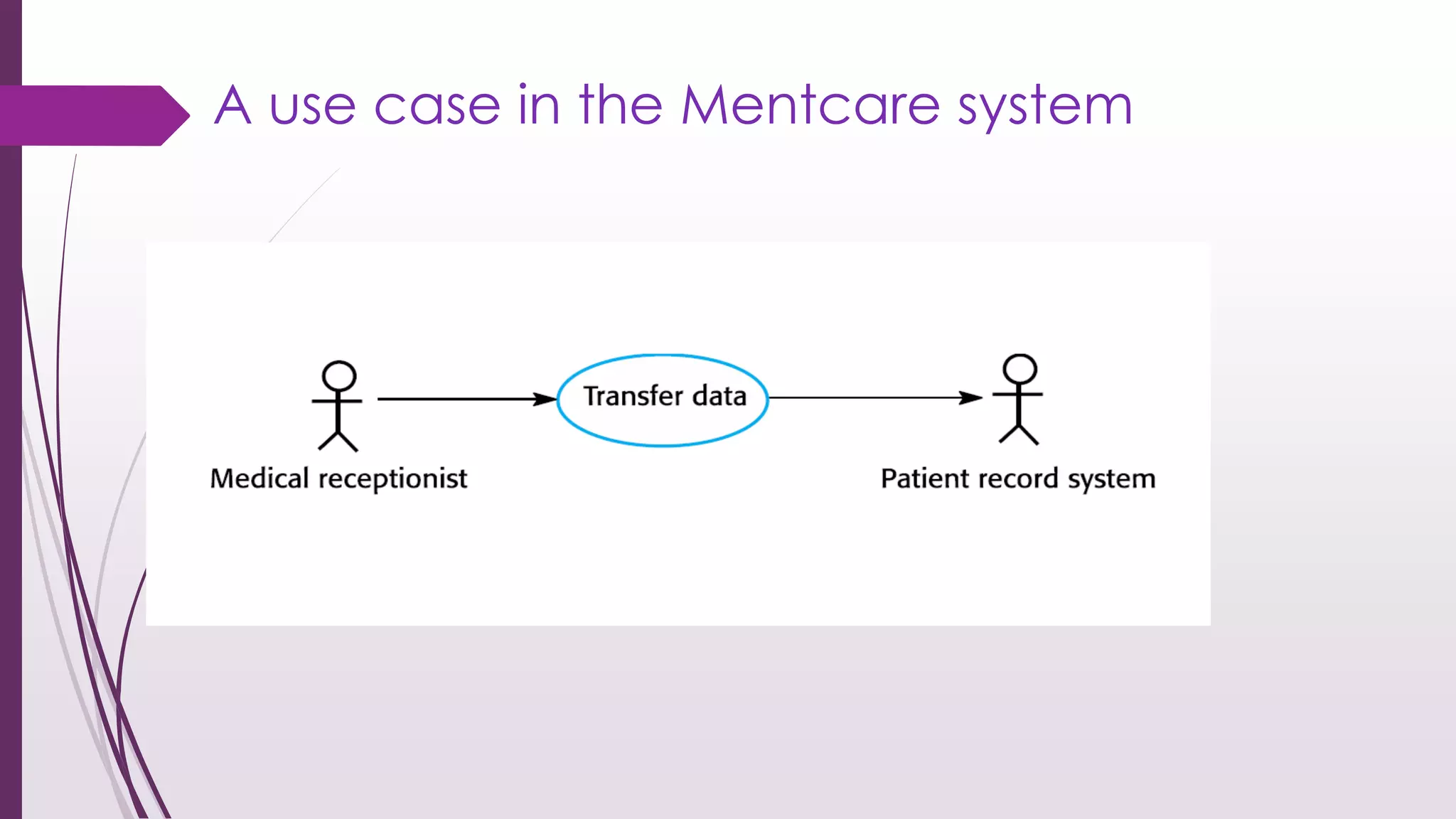
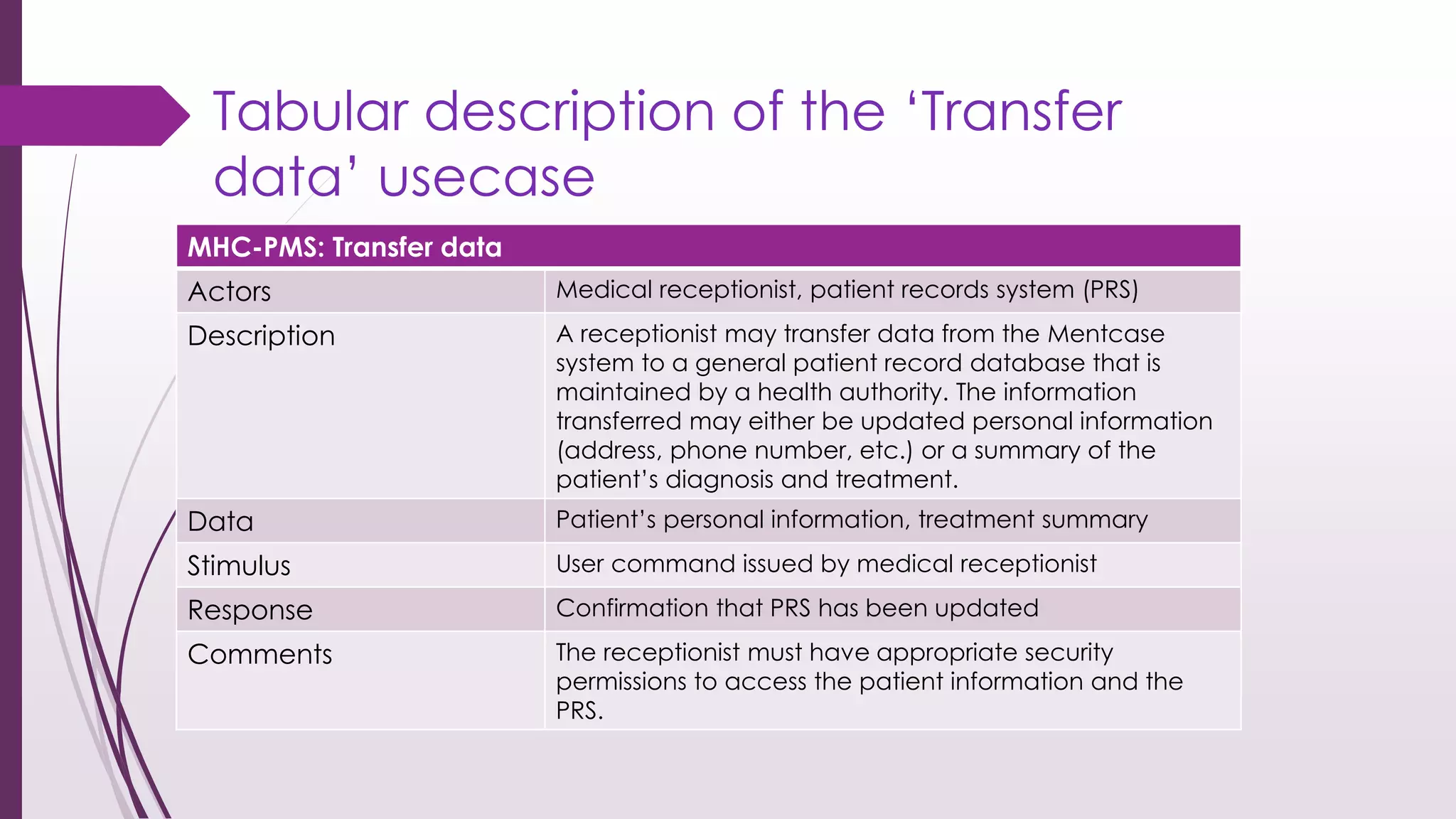
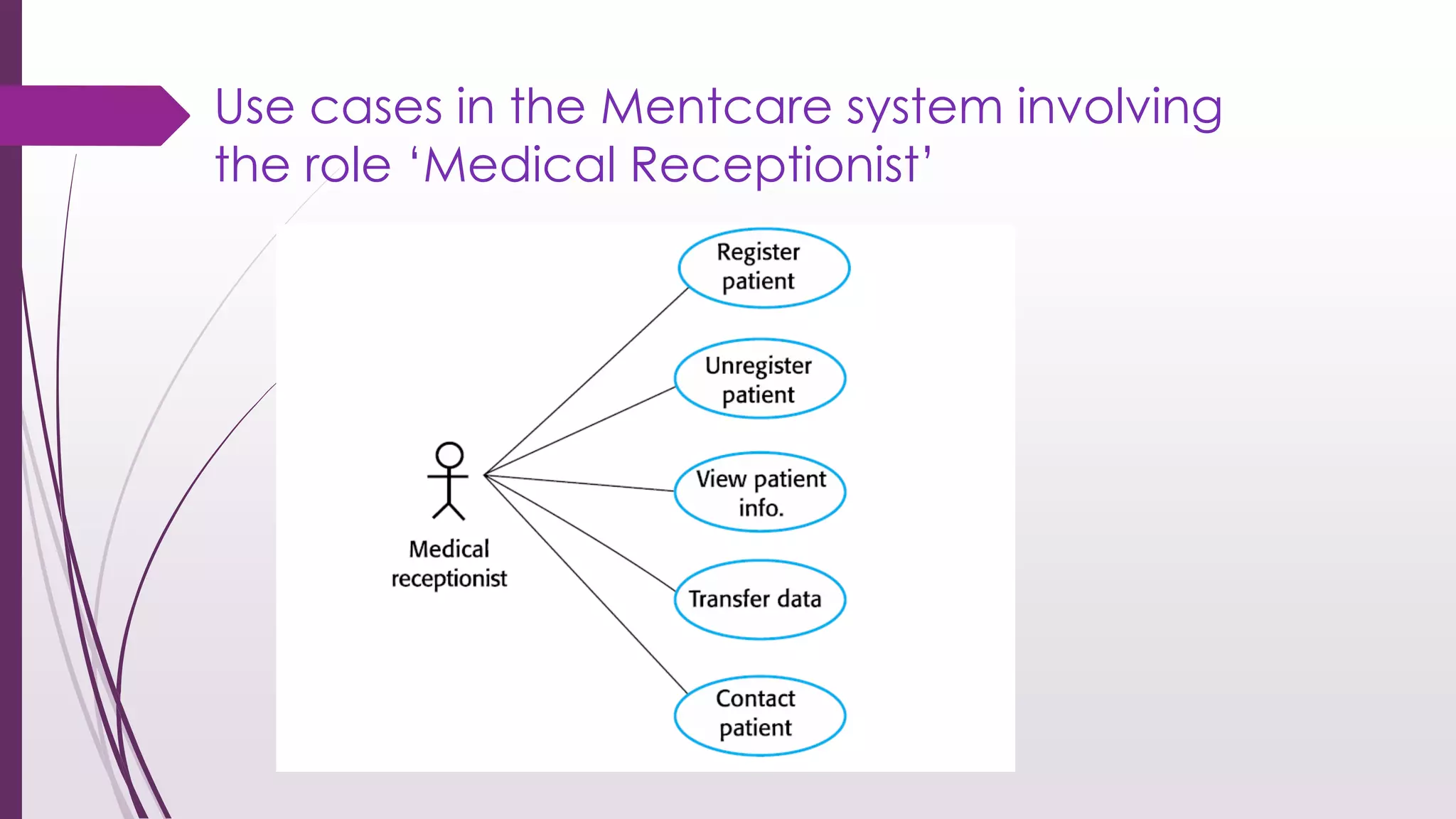
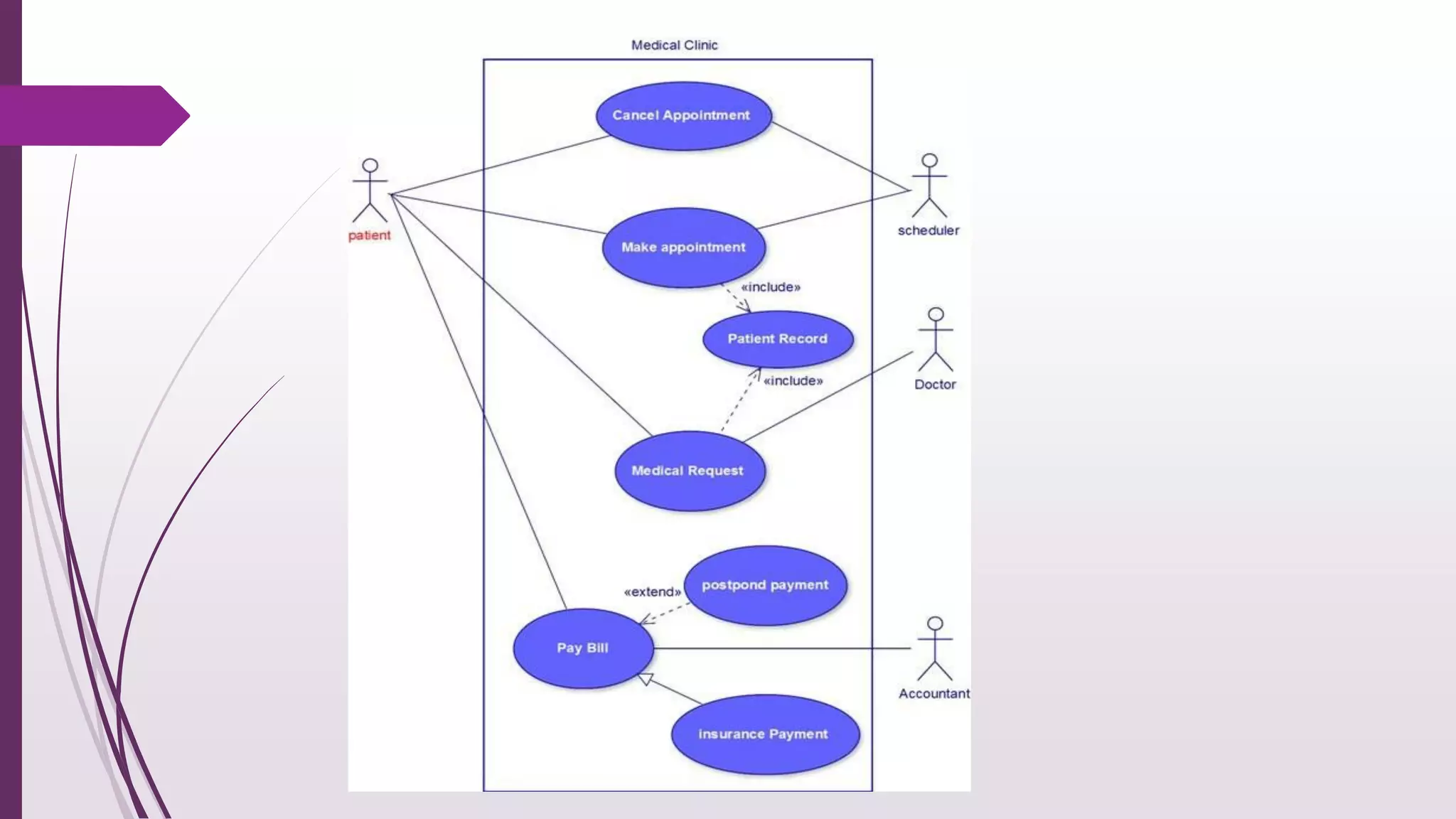
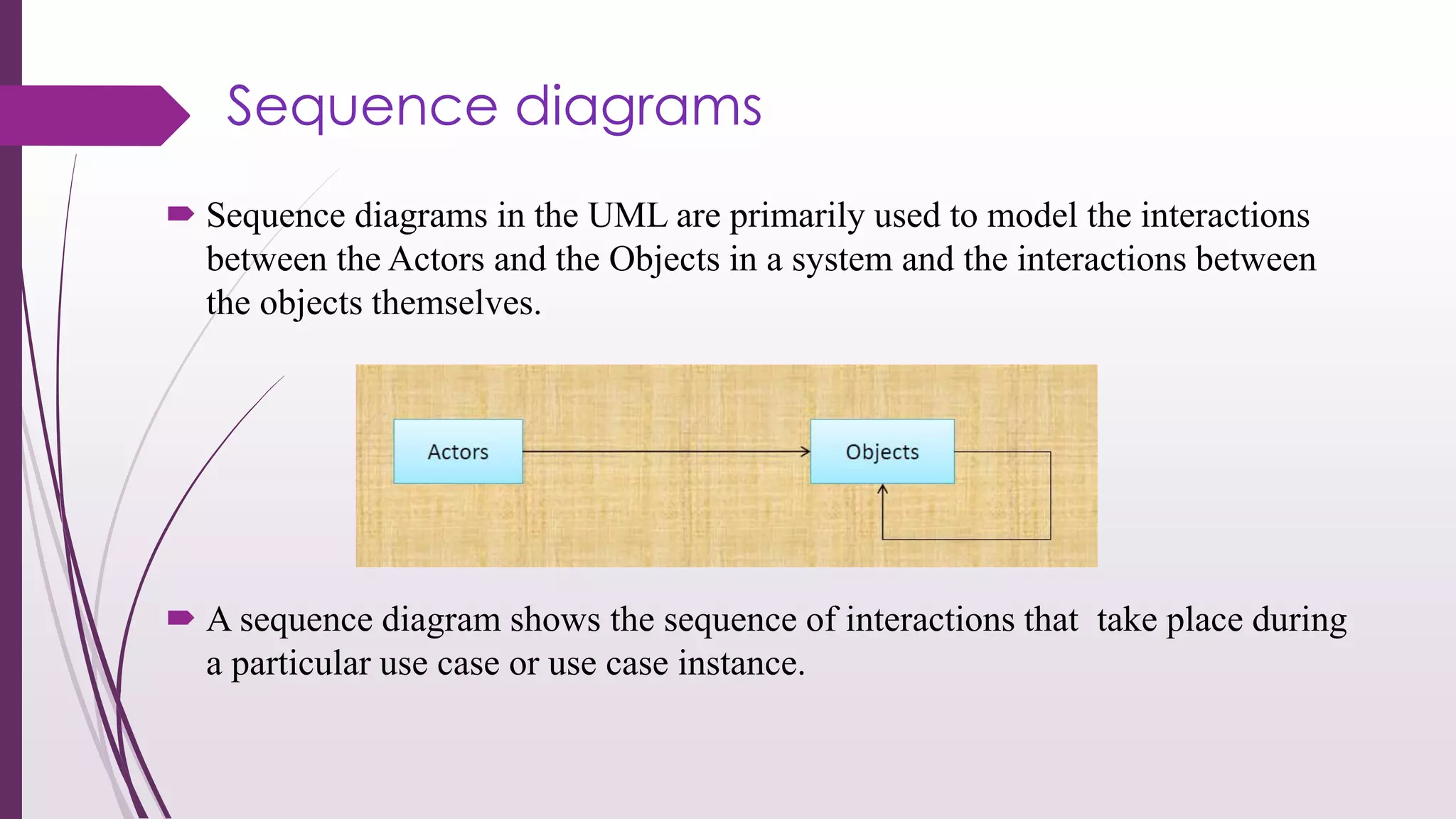
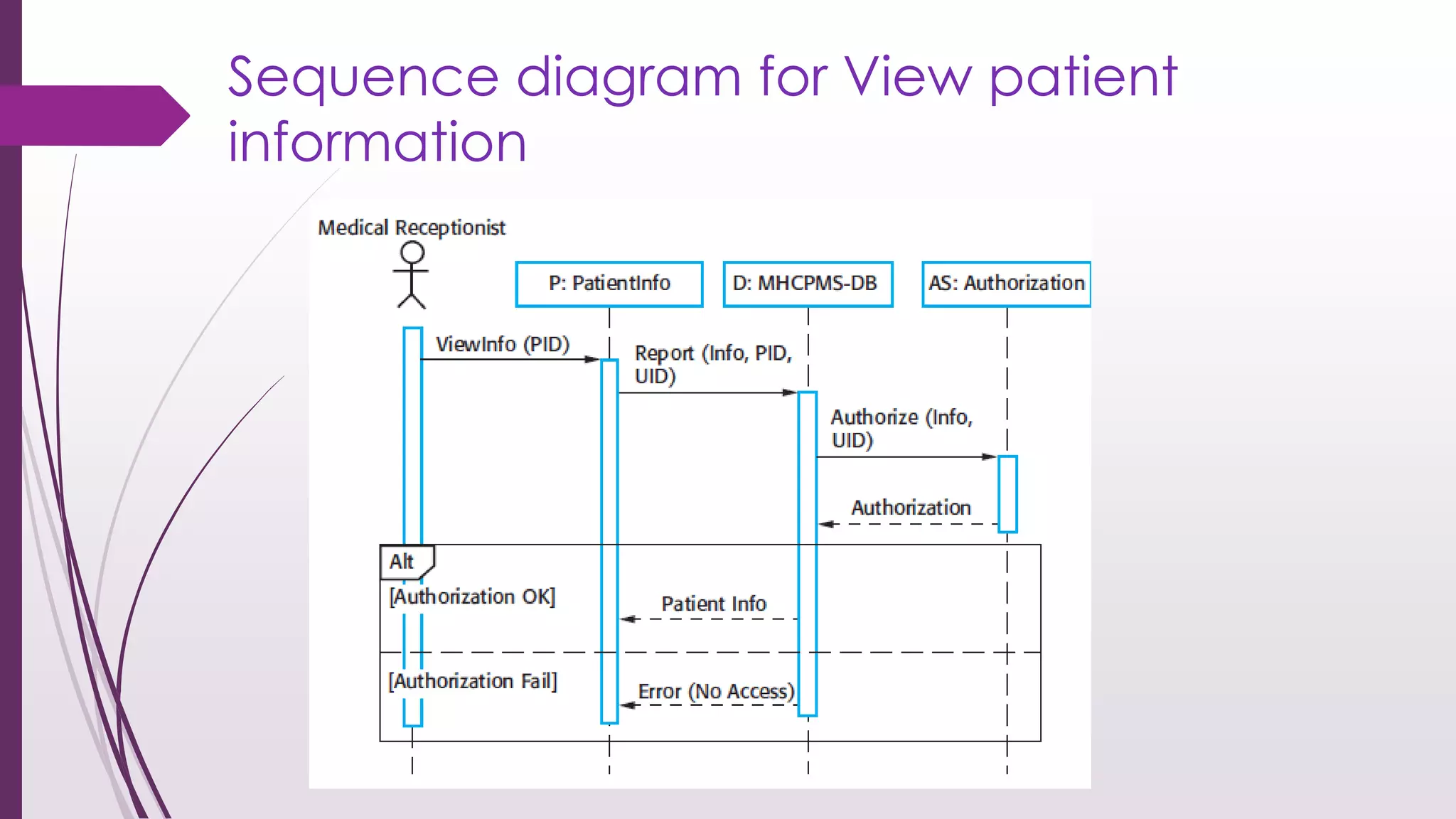
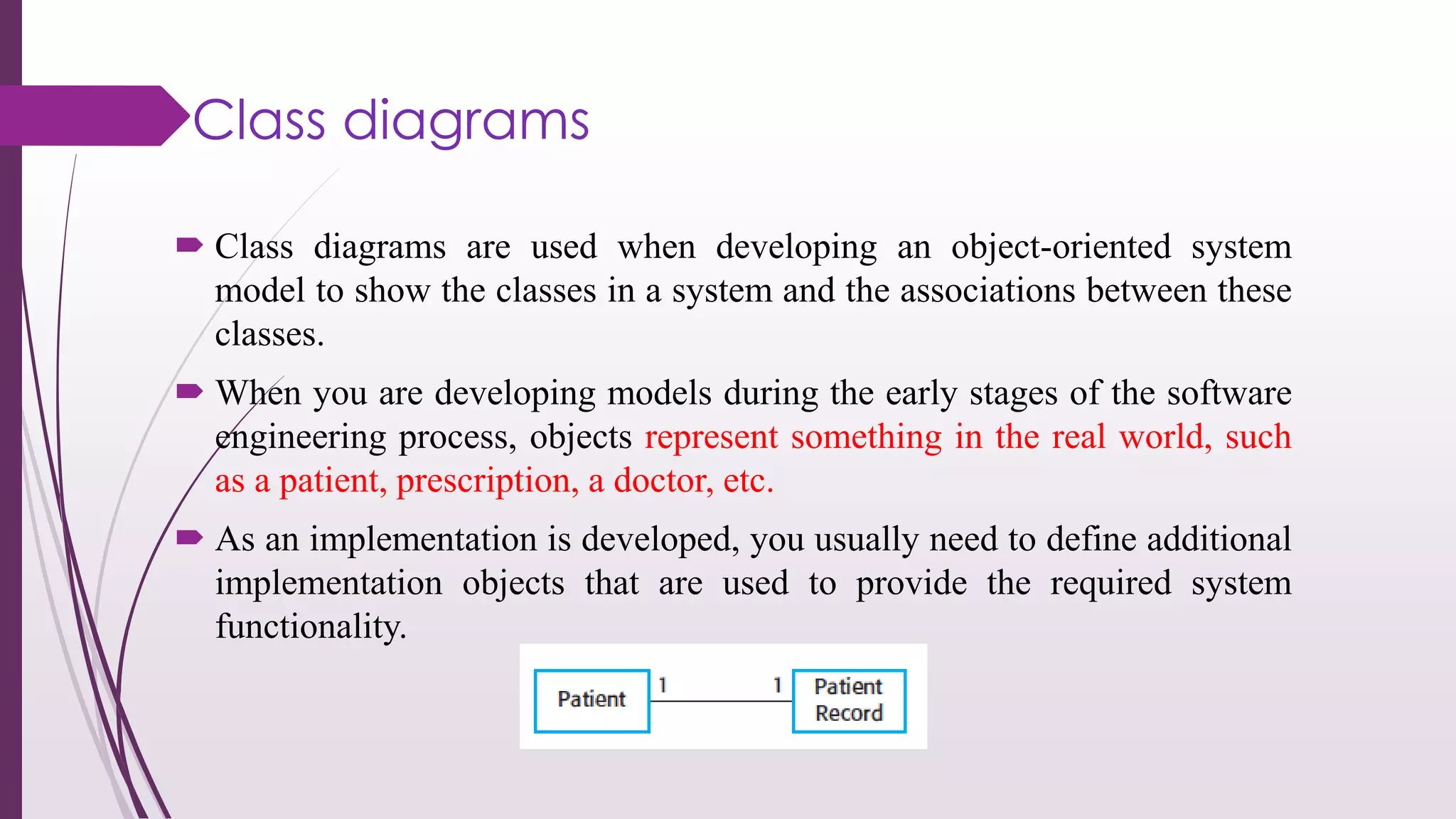
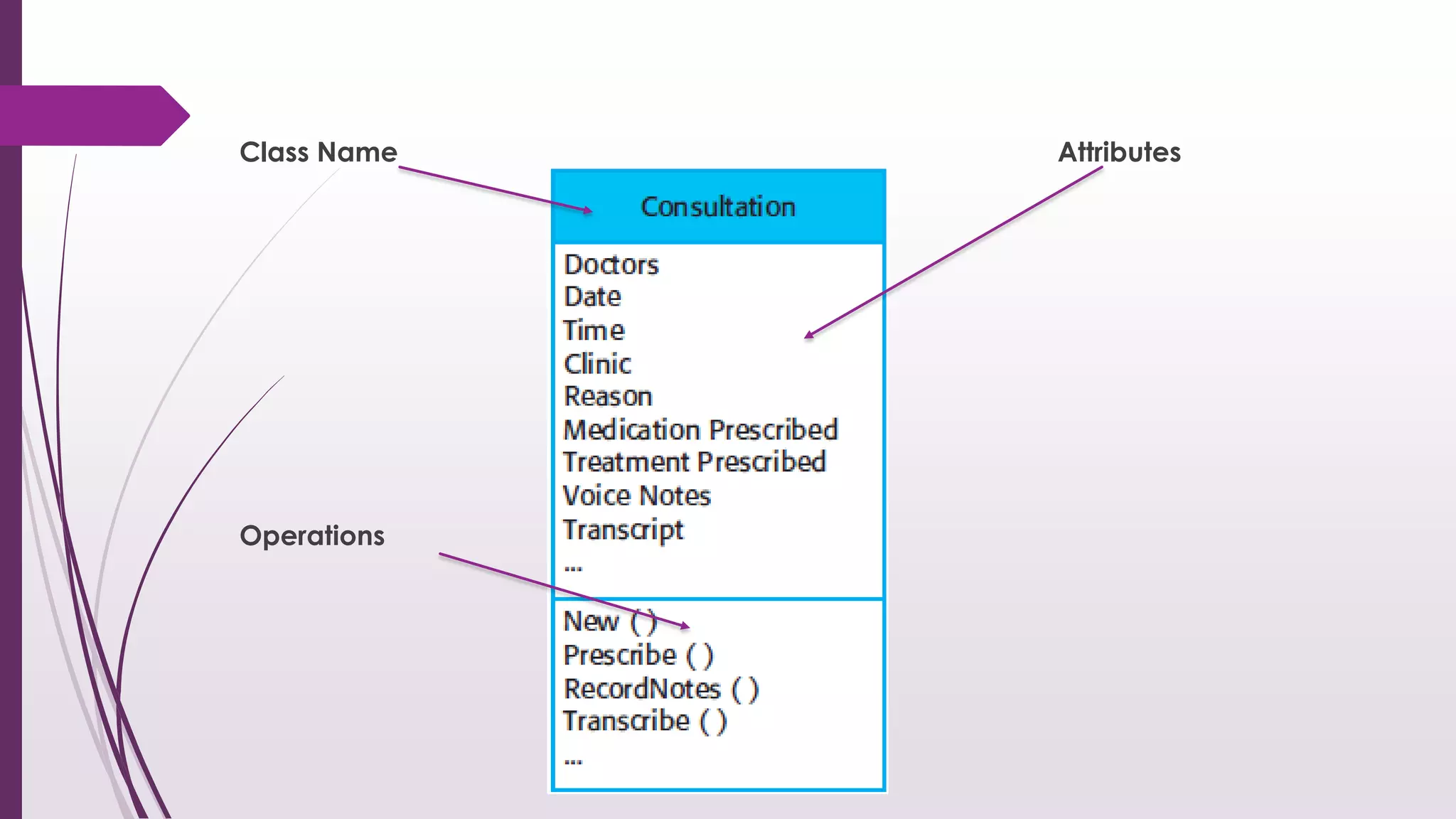
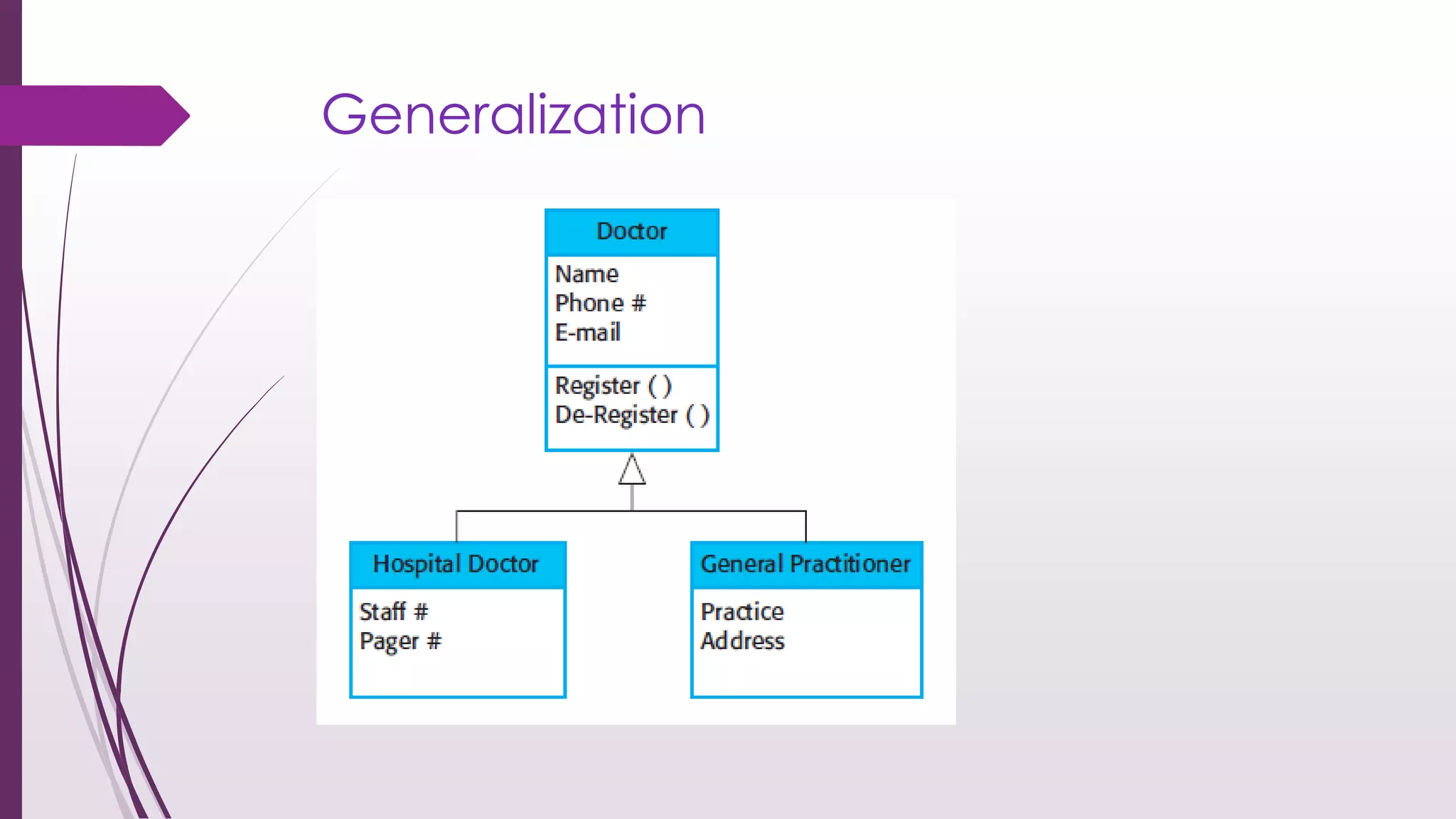
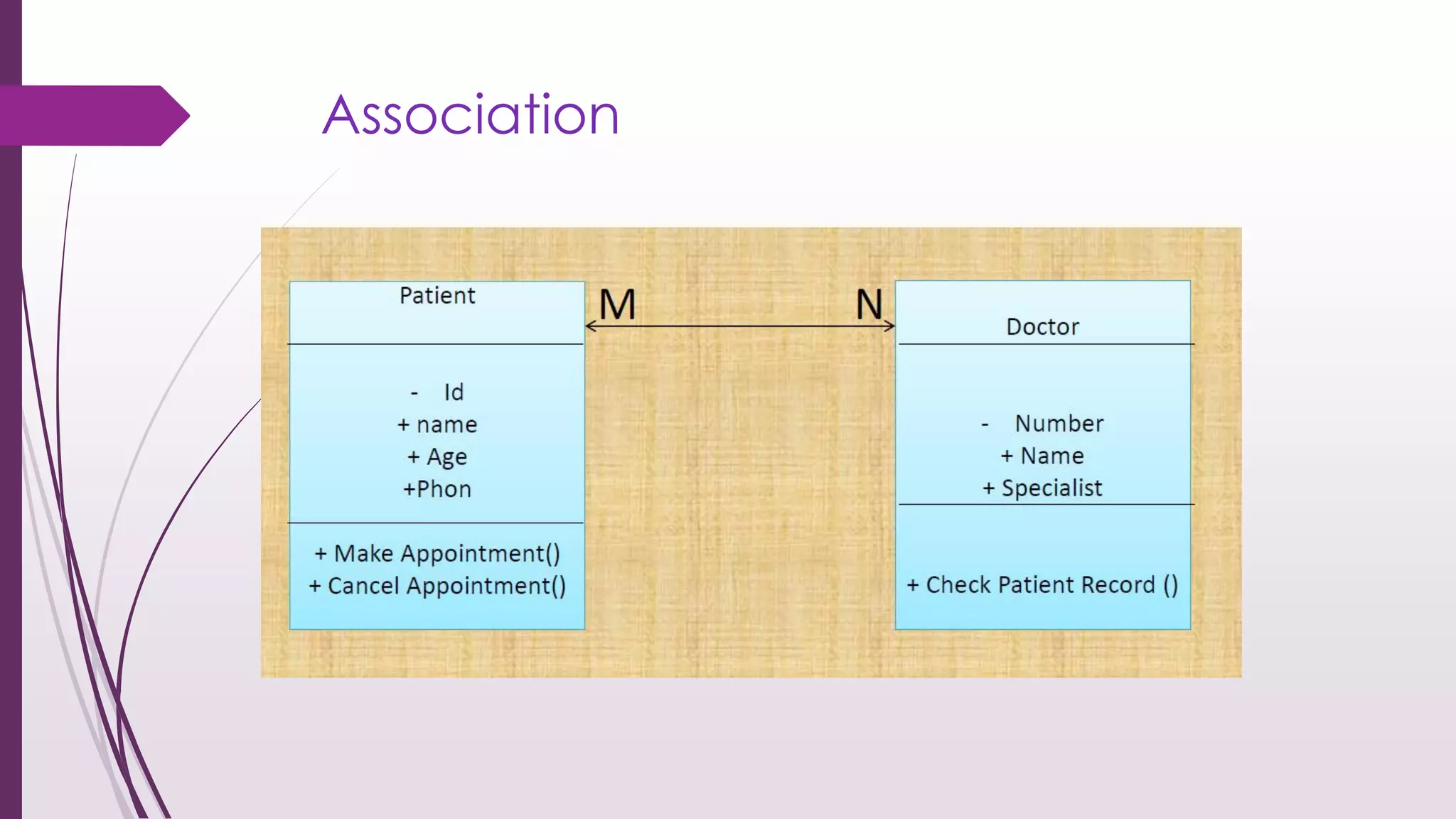
This document discusses system modeling and the Unified Modeling Language (UML). It provides an overview of different types of UML diagrams including class, sequence, use case, state, and activity diagrams. It also discusses modeling concepts such as system boundaries, interactions, and structural models. Specific examples are provided including a use case diagram for a patient data transfer process and a sequence diagram for viewing patient information in a mental healthcare system.