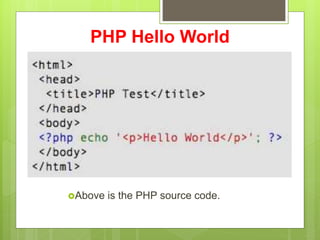
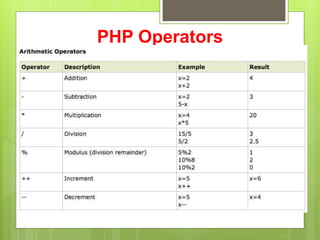
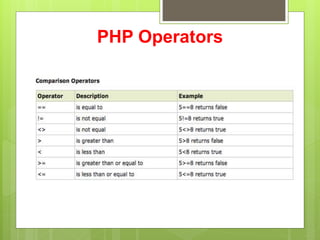
PHP is an open source scripting language used for web development that can be embedded into HTML. It is executed on the server and allows code to be enclosed in special PHP tags. Variables in PHP start with a $ sign and automatically take the correct data type. Strings can be concatenated using the . operator and PHP supports various operators like arithmetic, assignment, comparison, and logical for working with values.