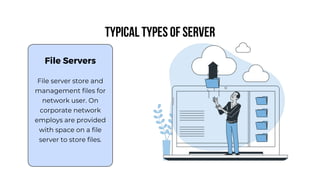
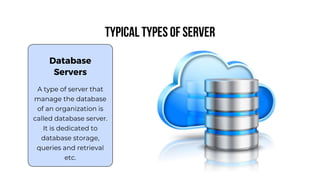
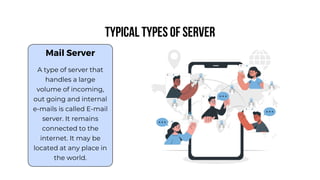
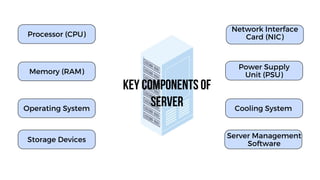
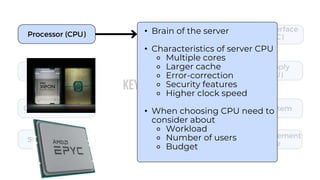
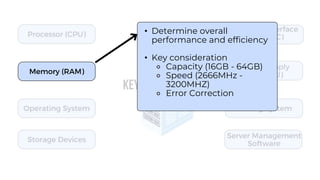
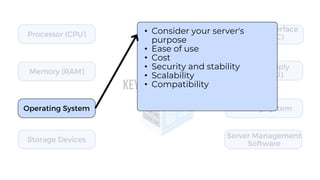
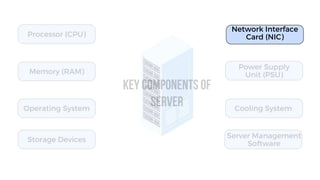
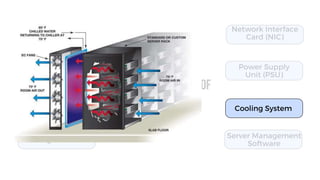
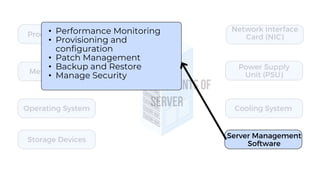
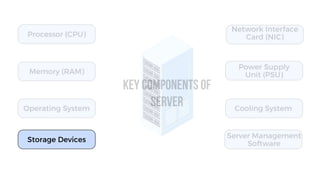
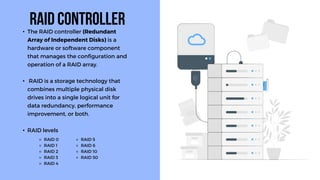
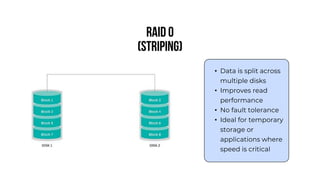
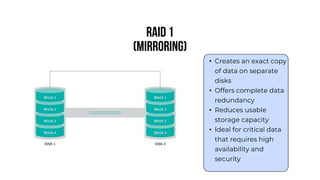
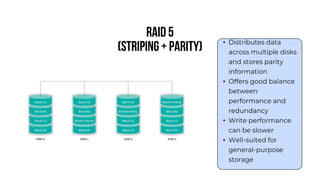
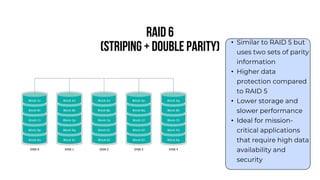
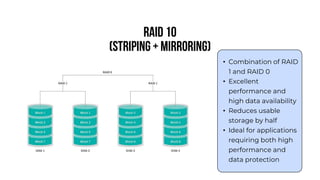
A server is a specialized computer that manages resources and provides services to other computers over a network. There are several typical types of servers including web servers, file servers, database servers, and mail servers. Servers provide advantages like efficient resource management, improved security, hosting applications and websites, backup processes, and centralized storage and file sharing. Key components of a server include processors, storage devices, memory, network interfaces, power supplies, cooling systems, and server management software. Common RAID levels for storage devices include RAID 0, 1, 5, 6, and 10, each offering different balances of performance, redundancy, and capacity.