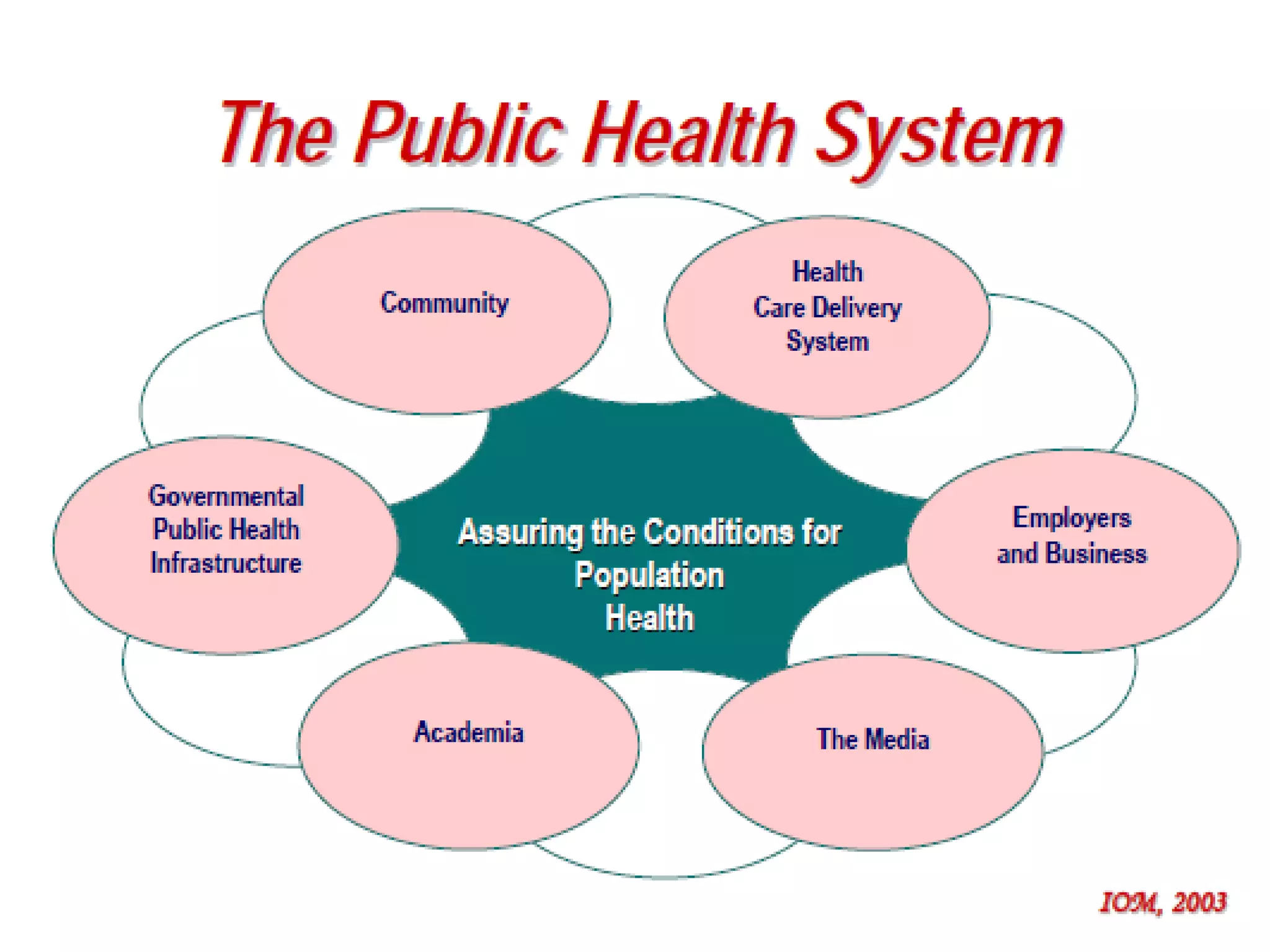
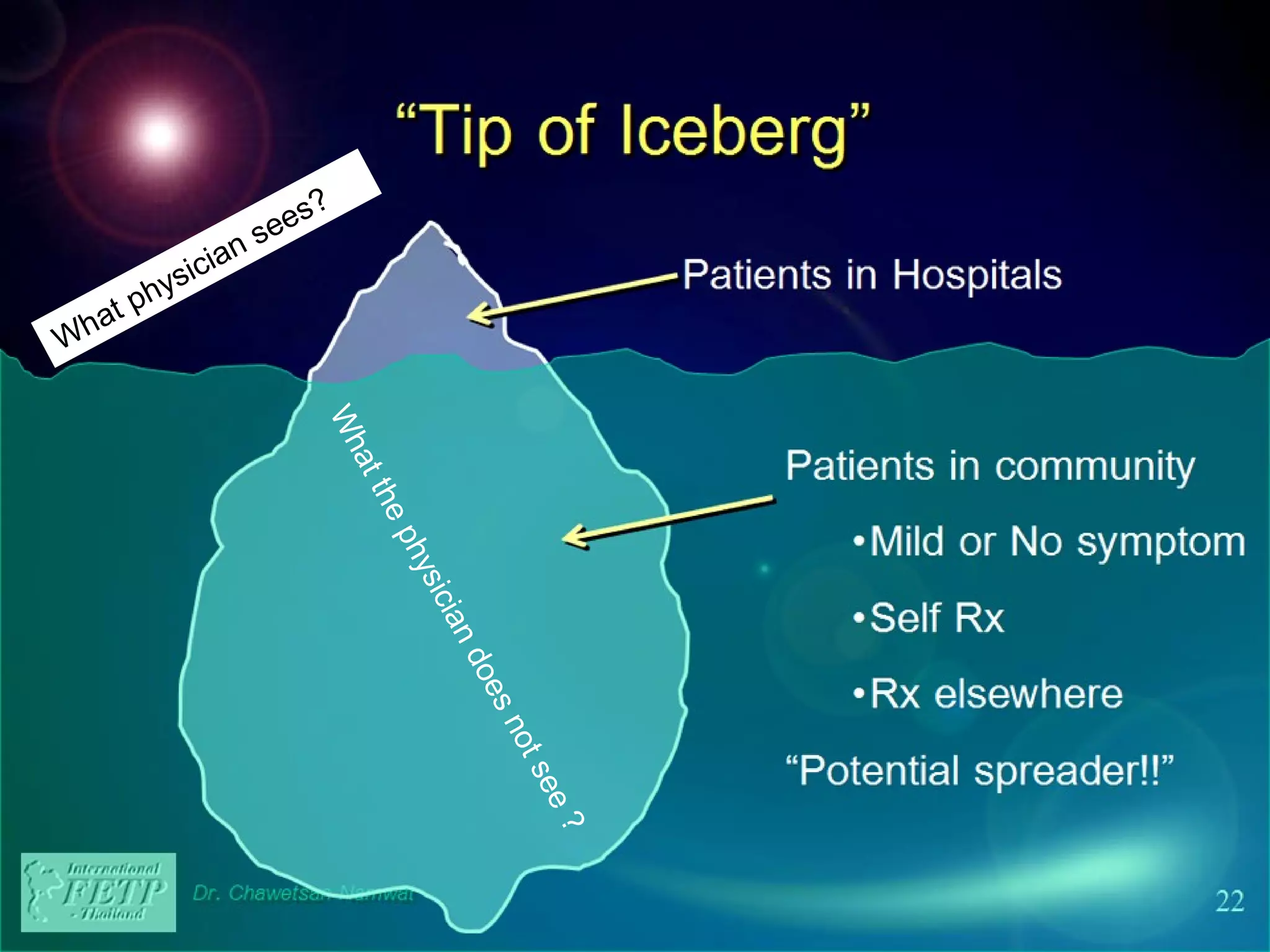
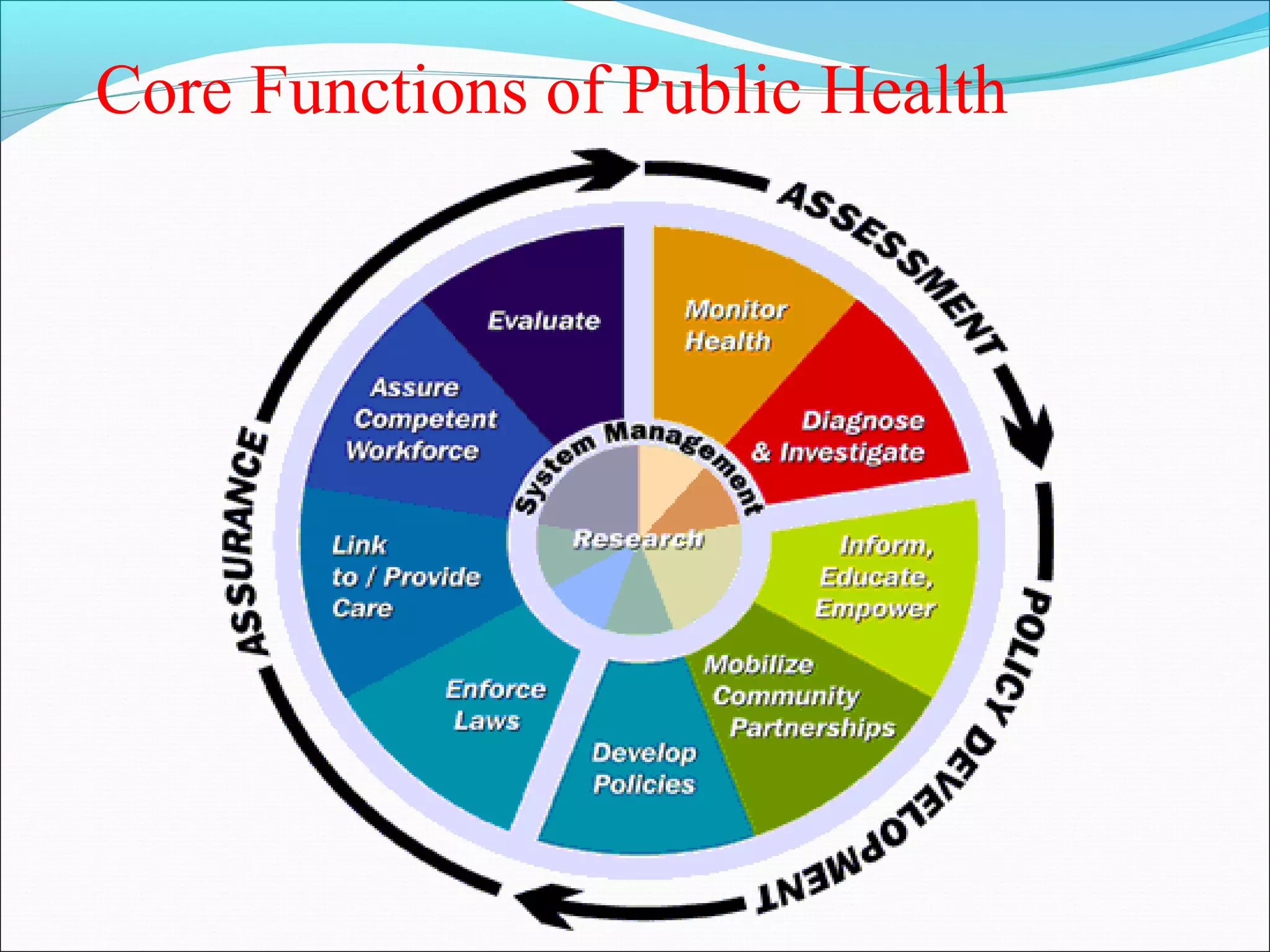
Public health involves organized community efforts and government interventions to promote health and prevent disease. It aims to protect the health of entire populations. Public health focuses on populations, disease prevention, health promotion, and environmental/behavioral factors rather than individual treatment. Some key aspects of public health include monitoring health status; ensuring access to quality health services; implementing programs for health promotion, disease prevention, and injury prevention; and developing health policy. Public health organizations at both the governmental and non-governmental level work to address a wide range of public health problems.