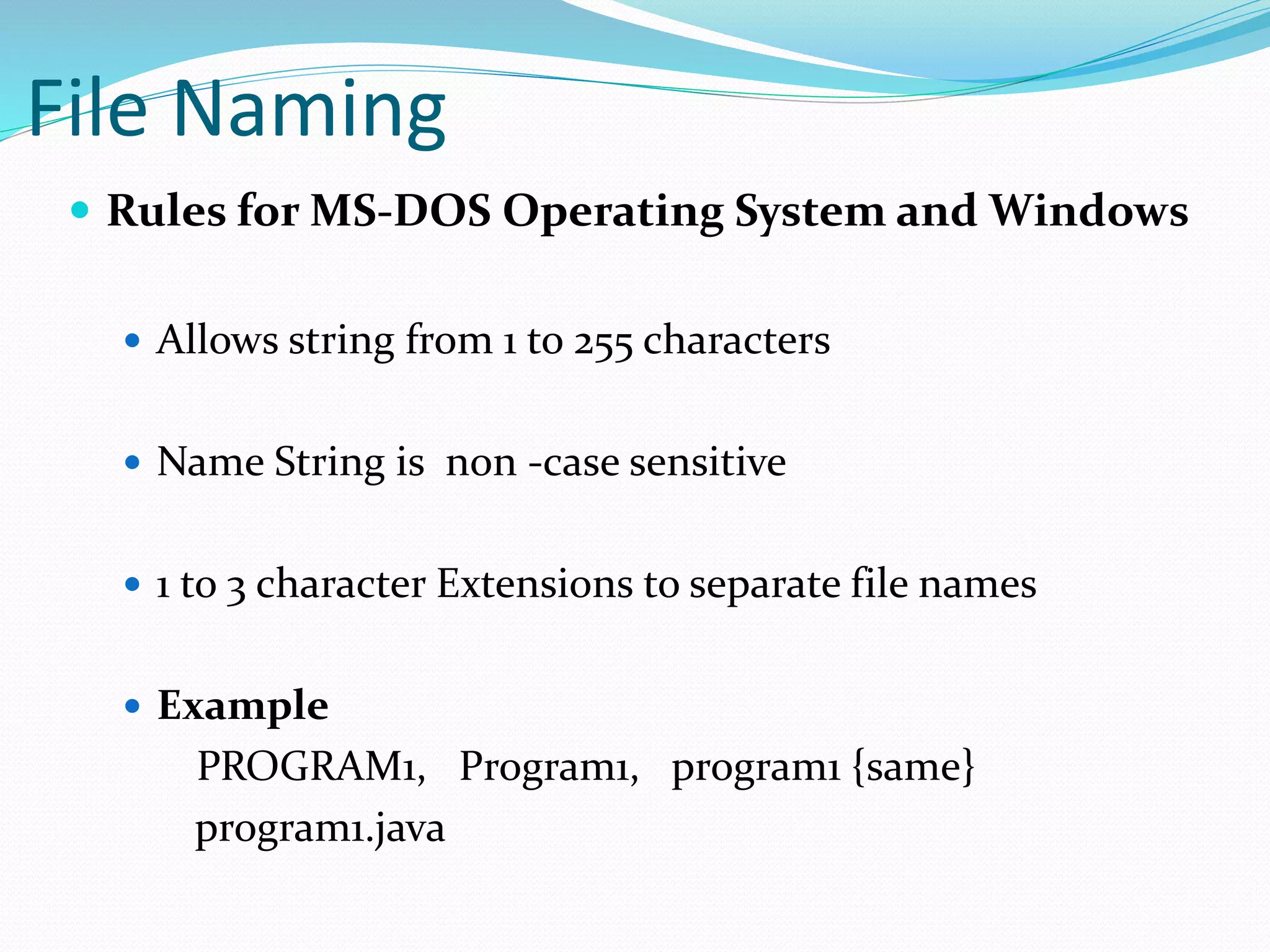
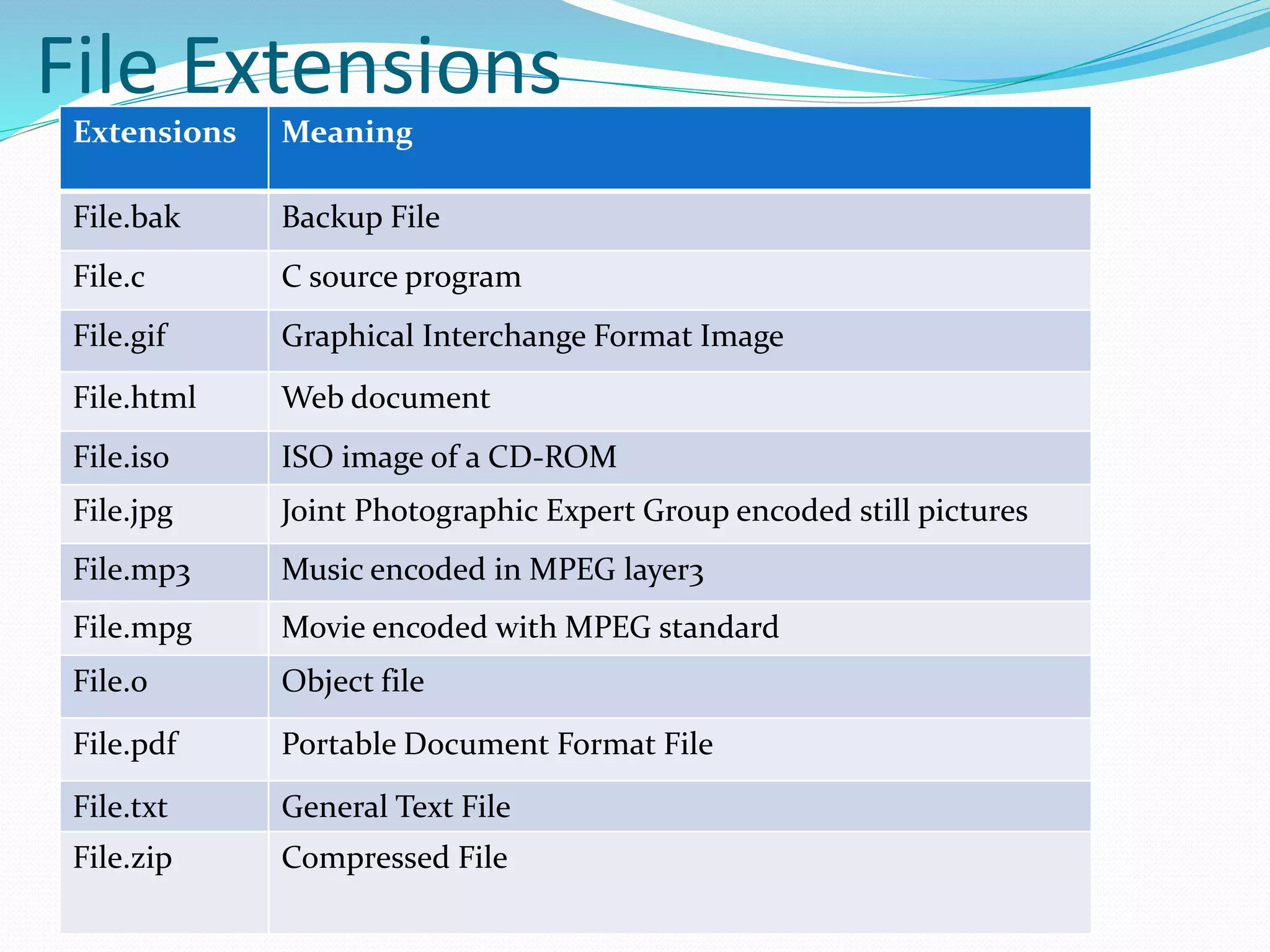
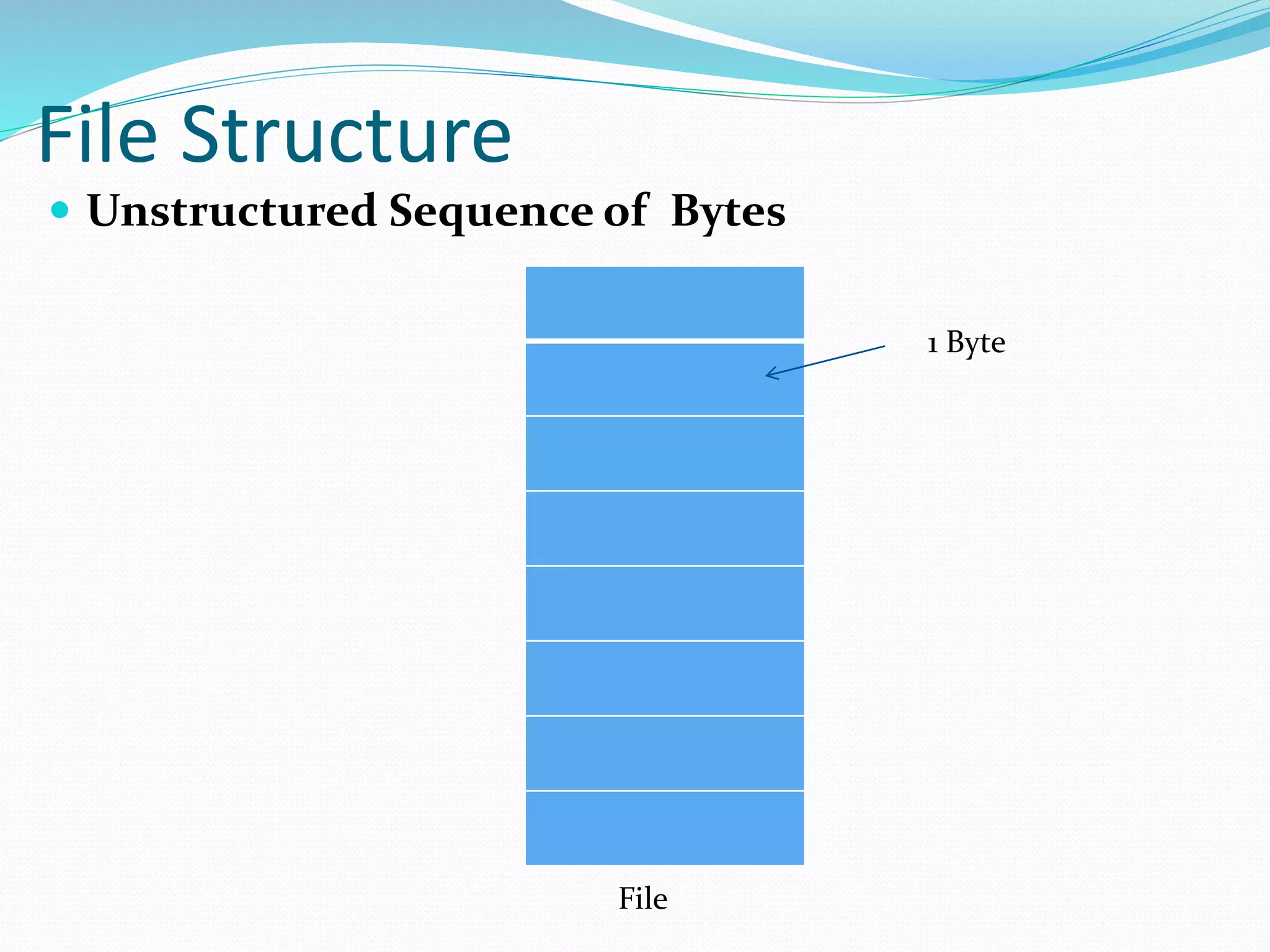
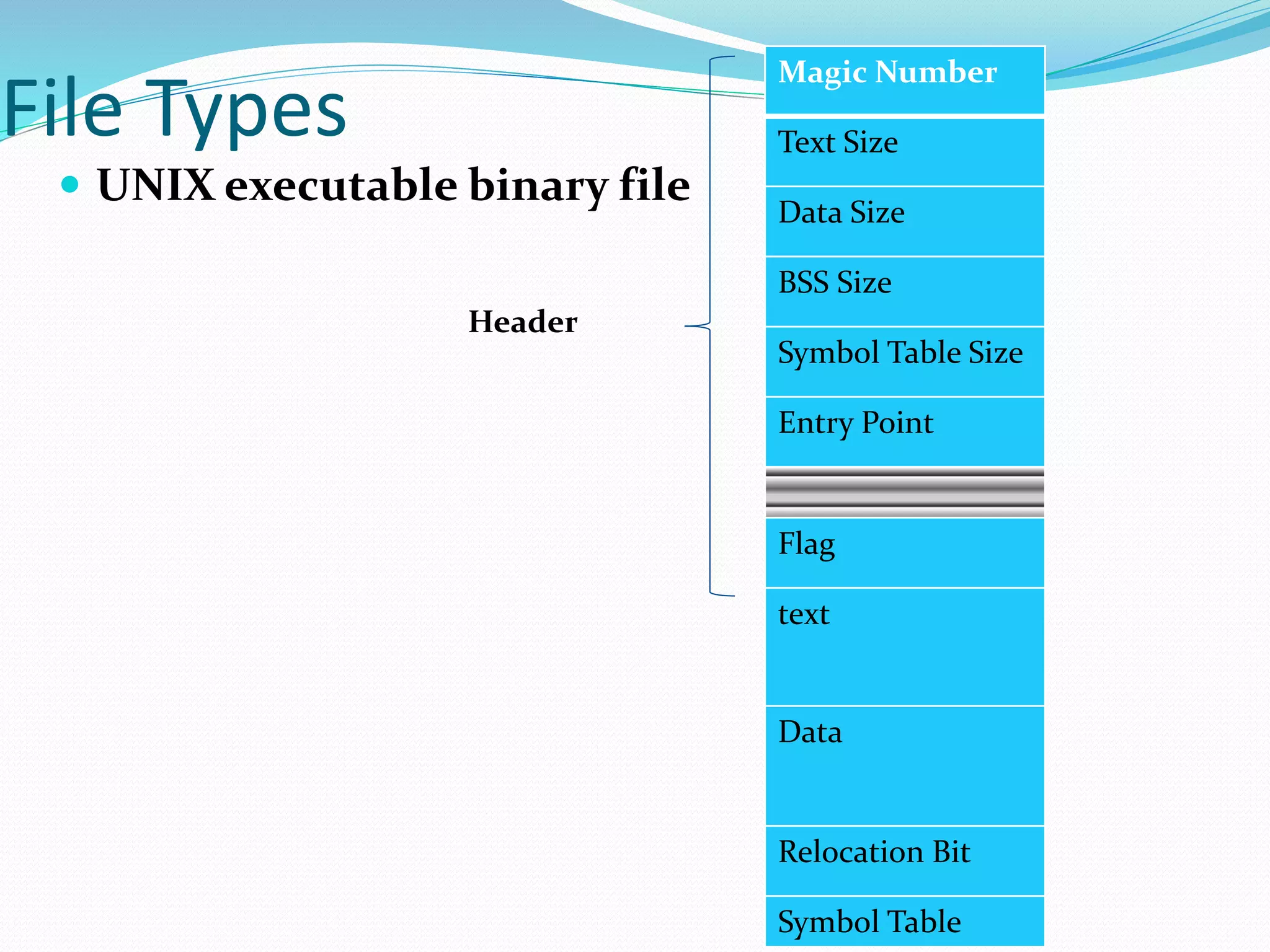
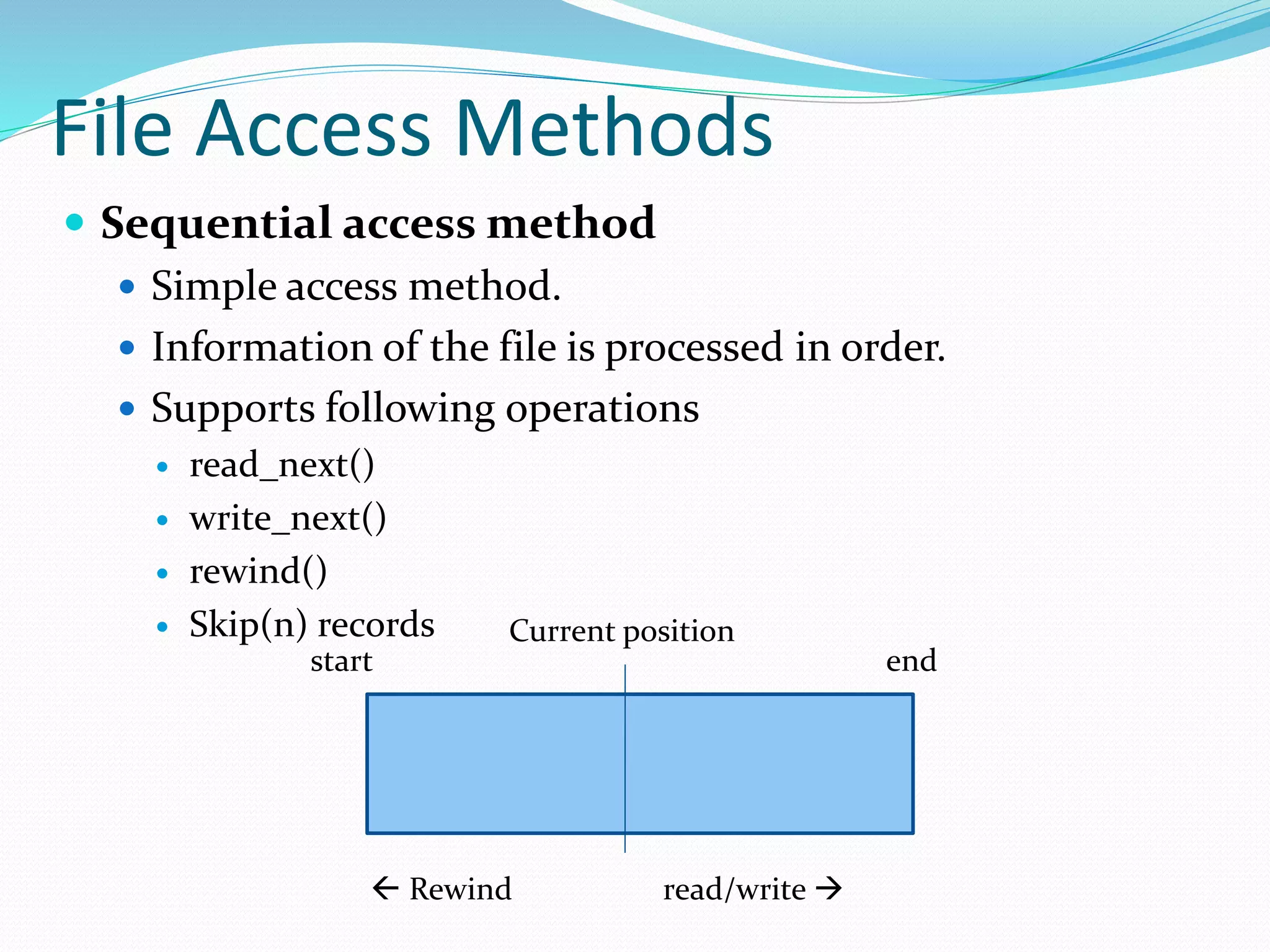
This document discusses computer file systems. It explains that files are used to store information on disks and external storage in a persistent way that allows multiple processes to access the data concurrently. The document then covers file naming conventions, structures, types, attributes, access methods and basic file operations supported by operating systems.