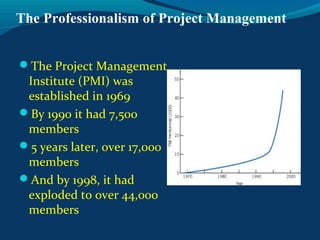
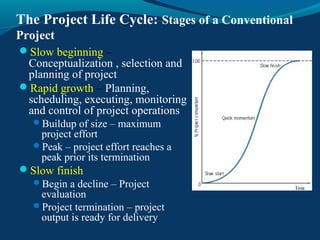
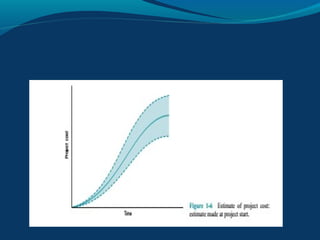
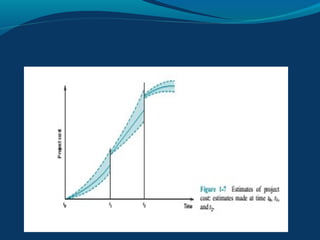
A project is a temporary endeavor with a defined start and end date, undertaken to create a unique product or service. It involves planning a sequence of interrelated activities and allocating resources to accomplish defined objectives within constraints. Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet project requirements. The key project management process groups are initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and control, and closure. Effective project managers need skills in areas like conflict resolution, flexibility, change management, planning, and negotiation.