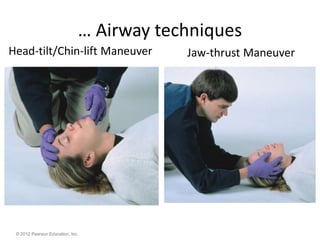
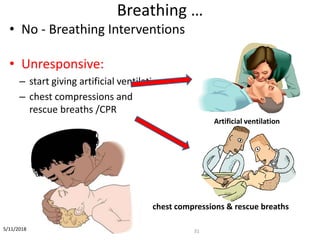
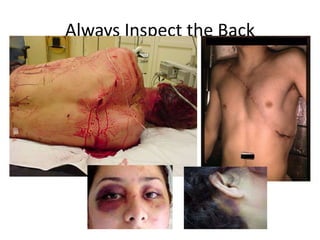
The document provides an introduction to first aid principles including the importance of timely emergency care. It discusses the primary survey process (DR-ABCDE) for assessing patients which focuses on identifying life-threatening issues like airway obstruction, lack of breathing, or severe bleeding. The priorities for first aid interventions are to ensure an open airway, support breathing, and control hemorrhaging. Victims should only be moved if necessary to prevent further injury, and definitive medical care needs to be arranged as soon as possible.