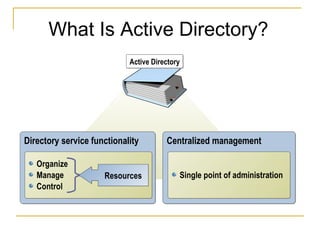
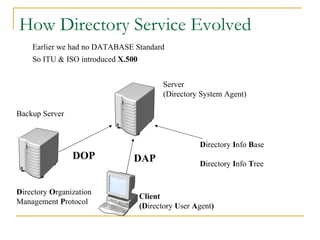
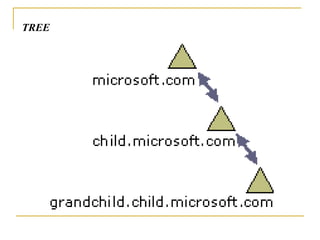
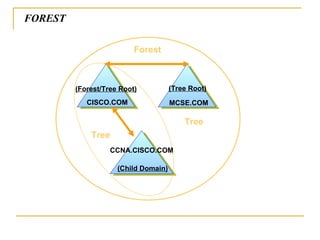
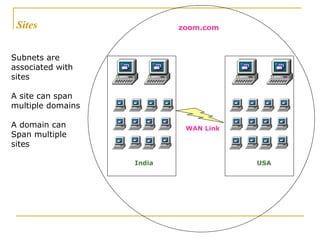
Active Directory is a centralized hierarchical directory database that contains information about all user accounts and shared network resources. It provides user logon authentication services and organizes and manages user accounts, computers, groups and network resources. Active Directory enables authorized users to easily locate network resources. It features include fully integrated security, easy administration using group policy, scalability to large networks, and flexibility through features like cross-forest trusts and site-to-site replication.