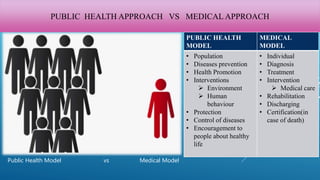
This document provides an overview of public health. It defines public health as maintaining, protecting, and improving population health through organized community efforts. The core functions of public health include preventing diseases, responding to disasters, promoting healthy behaviors, and monitoring health status. Public health takes a population-based approach and focuses on prevention, while the medical model focuses on individual treatment. Key public health problems addressed include communicable and non-communicable diseases. Major public health achievements have resulted in vaccines, reduced heart disease deaths, and recognition of tobacco as a health hazard. The document also outlines the scopes and roles of various public health organizations.