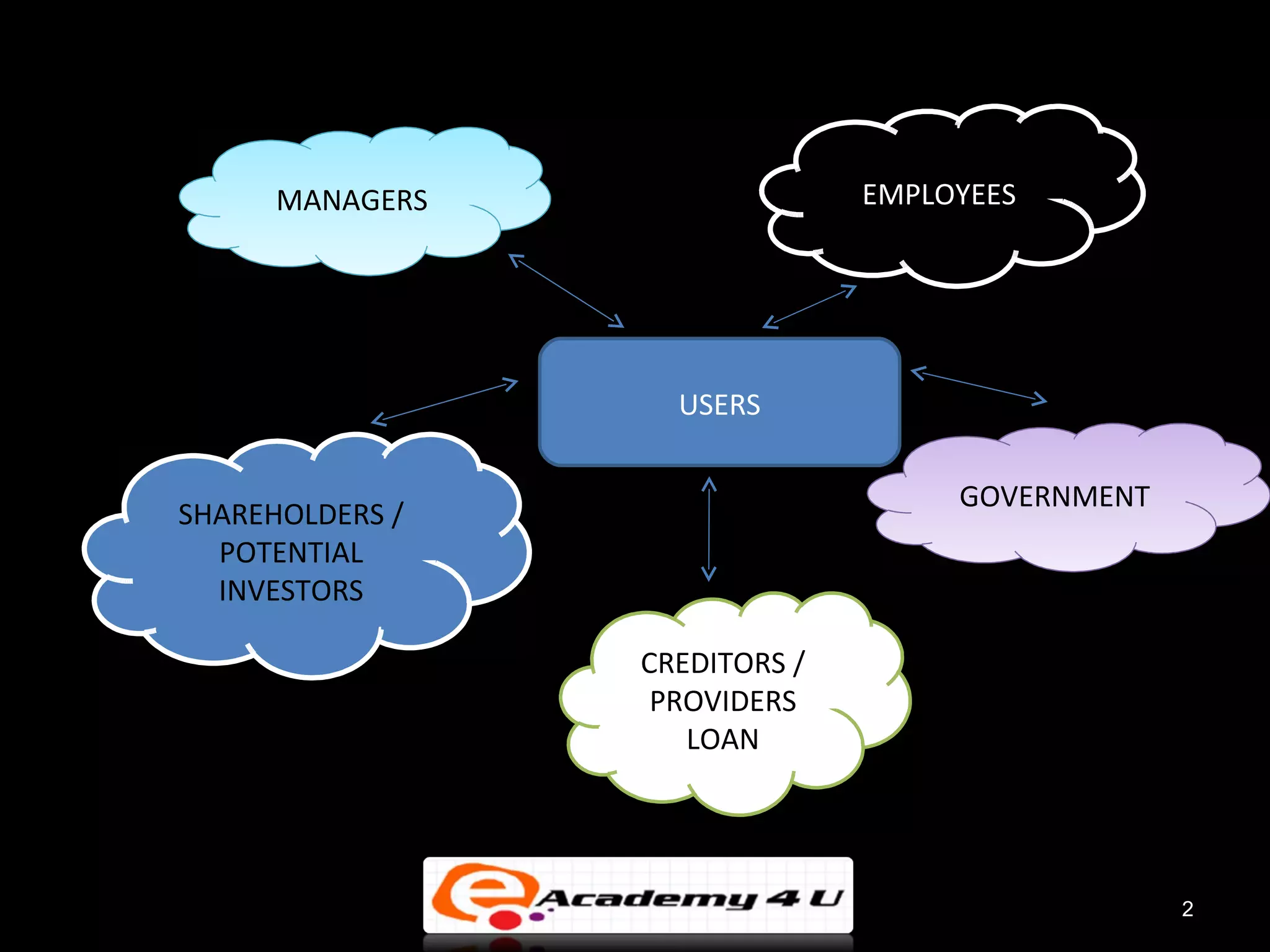
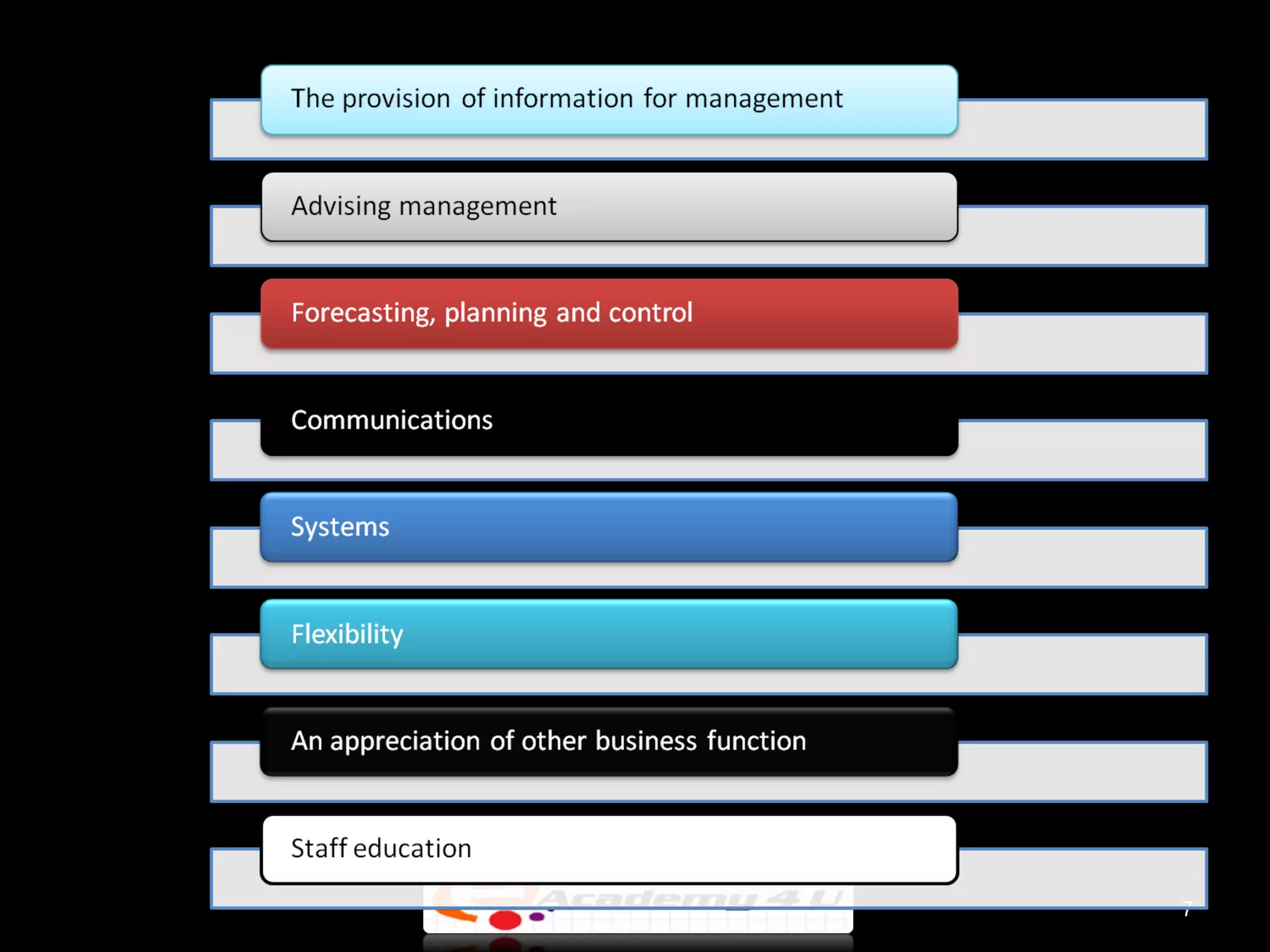
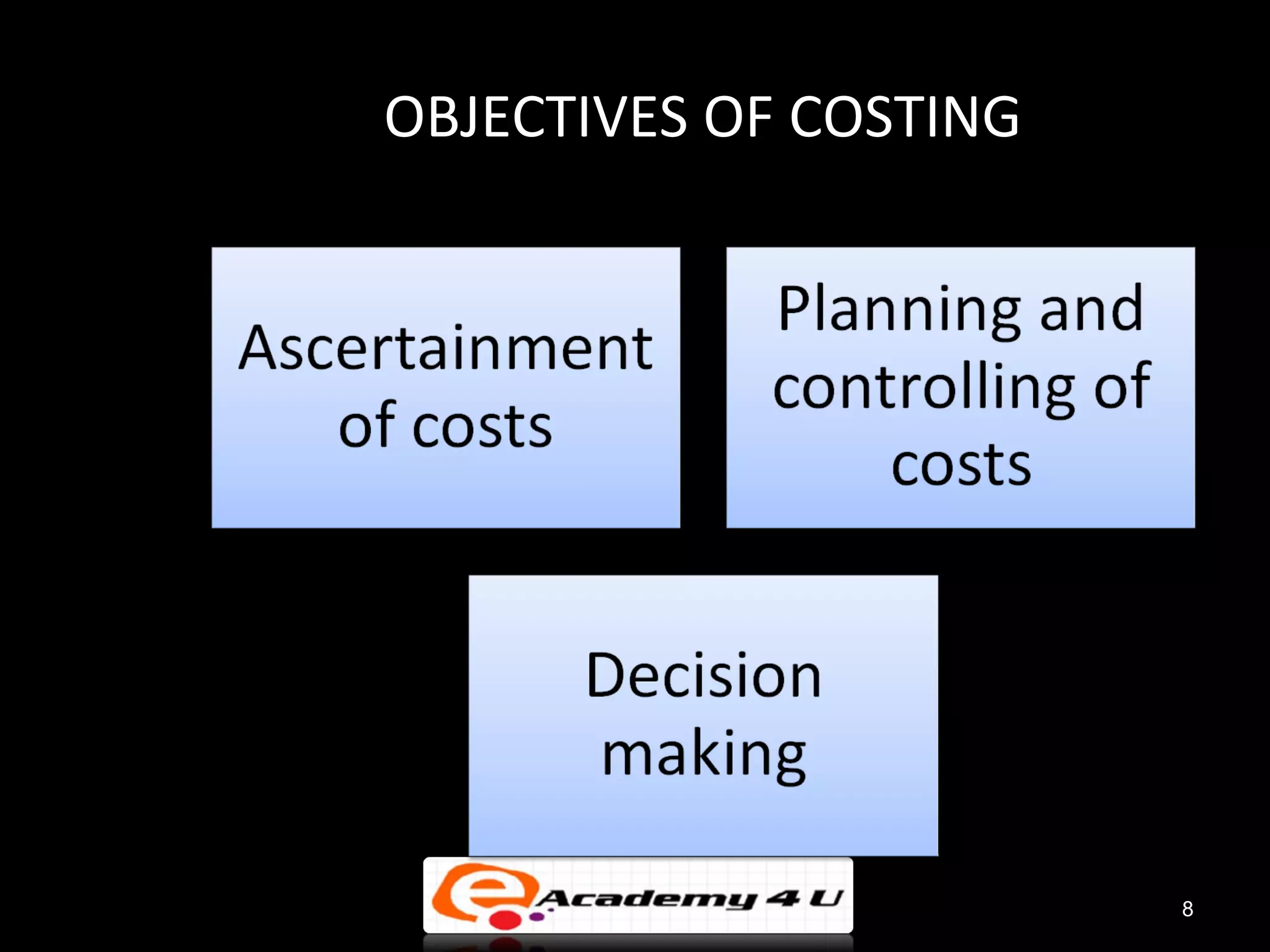
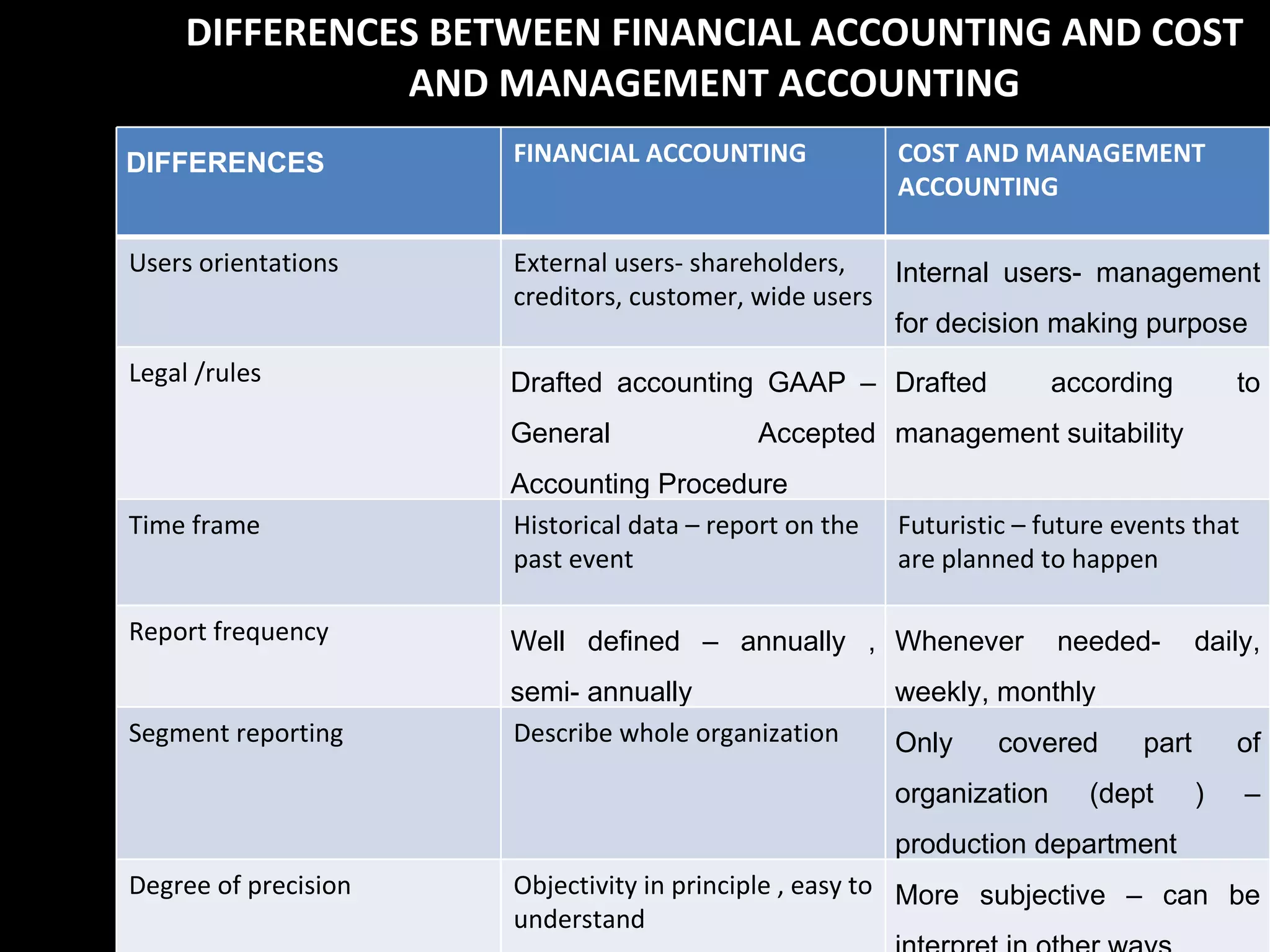
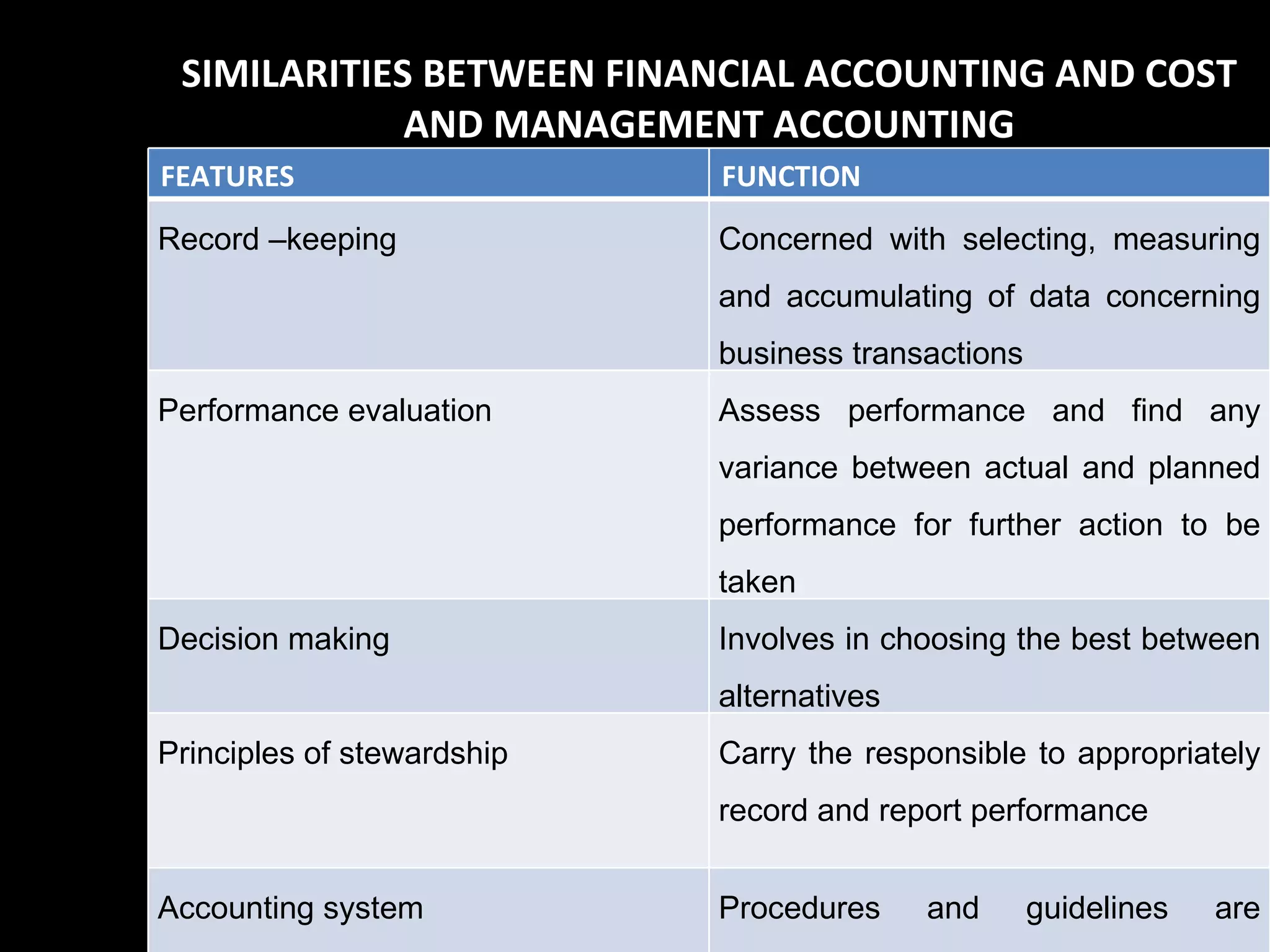
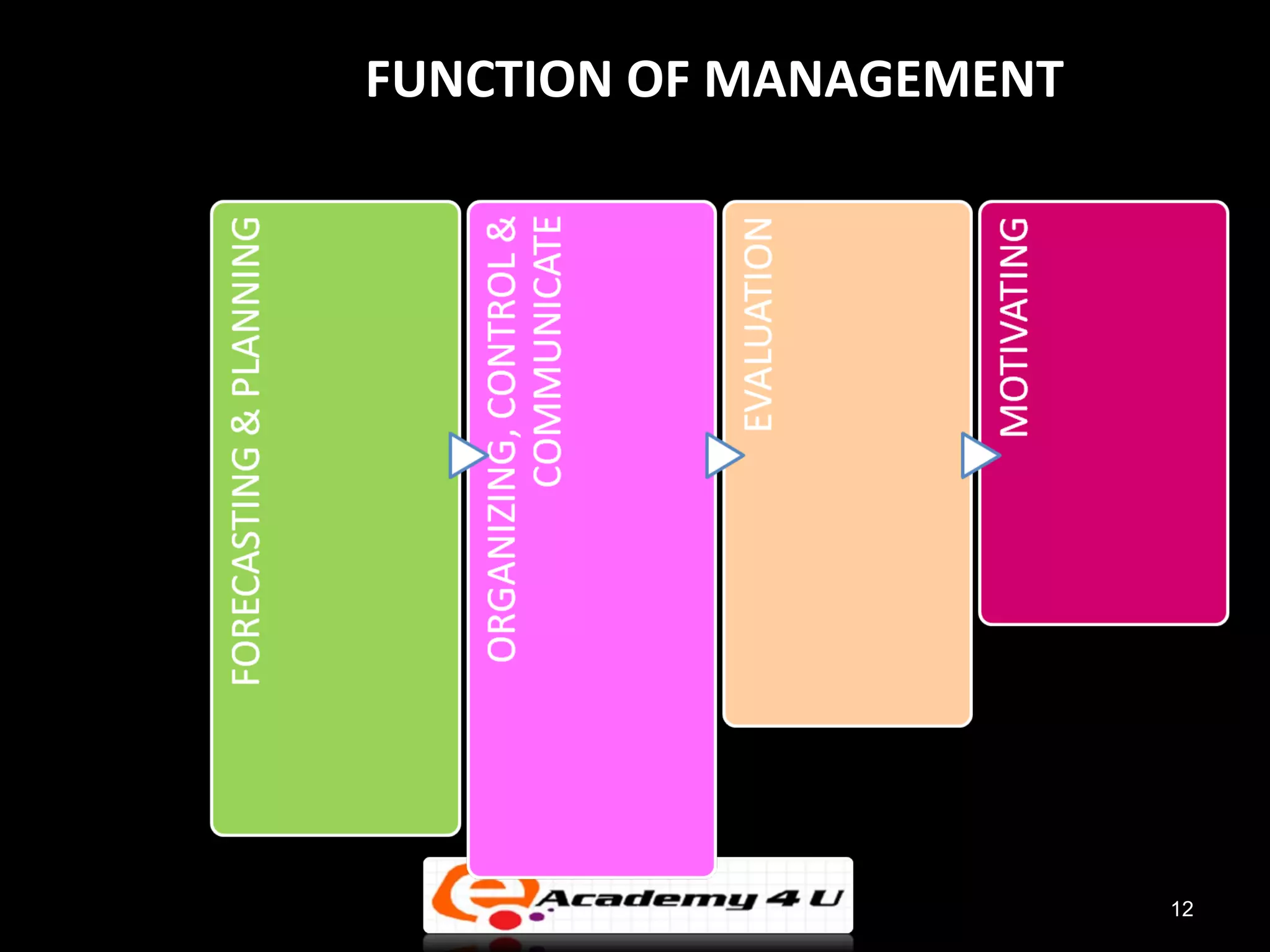
The document provides an introduction to managerial accounting, explaining that it is concerned with providing internal users within an organization information to help them make better decisions, as opposed to financial accounting which provides information to external parties. It discusses the key users and objectives of management accounting, including cost allocation, decision making, planning, and performance measurement. The roles and functions of management accountants are also outlined, such as assisting with information systems, interpreting reports, and analyzing data to support decision making.