The document discusses various SQL queries and clauses:
1. The CREATE TABLE statement is used to create a new table with specified columns and data types.
2. The ALTER TABLE statement modifies existing table structures by adding, deleting, or modifying columns.
3. The INSERT INTO statement inserts new rows of data into an existing table.
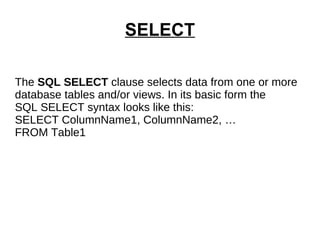
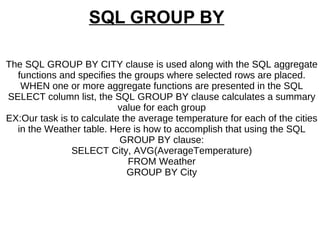
4. The SELECT statement retrieves data from one or more tables and can be used with clauses like WHERE, DISTINCT, GROUP BY, ORDER BY, and JOIN.


![This ALTER TABLE sql command is to make changes in the table. The synatx is: ALTER TABLE[ owner_name ] table_name [ADD column_name datatype attributes] [MODIFY{column_name datatype | column_constraint}] Example Query: ALTER TABLE STUDENT ADD(PERCENTAGE NUMBER(5,2));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/babitha2-mysql-100604000137-phpapp01/85/Babitha2-mysql-3-320.jpg)










![AND/OR The Syntax for AND/OR SELECT "column_name" FROM "table_name" WHERE "simple condition" {[AND|OR] "simple condition"}+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/babitha2-mysql-100604000137-phpapp01/85/Babitha2-mysql-16-320.jpg)


