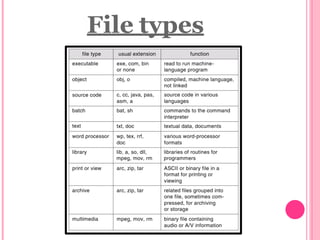
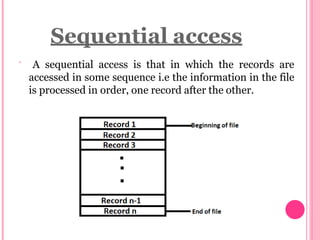
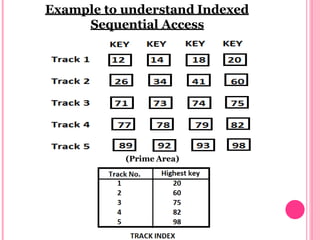
This document provides an introduction to files and file systems. It defines what files are, including that they are containers for storing information and come in different types like text, data, binary and graphic files. It outlines key file attributes like name, size, permissions. It also describes different file access methods like sequential, direct/random, and indexed sequential access. File operations like create, write, read, delete and truncate are also covered. The document concludes with definitions of flat file databases and their advantages and disadvantages compared to relational databases.