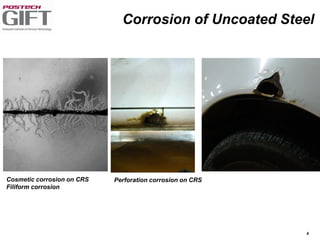
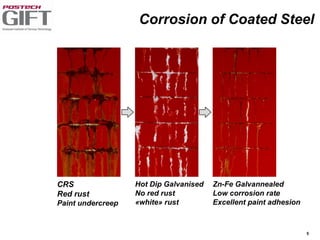
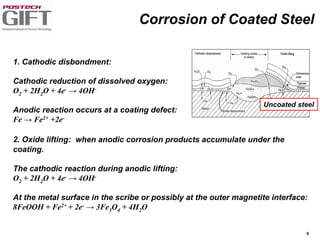
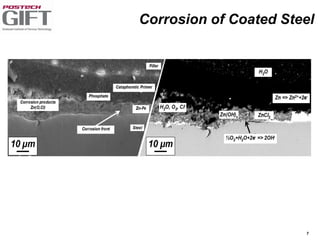
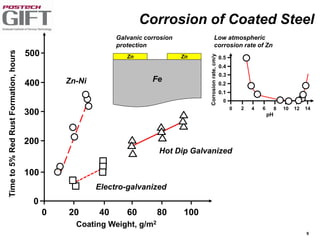
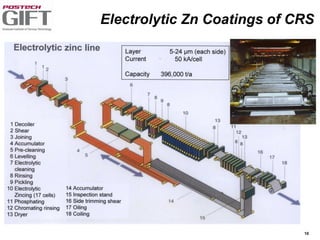
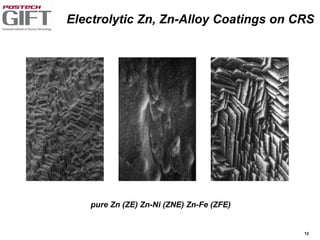
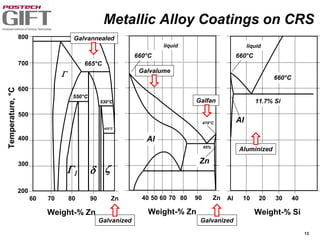
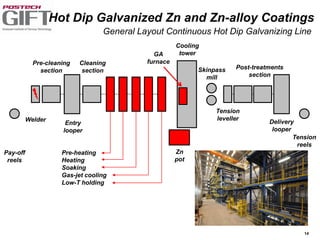
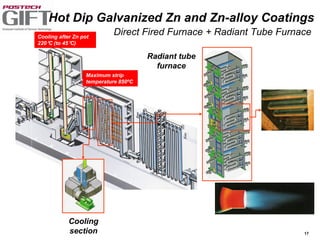
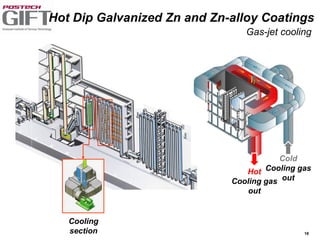
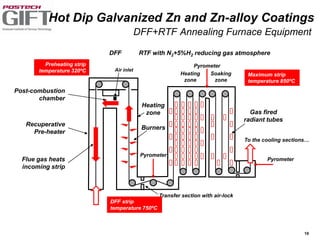
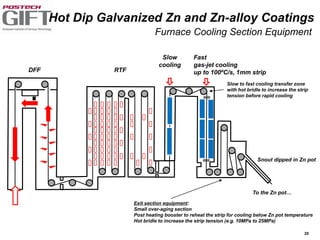
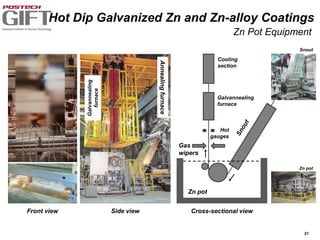
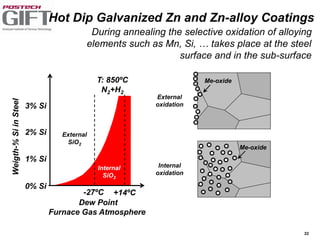
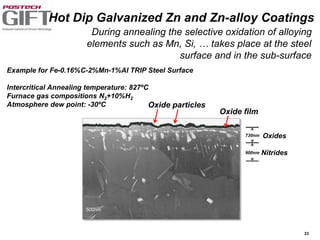
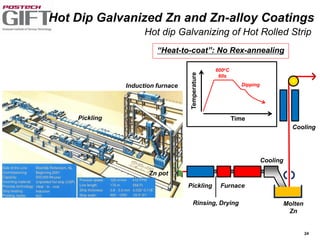
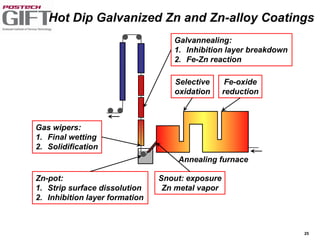
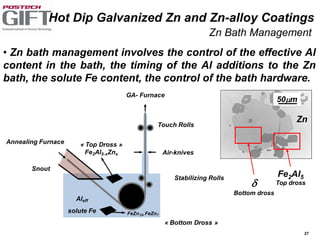
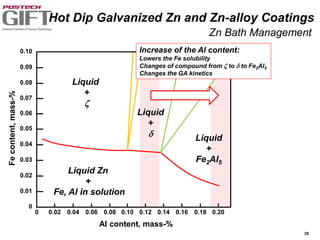
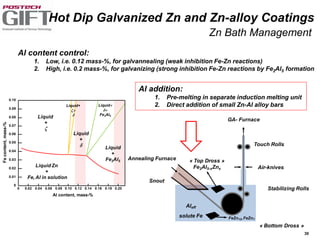
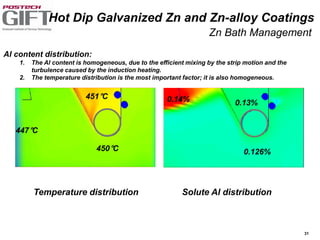
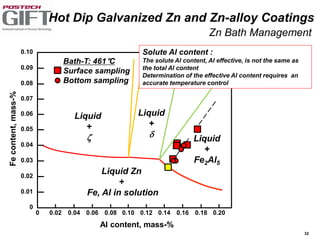
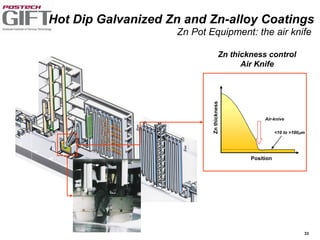
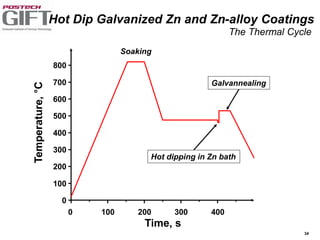
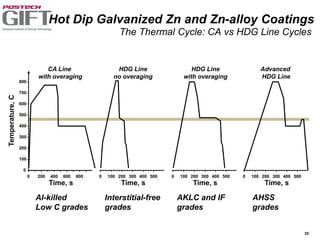
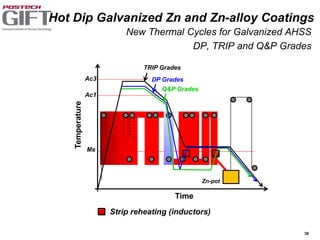
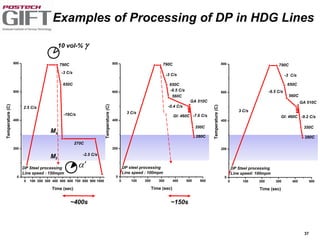
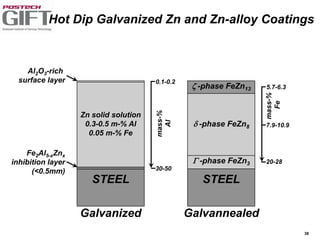
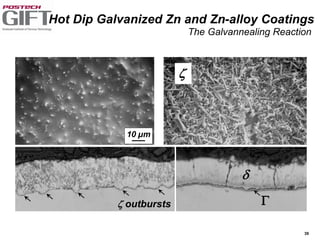
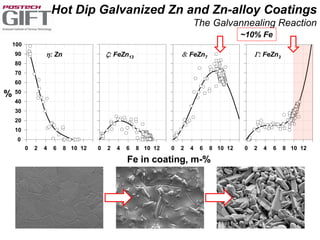
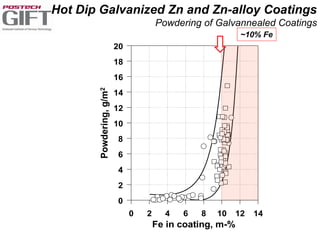
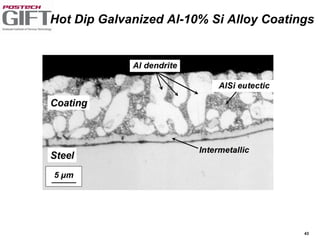
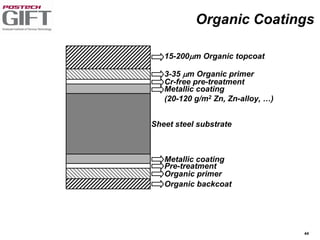
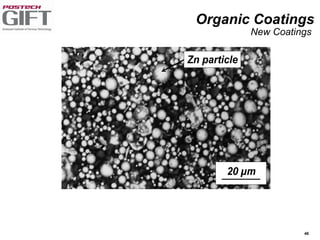
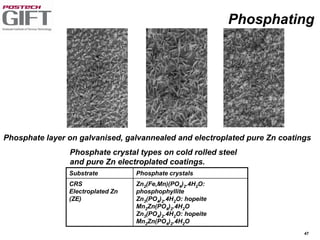
Coating technologies provide sheet steel with superior corrosion resistance at low cost without impacting recyclability. Widespread use in manufacturing is due to a switch from uncoated to coated sheet in automotive and building industries. Coatings include metallic and organic types applied via hot or cold rolling and provide favorable application characteristics like excellent adhesion and formability.