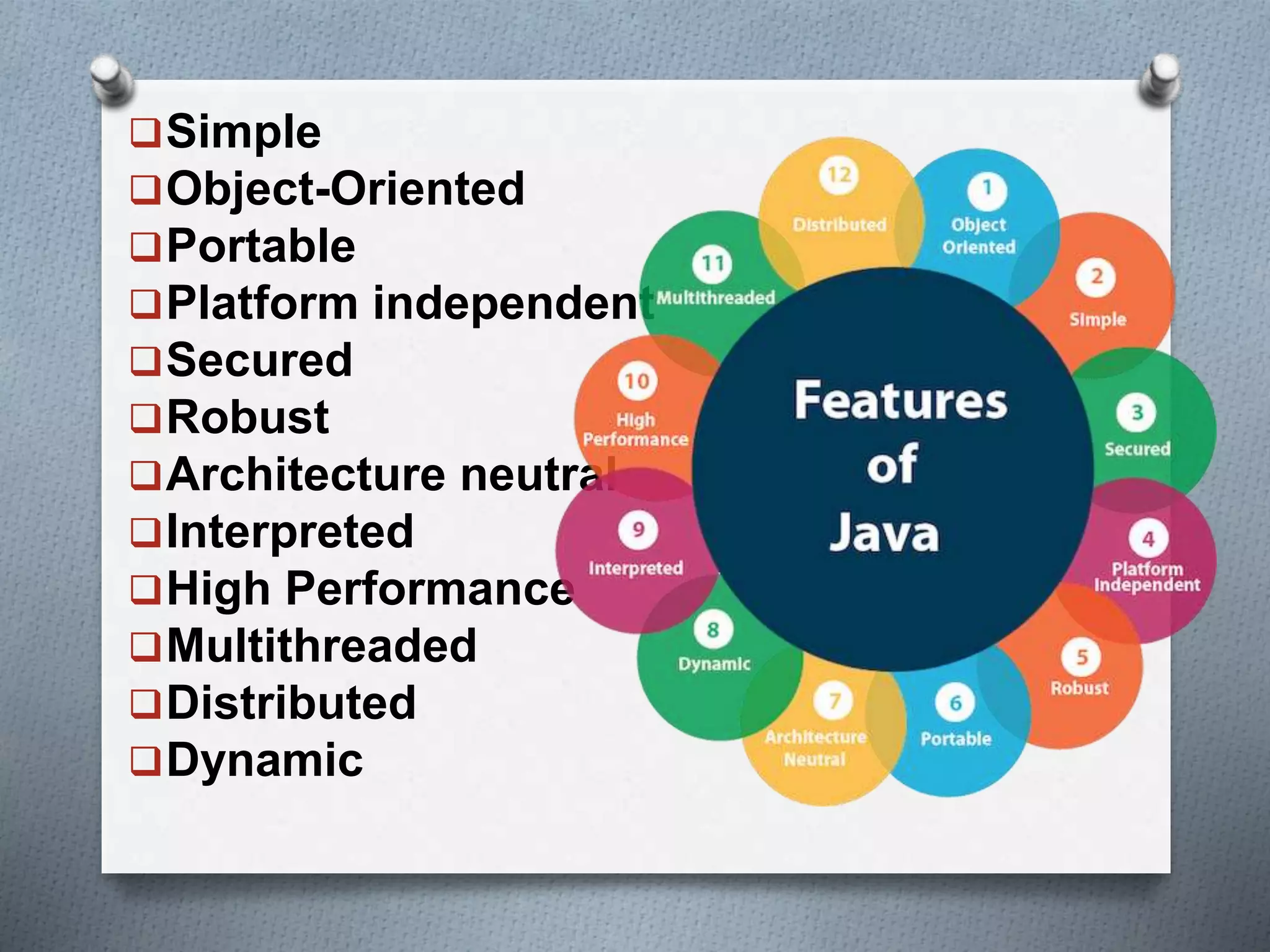
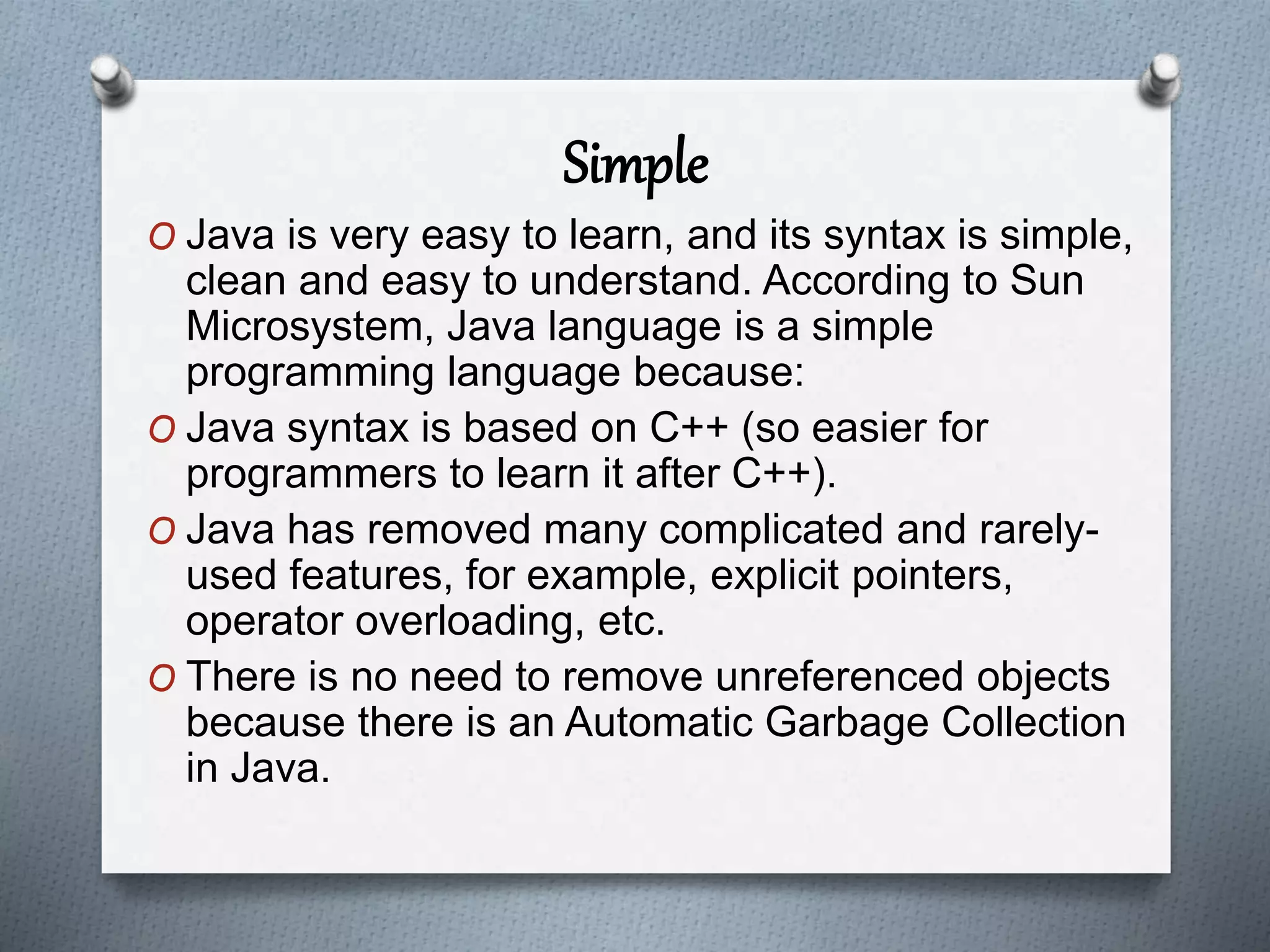
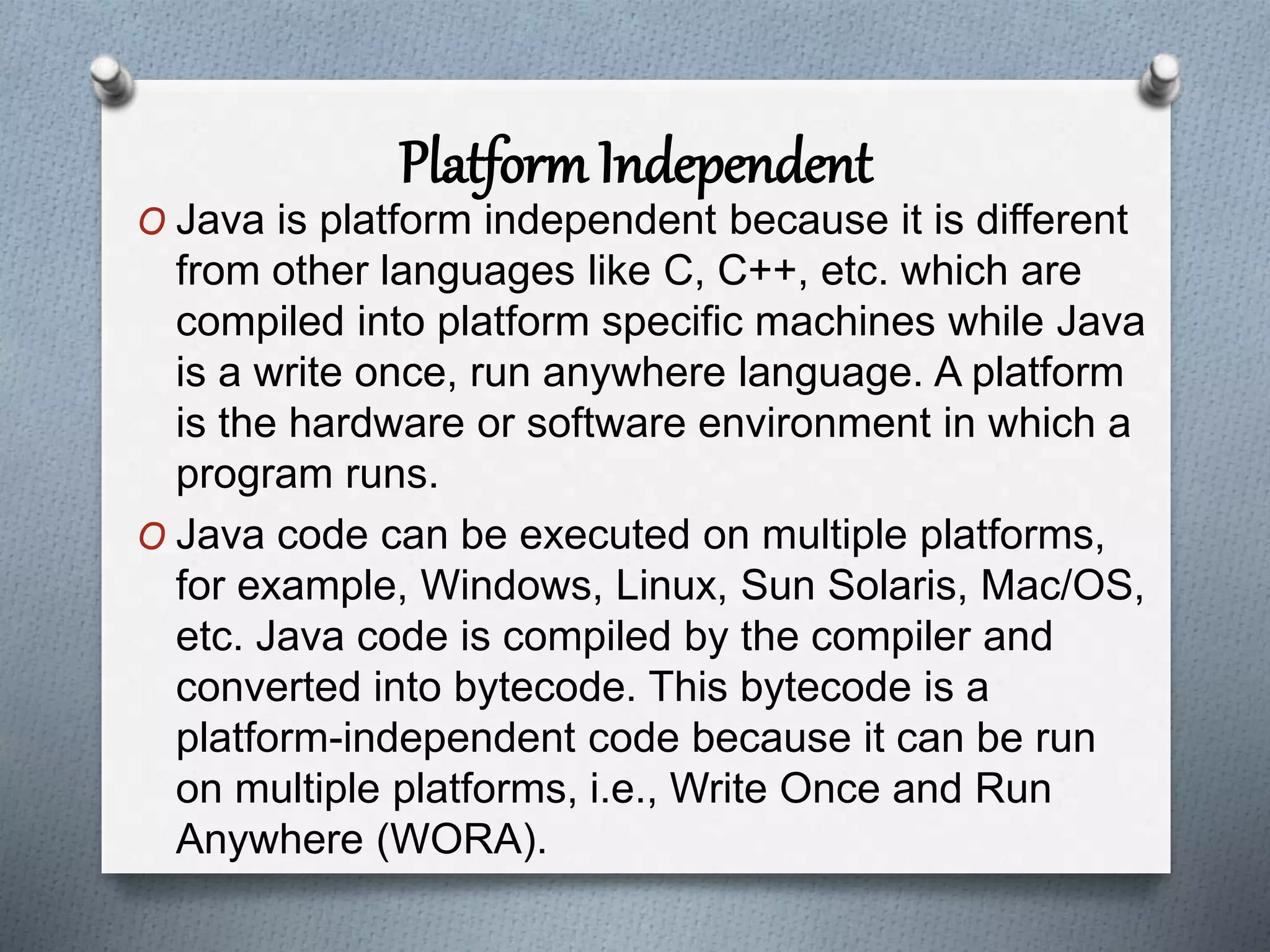
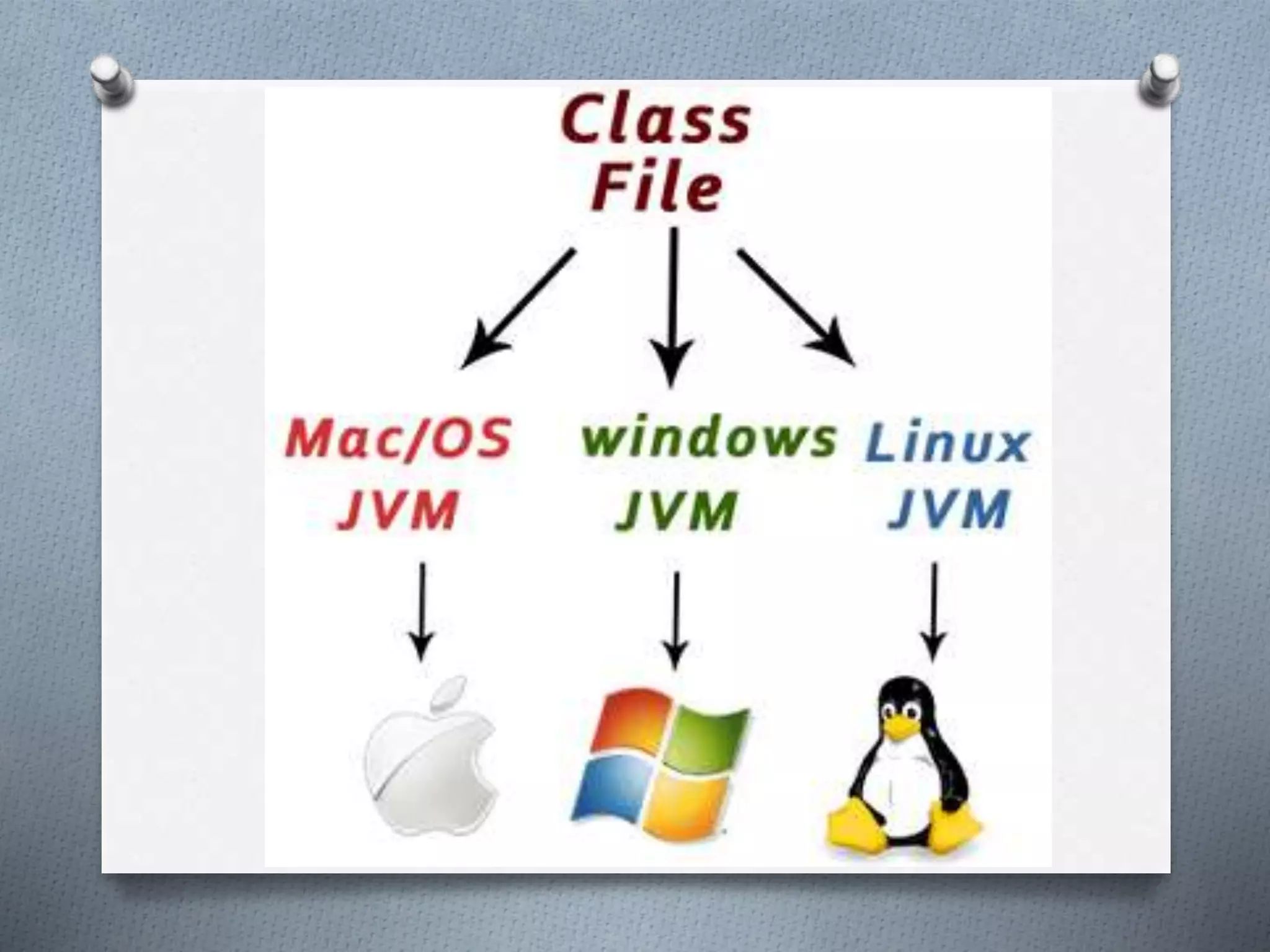
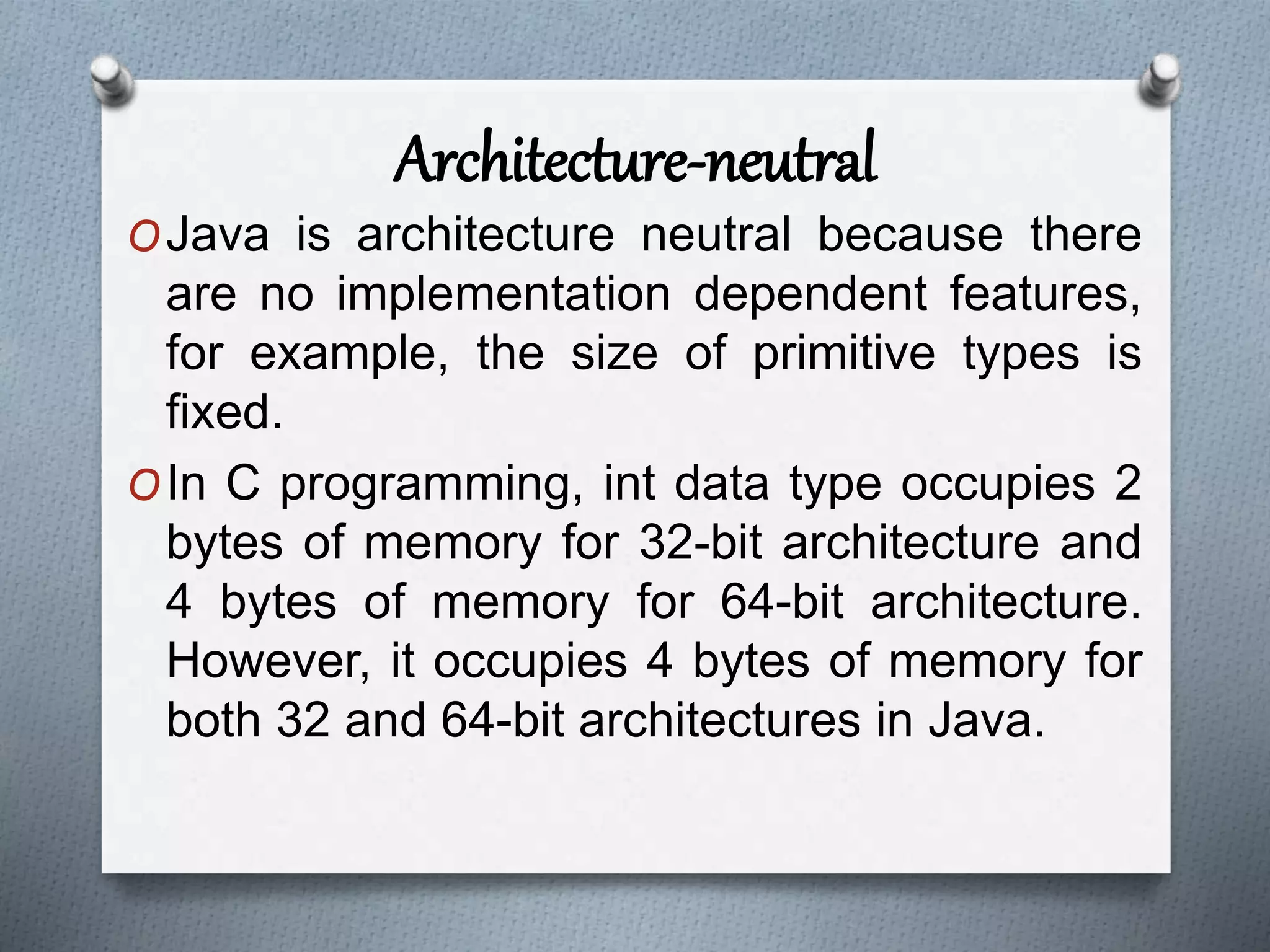
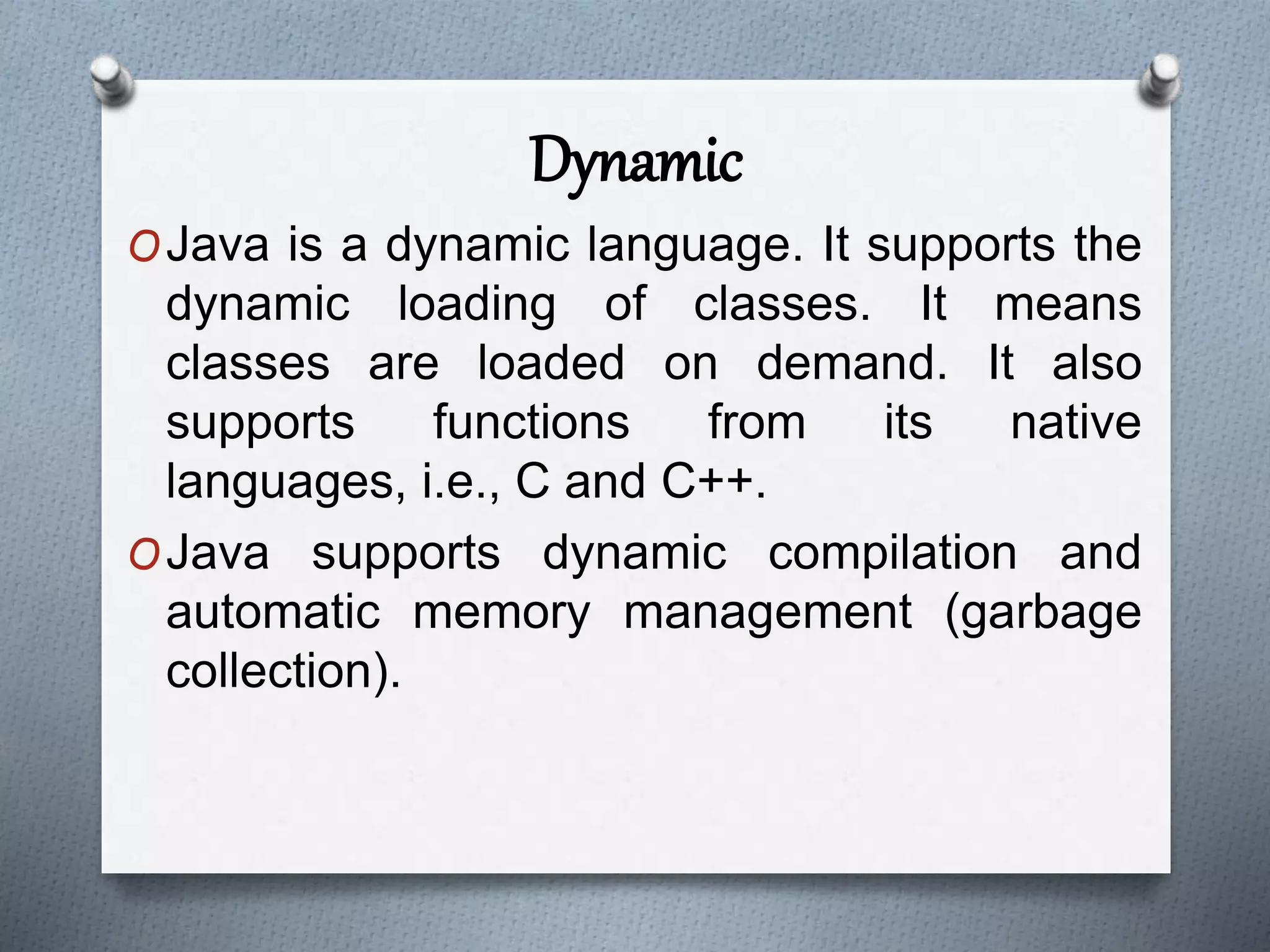
The document outlines the essential features of the Java programming language, highlighting its portability, simplicity, and security. Key characteristics include being object-oriented, platform-independent, robust, and dynamic, along with support for multiple threading and distributed applications. The document emphasizes Java's user-friendly syntax and efficient memory management, contributing to its popularity in software development.