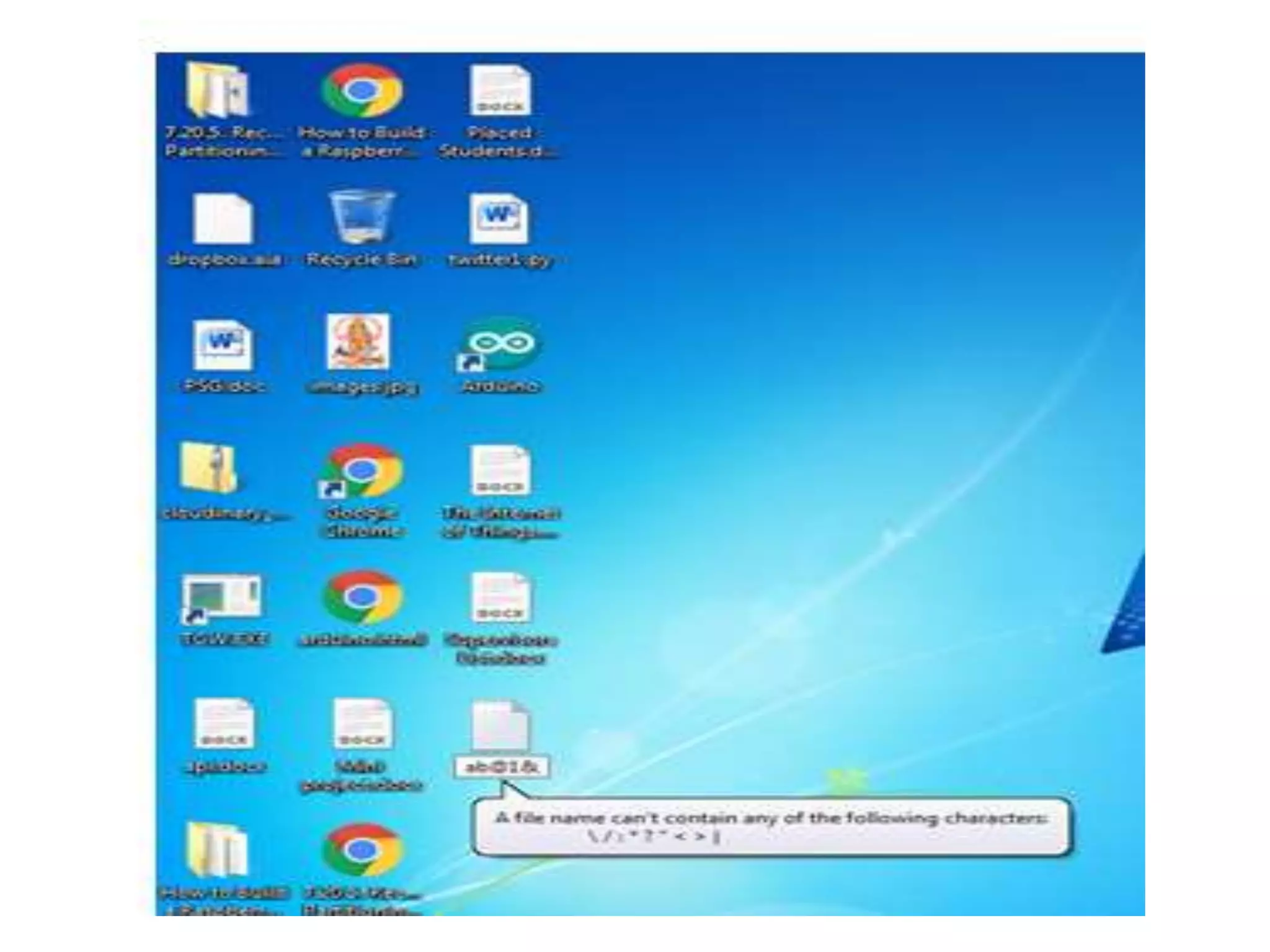
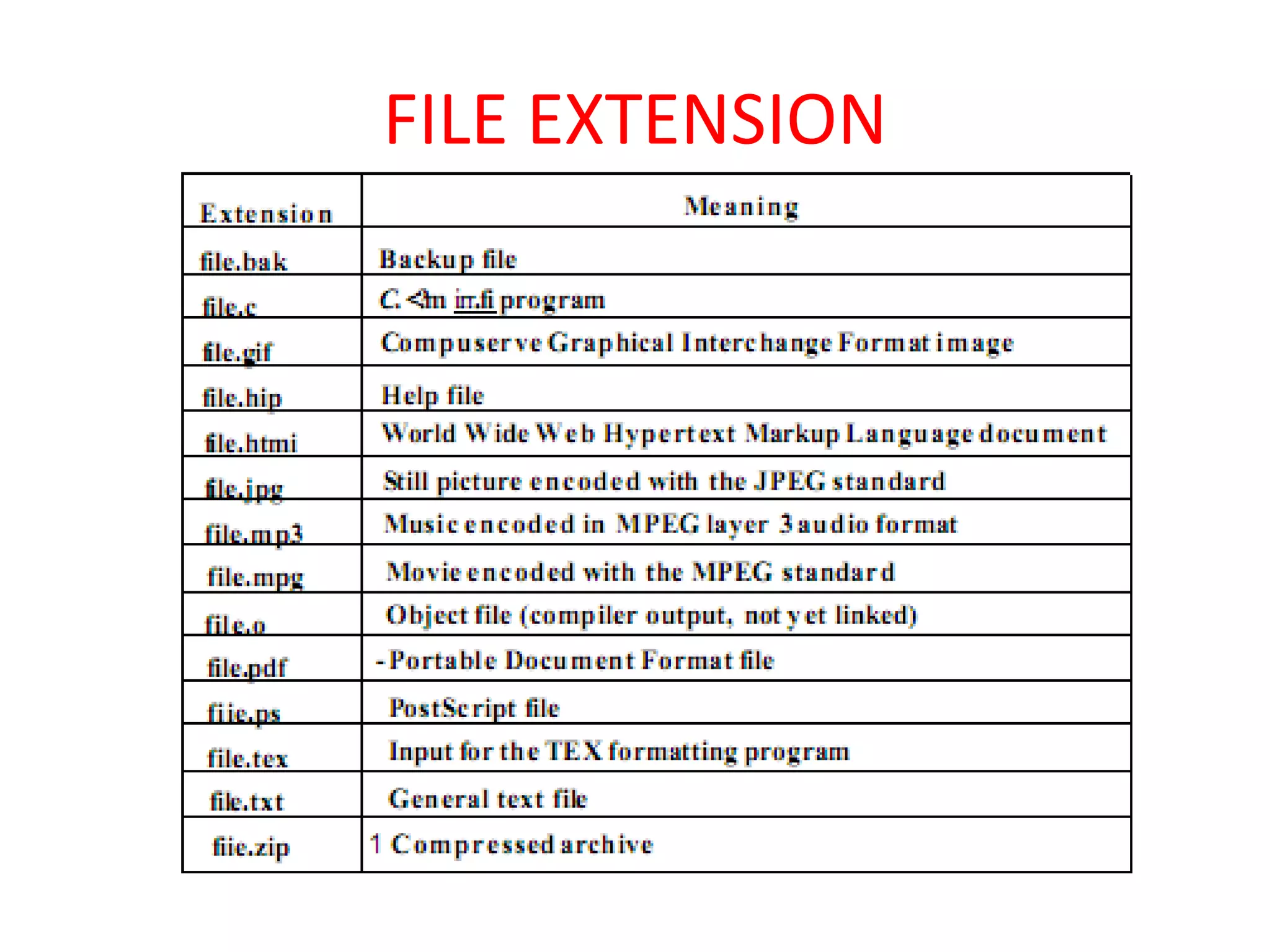
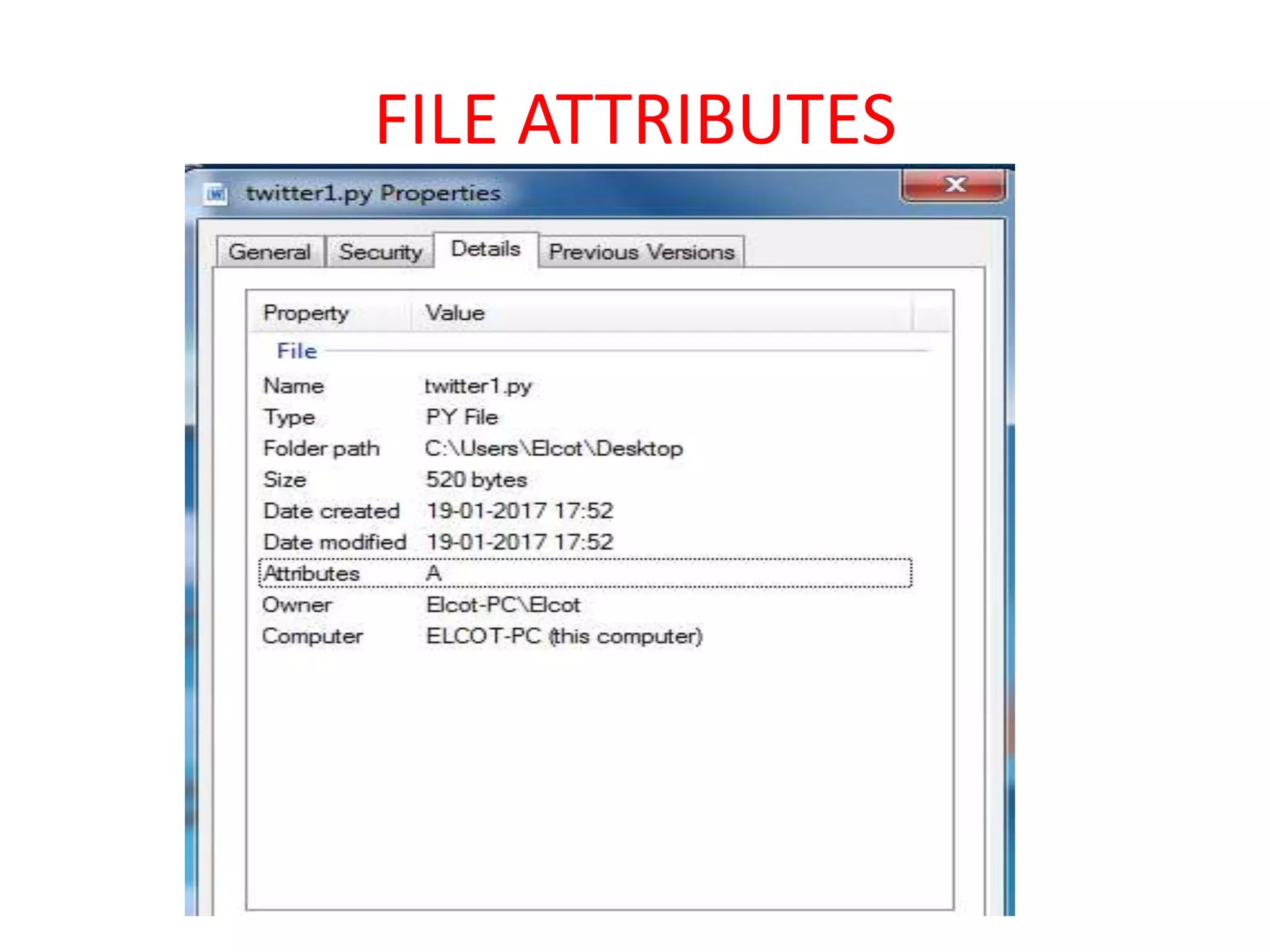
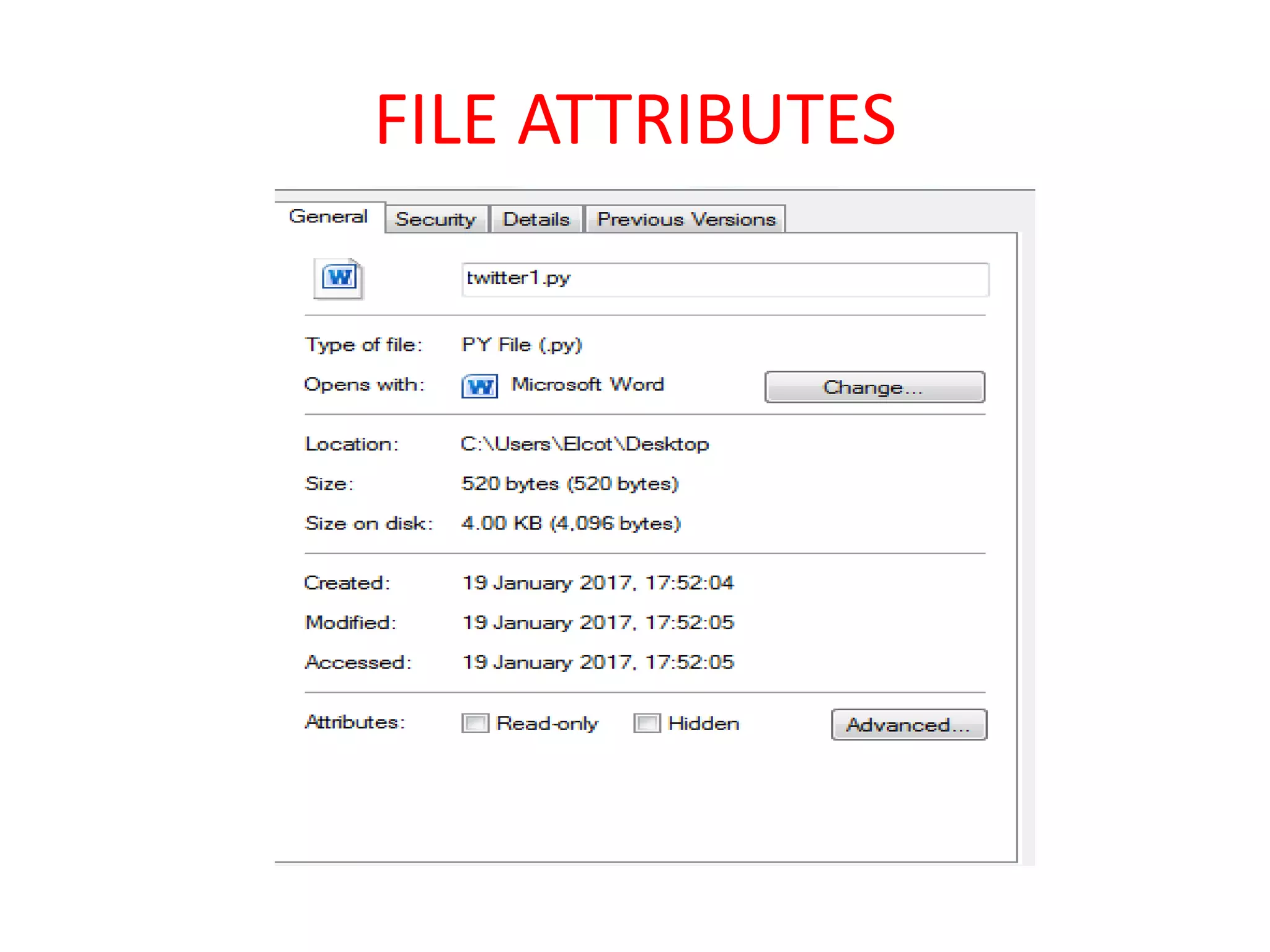
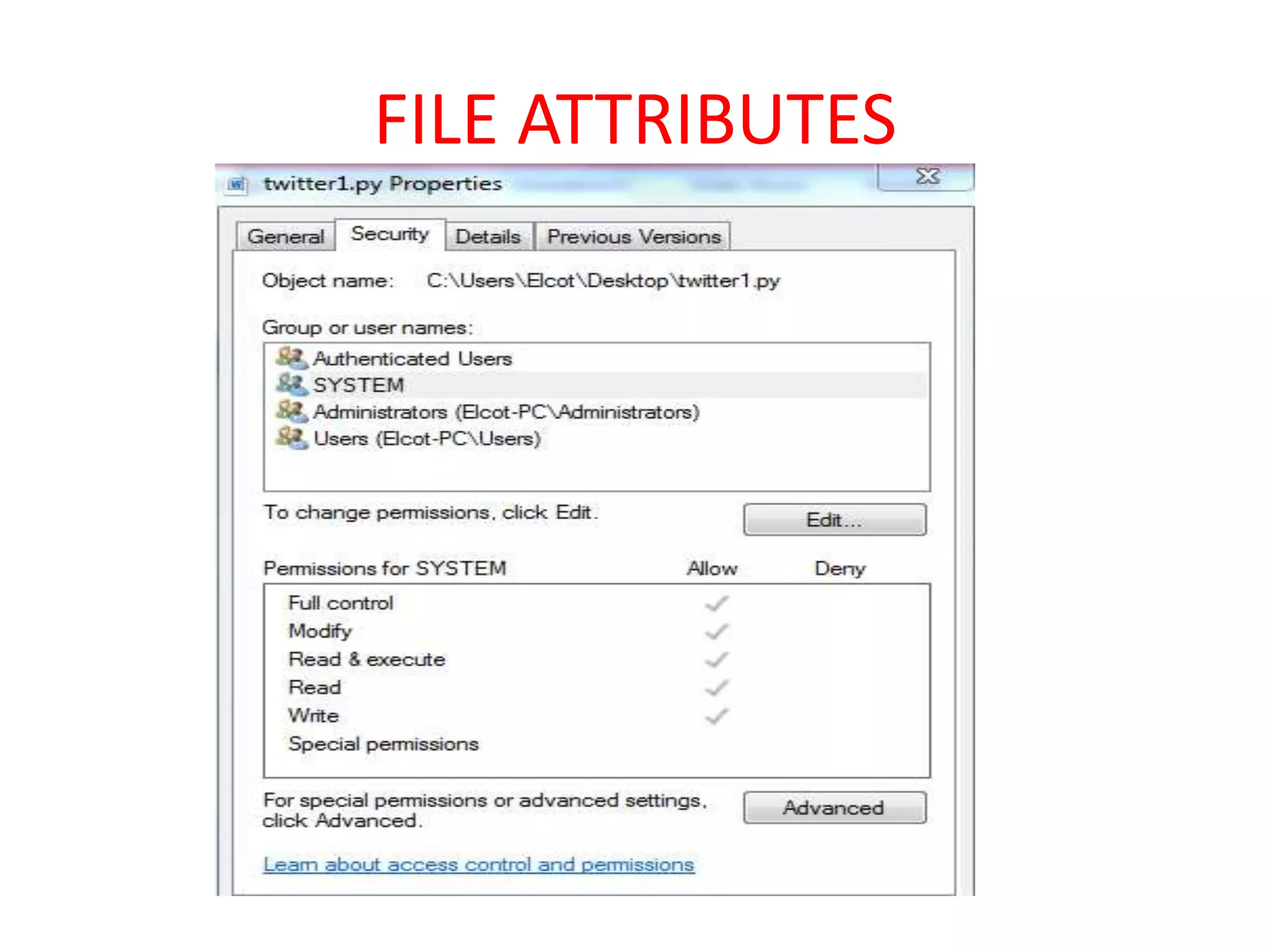
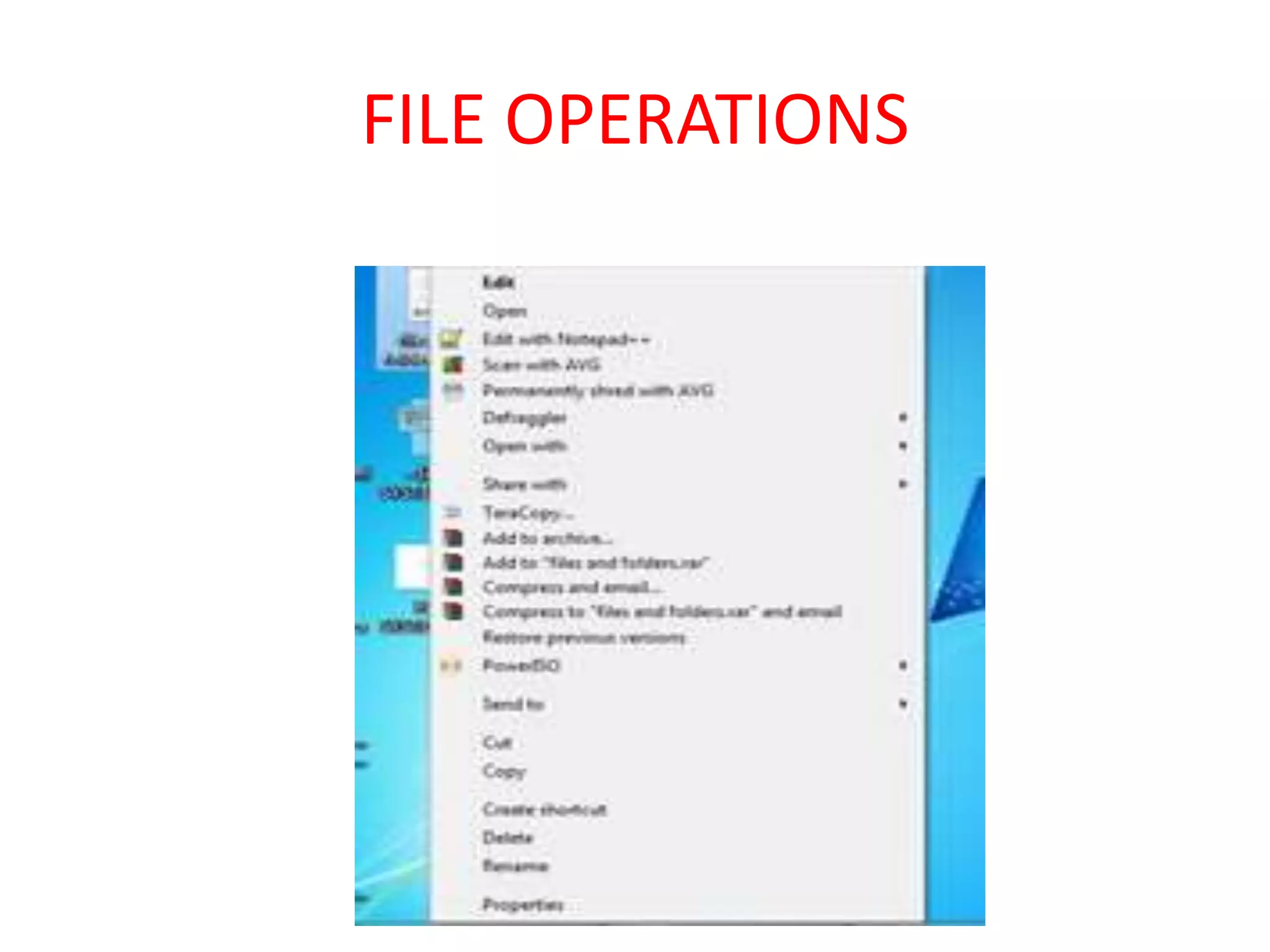
Files are the basic unit of storage in a computer system. They contain information that is persistent, even after the creating process ends. Files have various attributes like name, type, size, location and protection settings. Operating systems support basic file operations like create, open, read, write, delete and rename. Files can be accessed sequentially from beginning to end or randomly by seeking specific locations or records.