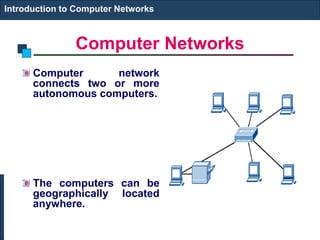
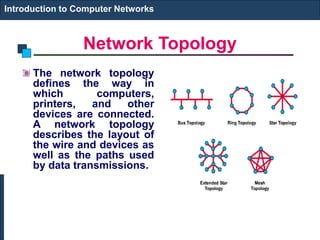
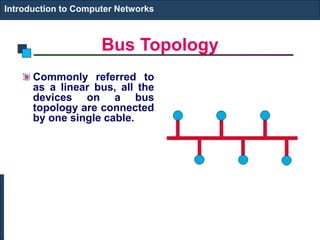
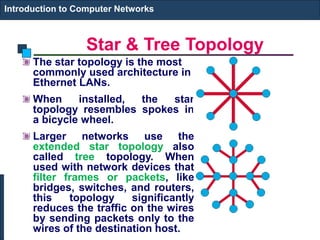
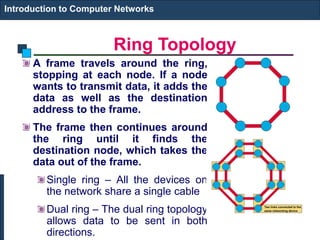
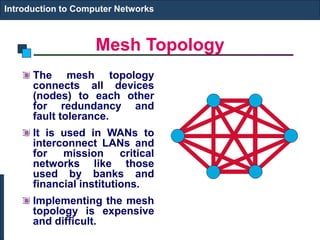
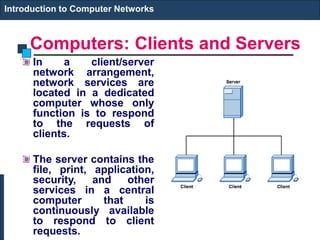
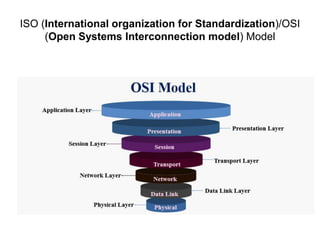
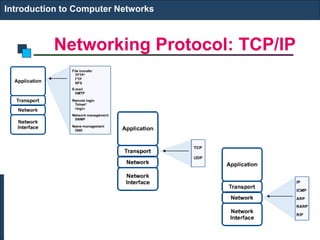
The document provides an introduction to computer networks. It discusses network topologies including bus, star, tree, ring and mesh. It describes the components of a network including physical media, networking devices, computers that can serve as clients or servers, networking protocols like TCP/IP, and applications like email, the web, and video conferencing. It also introduces concepts like LANs, MANs, WANs and the ISO/OSI reference model. The document appears to be an introductory lecture on computer networks covering fundamental topics at a high level.