Embed presentation
Download to read offline

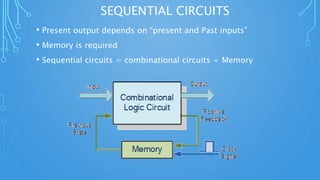

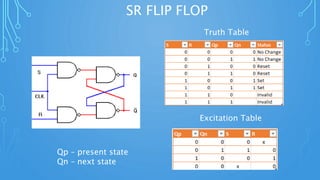
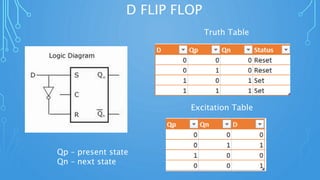
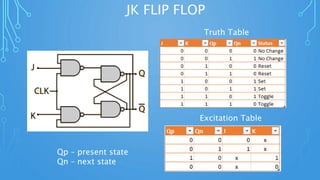
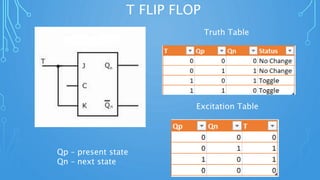

This document discusses sequential circuits and various flip flop circuits. It defines non-clocked and clocked flip flops, and describes positive and negative edge triggering. It provides diagrams, truth tables, and excitation tables for SR, D, JK, and T flip flops. Sequential circuits have memory and their output depends on present and past inputs.






