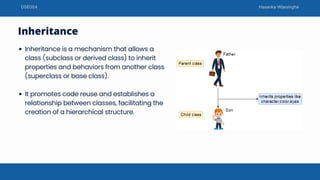
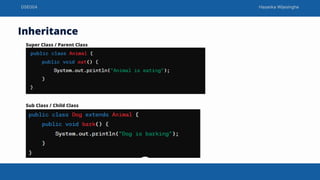
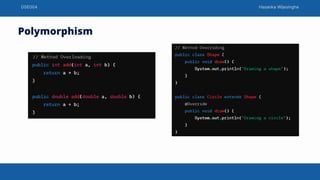
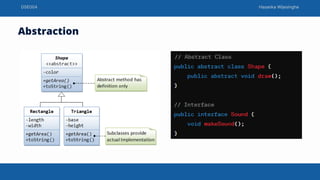
This document discusses object oriented programming concepts taught by Hasanka Wijesinghe. It covers Java classes and methods, object creation, access modifiers including public, private and protected. It also explains core OOP concepts - encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism and abstraction. Encapsulation bundles data and methods into a class. Inheritance allows a class to inherit properties from another class in a hierarchy. Polymorphism allows an entity to have multiple forms via method overloading and overriding. Abstraction simplifies complex systems by modeling classes based on essential properties.