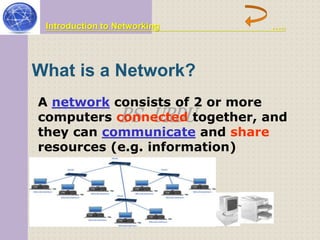
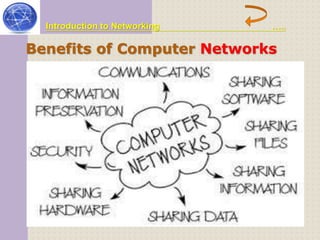
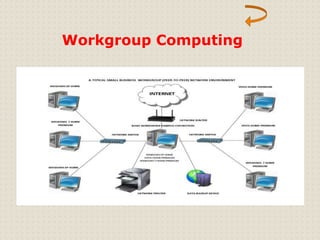
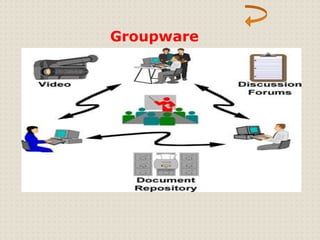
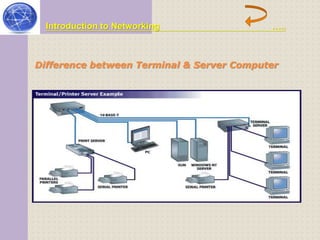
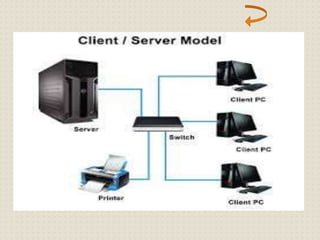
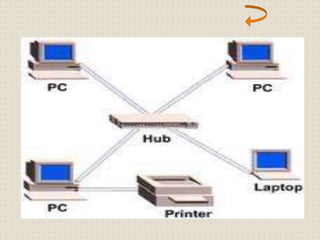
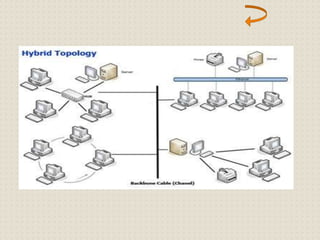
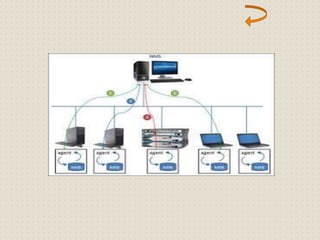
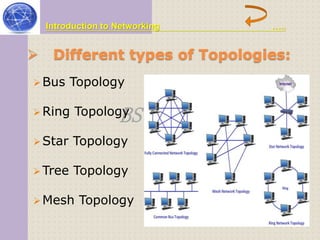
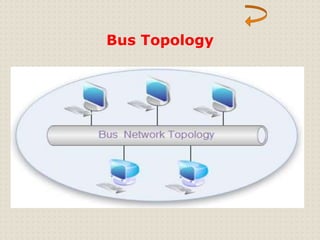
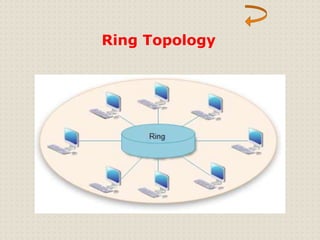
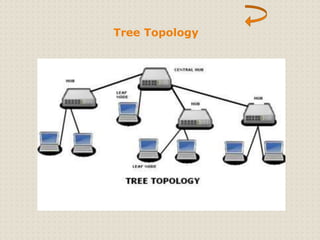
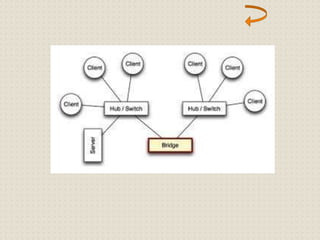
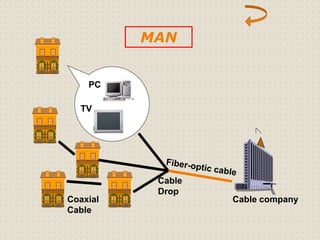
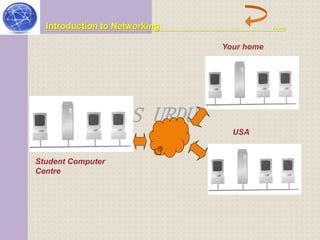
This document provides an introduction to computer networking concepts. It discusses what a network is, the benefits of networks, and different network models including client-server, peer-to-peer, and hybrid models. It also describes common network devices like routers, gateways, and bridges. Various network topologies are defined, such as bus, star, ring, tree and mesh. Finally, it distinguishes between local, metropolitan, and wide area networks. The presentation was given by a group of 4 students in Pakistan on the topic of an introduction to computer networking.